Enterprise Service Management (ESM) is the extension of IT Service Management (ITSM) principles and capabilities to other areas of an organization, encompassing a wide range of enterprise services. It typically includes not only using the same processes or practices used in ITSM but also the same technology (for example, tools such as a service desk) as a means of work enablement.
Get ready to redefine Service Management as you know it!

What is Enterprise Service Management? ESM meaning
Enterprise Service Management is a comprehensive approach that allows organizations to streamline and optimize their service delivery processes across various departments and functions.
An integrated service management platform, such as InvGate Service Management, allows operations, development, and business teams to collaborate and track work across the enterprise.
At its core, ESM focuses on leveraging the principles, processes, and tools of ITSM and applying them to non-IT functions within an organization.
It aims to break down departmental silos and promote collaboration and integration among functional areas like finance, sales, legal, Human Resources (HR), facilities, and marketing, facilitating a holistic and cohesive approach to service delivery.
By adopting an ESM framework, businesses can standardize and automate service management capabilities, ensuring consistent service quality, reducing costs, and driving operational efficiency.
Who can benefit from ESM?
Enterprise Service Management can be helpful to various stakeholders within an organization, particularly those involved in multiple business functions.
Here are the key groups that can benefit from implementing ESM practices:
- Organizations of all sizes - Whether it’s a small startup, a mid-sized company, or a large enterprise, any organization can benefit from implementing ESM practices.
- Service providers - Both internal and external service providers benefit from standardized processes, improved visibility into service requests, and streamlined communication, resulting in better service delivery.
- IT departments - ESM originated from ITSM frameworks like ITIL. By extending ITSM principles to other departments, IT professionals can leverage their expertise and contribute to the broader organizational goals.
- Employees and managers - With streamlined processes, self-service portals, and automated workflows, employees can access the services they need more efficiently, enhancing their productivity and job satisfaction. Managers, meanwhile, can monitor service quality, foster a culture of continuous improvement, and support the organization’s overall goals and objectives.
- Compliance and governance teams - By implementing standardized and auditable processes, organizations can demonstrate compliance, improve Risk Management, and maintain better control over service delivery.
- Customers - ESM ultimately aims to enhance the customer experience, both internal and external. Organizations can provide their customers with a seamless and integrated service experience by adopting ESM practices.
Why is Enterprise Service Management important?
ESM holds significant importance for organizations in today’s dynamic and customer-centric business landscape, as it addresses key areas crucial for businesses. For example:
- Streamlined service quality and experiences.
- By implementing ESM, organizations can efficiently increase the capacity and scope of services offered by different business units, leading to improved service reliability and scalability.
- Increased operational efficiency and effectiveness.
- Reduced operational costs.
- Greater insight into operations and outcomes, plus improvement opportunities.
Jason Wischer, advisor and consultant at KANINI, came onto the 12th episode of our podcast, Ticket Volume to talk about the importance of a customer-centric approach:
|
|
We need to connect our workflows straight back to the customer. So it goes back to that employee experience, identifying the pathway and the impact you have on the customer. It needs to be comprehensive from beginning to end from the customer’s perspective, not our own." Jason Wischer |
According to a survey conducted by AXELOS and ITSM tools, 68% of organizations currently have Enterprise Service Management strategies in flight. Over half of these organizations consider themselves to be well advanced with their ESM strategy, and only 11% of organizations had no plans to adopt ESM.
So, it’s fair to say that it’s a hot topic. But, what’s driving the growth of ESM adoption? Some factors relate to how ESM helps business functions and the parent organization. Others can be viewed through the lens of evolving business function needs.
High-level facilitators of ESM’s growth include:
- Ever-increasing employee expectations – Quite simply, employees now expect more from their corporate service providers, and this has accelerated with the need for remote and distributed working forced by the pandemic. As a result, service providers need better and more employee-centric ways of working. ITSM, in the form of Enterprise Service Management, provides a ready-made solution for the corporate and business functions that need improvement.
- The need for improved business-function operations and outcomes – This driver was in play even before the pandemic, and the negative economic impact of the crisis has exacerbated the need.
- Digital transformation enablement – The acceleration of digital transformation strategies across various industries has increased the demand. ESM delivers the much-needed digital workflows and other digital enablement capabilities across business functions.
- ITSM tool enhancements – ITSM tools have been able to improve and adapt to the needs of Enterprise Service Management over the past half-decade as the demand has grown. These tools, which include additional capabilities and increased flexibility (especially the ability to change ITSM capabilities to meet specific business function use cases), are additional enablers for cross-departmental use.
- The increased sales and marketing of ESM – Enterprise Service Management was once an afterthought in the ITSM tool sales process. Now the ESM opportunity is front and center both on the demand side – with customers requesting it – and on the engagement side of ITSM tools. The availability of customer ESM success stories has also strengthened the value proposition for prospective tool customers.
|
|
Phyllis Drucker |
What is the difference between ITSM and ESM?
ESM and ITSM can be seen as two sides of the same coin, but they should be recognized as distinct entities to effectively extend Service Management best practices throughout the organization.
While ESM is built upon ITSM best practices, it has its unique characteristics. It can be seen as a derivative of ITSM, but with a focus on adopting and adapting practices to fit specific organizational needs.
This applies not only to the processes and practices that are appropriated but also to how they are implemented and the terminology used. For instance, non-IT business functions may prefer to use alternative terms that resonate better within their respective domains. A prime example of this can be observed in HR teams, who often prefer to use the term "Case Management" rather than the traditional ITSM terminology of "Incident Management" and "Problem Management".
As ESM matures it is turning into an enterprise-wide operating model. Because of this, there is a growing argument that ITSM will be viewed as one more flavor of Enterprise Service Management, similar to HR Service Management or Customer Service Management. This shift in perspective acknowledges that ESM encompasses various departments and functions, and ITSM becomes a specialized subset within the broader ESM framework.
Enterprise Service Management principles
As explained earlier, ESM builds upon ITSM best practices and extends them to incorporate non-IT business functions. The uniqueness of ESM lies in its ability to adapt and tailor ITSM practices to meet the specific needs and terminology of different business functions.
ESM principles, described below, encompass those of ITSM while incorporating flexibility and customization to cater to the diverse needs of various business functions within an organization.
1. Process-driven methodology
Both ITSM and ESM emphasize the importance of well-defined processes and workflow automation to achieve consistent and efficient service delivery. Processes such as Incident Management, Change Management, and Request Fulfillment are commonly adopted in both ITSM and ESM.

What Does The No-Code Movement Have to do With Adopting ESM? Everything
2. Service-oriented approach
Both IT Service Management and Enterprise Service Management follow a service-oriented approach, focusing on delivering value and meeting the needs of stakeholders, whether they are internal or external customers.
3. Continuous improvement
ITSM and ESM encourage organizations to regularly assess their services, identify areas for enhancement, and implement changes to drive ongoing optimization and better outcomes.
4. Customer-centricity
Both approaches prioritize the customer or end-user experience. They aim to understand customer needs, provide timely and effective support, and deliver services that align with customer expectations.
5. Collaboration and communication
Collaboration and communication are essential principles for both ITSM and ESM. They emphasize the importance of effective collaboration between different departments and teams, promoting cross-functional working relationships, and transparent communication to ensure seamless service delivery.
FREE Enterprise Service Management CourseElevate customer satisfaction and optimize organizational performance. |
Benefits and challenges of ESM
Enterprise Service Management offers numerous benefits and opportunities for organizations seeking to streamline their operations and enhance service delivery. However, organizations must also navigate certain challenges and considerations to successfully implement and leverage the power of ESM.
The key benefits and challenges associated with ESM are the following.
Benefits of Enterprise Service Management
The benefits of effectively adopting Enterprise Service Management can be split into four different groups:
- Internal to each business function.
- Enabling cross-business-function working.
- Business-level.
- IT department related.
Each of these groups is expanded upon below.
1. Business function benefits
- Improved productivity and speed - It streamlines processes, reduces clutter, and enables faster request processing and ticket tracking.
- Reduced costs and waste elimination - It eliminates non-value-adding activities and optimizes resource allocation.
- Improved external customer satisfaction - It enhances service reliability and aligns expectations between requesters and service providers.
- Enhanced visibility and control - It provides better reporting, metrics, and tracking to identify improvement opportunities.
- Effective Knowledge Management - It enables easy capture, reuse, and sharing of knowledge for faster and more comprehensive responses.
- More stability - It ensures consistent operations, improves service quality, and prevents errors and delays.
- Improved employee satisfaction - It provides best-practice processes, clarity of roles, and support for service-provider teams, resulting in a better employee experience.
2. Across business function benefits
- Improved alignment - It aligns operations, breaks down silos, and facilitates communication and accountability.
- Enhanced collaboration - It simplifies communication, automates workflows, and fosters collaboration across functions through workflow automation.
- Clearer visibility - It offers a clear view of end-to-end operations and facilitates performance monitoring and decision-making. It also creates the foundation for the application of business intelligence and facilitates value stream mapping, attribution, and the identification of process inefficiencies or bottlenecks.
- Better knowledge sharing between teams - It enables technology capabilities such as knowledge bases and self-service portals for sharing and accessing information.
3. Business-level benefits
- Increased competitive advantage through enhanced business capabilities.
- Improved governance, Risk management, and compliance practices.
- Agreed accountabilities – Both within and across teams.
- Business-wide continual improvement.
4. IT department-related benefits
- Driver of value-adding innovation - It allows the IT department to contribute to all-round Service Management operations and best practices.
- Economies of scale - It leverages corporate ITSM tools for beneficial scalability.
- Sharing of good practices - ESM encourages collaboration and knowledge sharing among various departments, enabling them to exchange successful strategies and approaches that go beyond the boundaries of established Service Management frameworks such as ITIL.

TOP 5 Best Enterprise Service Management Software for 2024
5 challenges of Enterprise Service Management
Enterprise Service Management is still evolving, and consequently (unlike ITSM that's been around for longer) there's little formalized industry best practice available to organizations looking to adopt it.
However, numerous organizations have already started to implement ESM practices and many of the common mistakes and barriers have already been captured.
To help those who are just starting out, or anybody who is looking to improve their implementation process, this section shares five of the most common ESM challenges that need to either be avoided or traversed:
- Treat ESM as a business initiative, not an IT project - Enterprise Service Management involves changing traditional working methods and requires organizational Change Management tools and techniques.
- Share optimized ITSM capabilities - Don't extend sub-par capabilities to other business functions. Ensure ITSM capabilities are refined before sharing them.
- Communicate ESM benefits in business terms - Use terms like digital enablement or transformation to resonate with colleagues outside of IT. Emphasize advantages such as improved employee experiences, agility, cost savings, and reduced risk.
- Consider differences between business functions - Each function may have varying levels of interest, priorities, capacity for change, objectives, working practices, and terminology.
- Avoid a rushed "big bang" approach - Go for a phased approach, starting with a specific business function or capability shared across all functions. Learn from smaller groups to benefit the wider implementation.
Adopting the Enterprise Service Management framework
Implementing ESM within an organization can present certain challenges, but with the right approach, these obstacles can be overcome, leading to a successful implementation.
Let's explore some tips shared by Service Management Consultant Darren Rose on the 36th episode of InvGate's weekly podcast Ticket Volume that can help organizations adopt ESM more smoothly.
- Break down language barriers - To foster acceptance and understanding, engage in open conversations and bridge the gap between different terminologies used across departments is crucial.
- Maintain silos while joining them - Rather than completely dismantling silos, selectively retain valuable aspects while fostering collaboration between different teams, creating a collective effort.
- Identify ideal transition candidates - Focus on cross-functional processes as the starting point for implementing Service Management platforms, with HR and Finance being prime candidates due to their existing connection to IT.
- Develop an implementation plan - Build a well-structured and sequenced plan to deliver the desired outcomes and improve the employee experience by simplifying request submissions and streamlining service delivery.
- Think beyond processes - Encourage knowledge sharing and value visualization beyond individual processes and silos, highlighting the positive impact on revenue and collective growth.
- Adapt to new ways of working - Given the significant digital transformation that has occurred in recent years, adapt to and support new ways of working by bringing employees together and understanding their evolving needs.
- Embrace agility - Stimulate agility to be able to manage workloads differently and scale effectively, foster adaptability and ensure a responsive approach in dynamic environments.
- Harness automation - Automation enables you to streamline repetitive tasks and provide employees with autonomy, extending its benefits beyond IT functions.
- Prioritize experience - Experience Management lies at the heart of ESM, so it's essential to optimize user and employee experiences. By focusing on both service recipients and providers, organizations can create a positive and meaningful environment.
- Motivate employees - Harness intrinsic motivators such as autonomy, mastery, and purpose, to create a work environment that inspires and motivates employees, leading to increased engagement, job satisfaction, and overall performance.
ESM training

Are you starting to be convinced that you need to implement Enterprise Service Management in your organization? Then you can't miss InvGate's course in Udemy: Introduction to Enterprise Service Management
Free for everyone, the ESM training contains 120 minutes of high quality education about ESM fundamentals, key concepts, and ESM in action.
What is an example of enterprise service?
Now let's explore some real-world examples of how ESM has been successfully implemented across various industries.
Peoples Bank implemented an Enterprise Service Management Strategy by centralizing its cross-department support into InvGate Service Management. They achieved a 75% increase in portal incident reporting (as opposed to email) and a 47% increase in satisfaction with ticketing.
Farmacity, one of the major retail store chains in Argentina, implemented an ESM strategy to guarantee uniform service delivery, streamline communications between teams, and ensure rapid incident resolution. In this sense, InvGate Service Management's flexibility was crucial to scale operations and efficiently add new areas, stores, and collaborators. They optimized by 30% the number of agents needed.
Enterprise Service Management software and must-have features
To effectively implement this approach, organizations need robust Enterprise Service Management software, which is a centralized hub for receiving, processing, and resolving service requests and incidents. It forms the foundation for managing and delivering services across various business functions.
There are several indispensable features that an ESM service management tool should possess to enable successful implementation.
Service Catalog Management
A comprehensive database that defines and presents all the services offered by each business function. It allows users to browse and request services based on their needs easily.
With InvGate Service Management, creating a service catalog becomes effortless. Its intuitive interface enables organizations to design and customize their service catalog seamlessly.
Incident and Problem Management
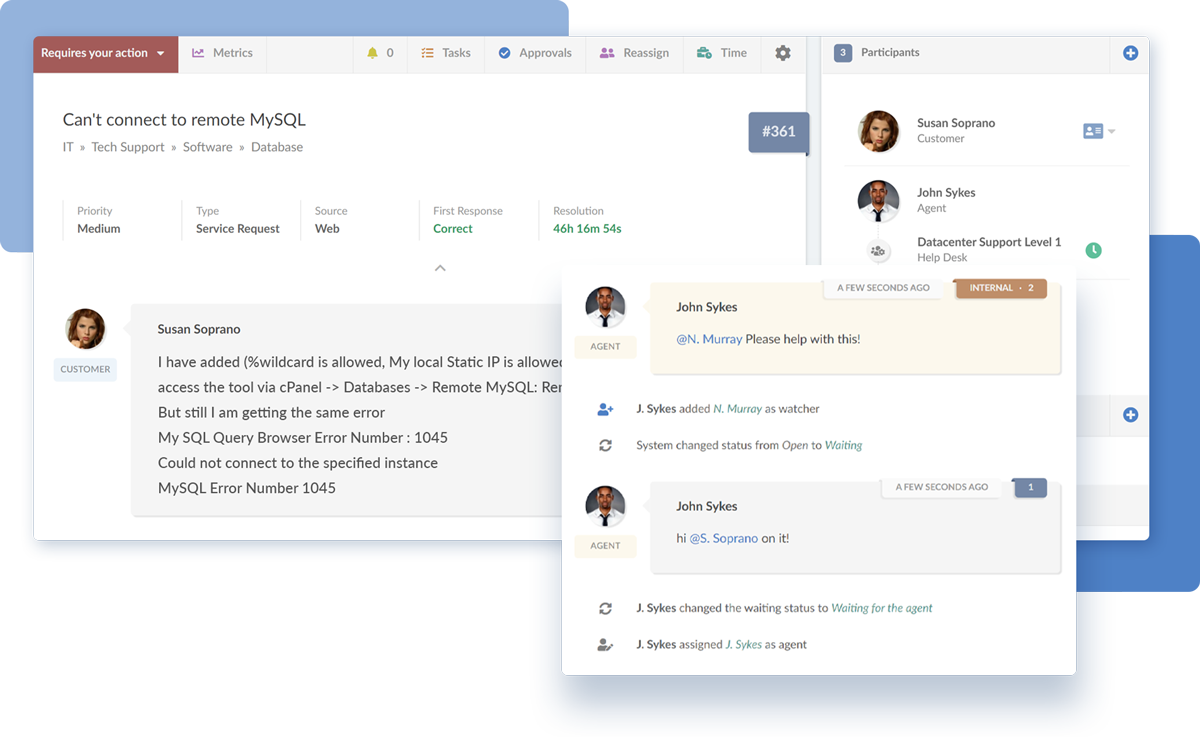
Capabilities to log, track, and resolve incidents and problems that occur across different business functions. This feature ensures timely incident resolution, minimizes disruptions, and addresses underlying issues.
InvGate Service Management excels in Incident and Problem Management. Its powerful ticketing system enables organizations to log and track incidents and problems consistently. With advanced automation and intelligent routing, the tool streamlines the resolution process, ensuring timely responses and minimizing disruptions.
Request fulfillment
An efficient request fulfillment process that enables users to submit service requests, such as onboarding new employees, ordering equipment, or requesting access to systems. The solution should automate and streamline the request fulfillment process to enhance efficiency and user satisfaction.
InvGate Service Management simplifies and accelerates request fulfillment. Its user-friendly interface allows users to easily submit service requests, while the automation capabilities automate the routing, approval, and fulfillment of requests.

How to Build a Flawless Onboarding Workflow [+Free Template]
Change Management

A robust Change Management module to handle planned changes across business functions. It ensures that changes are properly evaluated, approved, and implemented, minimizing potential risks and disruptions.
InvGate Service Management's workflow builder facilitates smooth coordination among stakeholders and minimizes the risk of unauthorized or disruptive changes.

Change Request: Definition, Form, And Free Workflow Template
Knowledge base and self-service portal
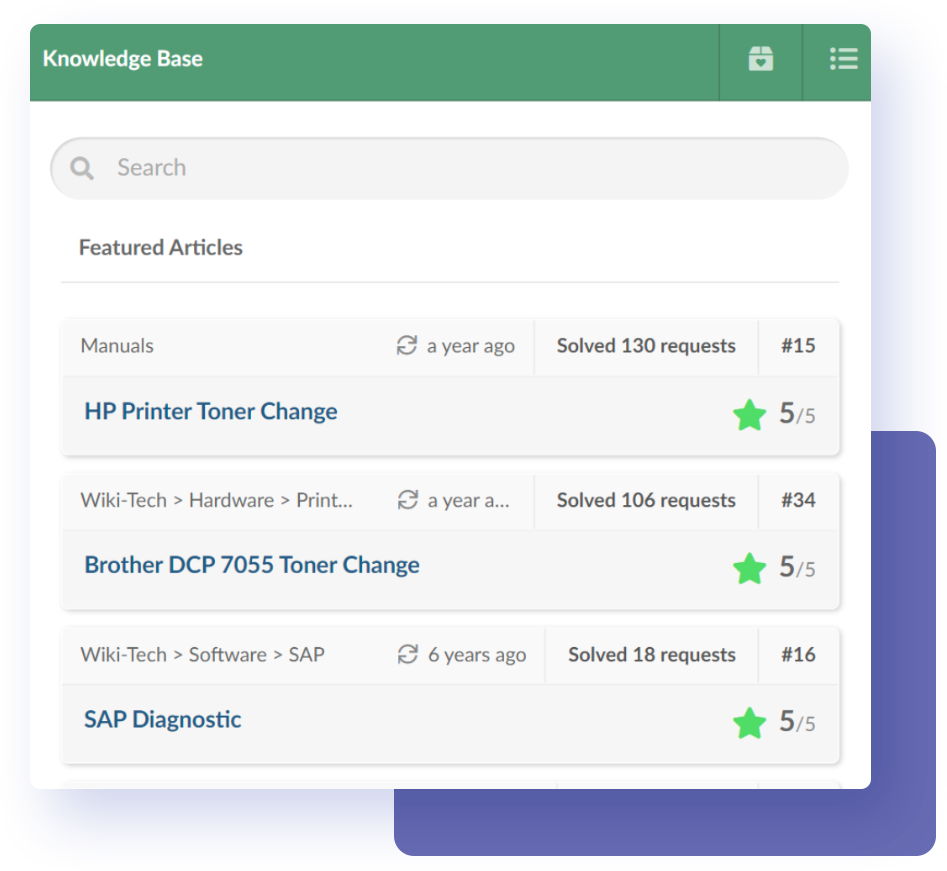
A centralized that captures best practices, solutions, and guides for various business functions. Coupled with a self-service portal, users can easily access relevant information and solutions, empowering them to resolve common issues independently.
Want to set up your self-service portal easily and effectively? With InvGate Service Management it is possible. With its powerful knowledge base capabilities, you can quickly establish a comprehensive self-service portal easy to access and navigate by all team members.
Integration capabilities
InvGate's Integrations database
Connect our solutions with the apps you use every day.
Explore InvGate's integrations

The ability to integrate with other essential business systems, such as HR or finance systems, to ensure a seamless flow of information and processes across different functions. Integration enables better collaboration, data consistency, and overall operational efficiency.
InvGate Service Management offers robust integration capabilities (you can check them out in this integration cheat sheet), allowing you to connect and synchronize data with your HR, finance, and other key business systems.
Reporting and analytics
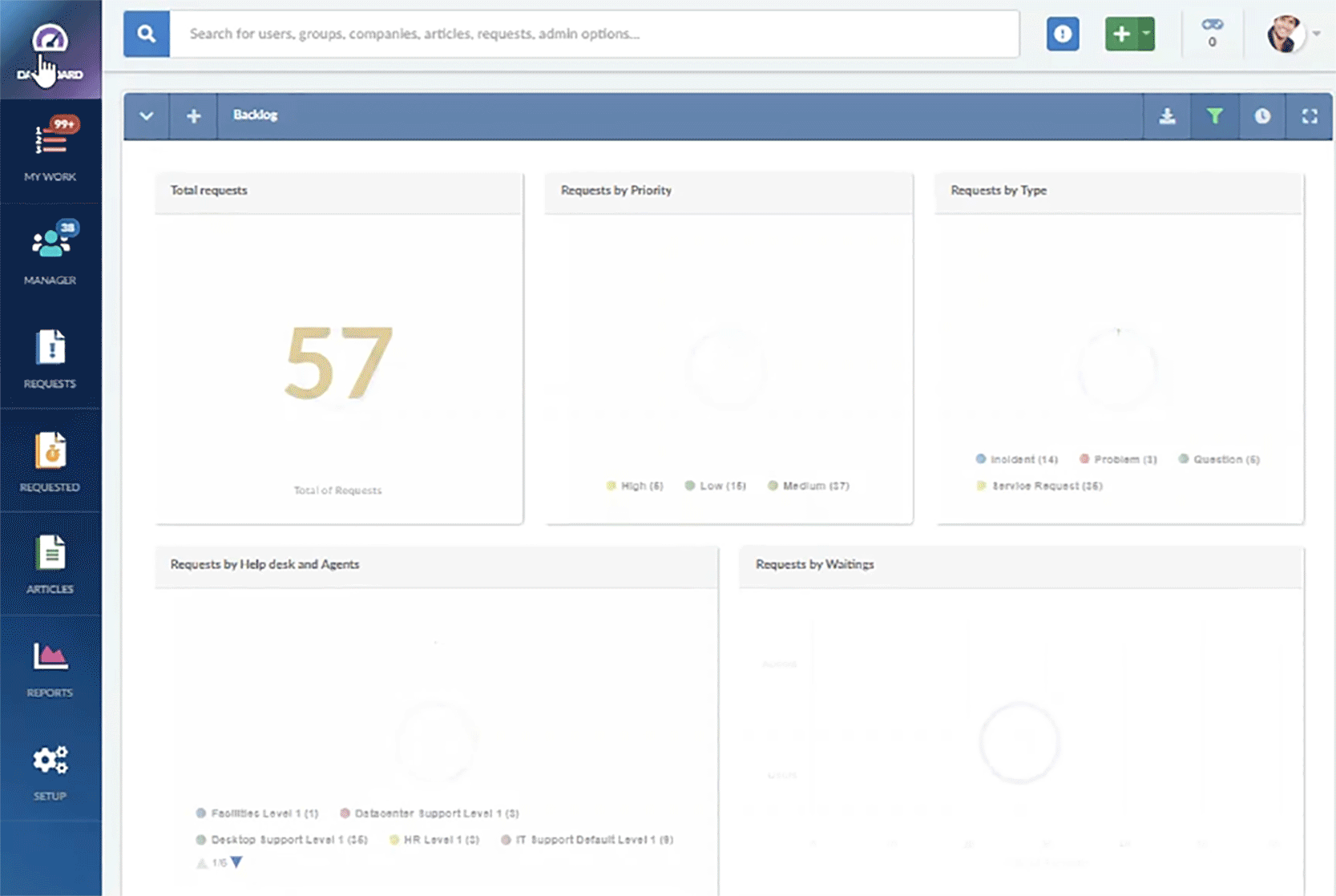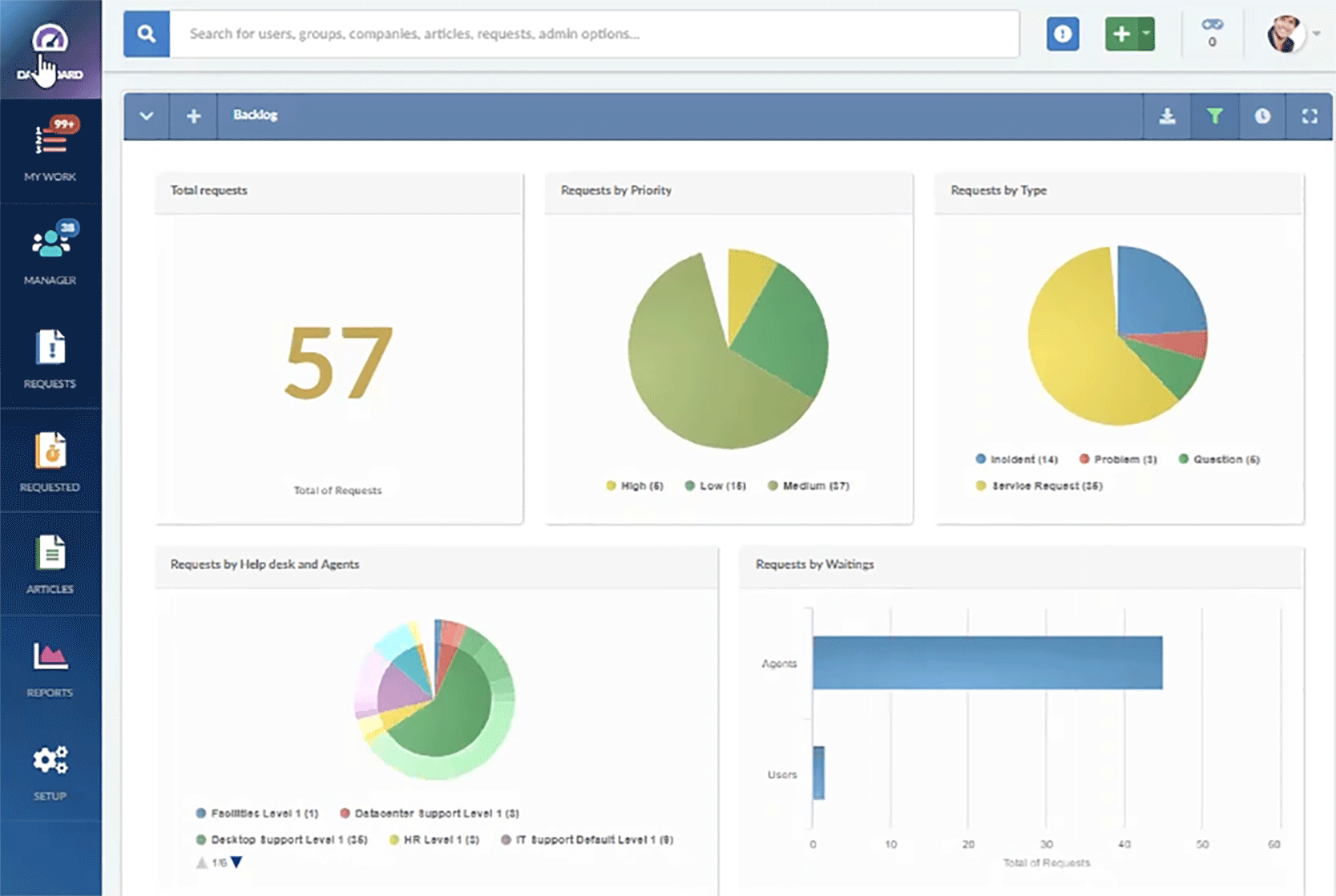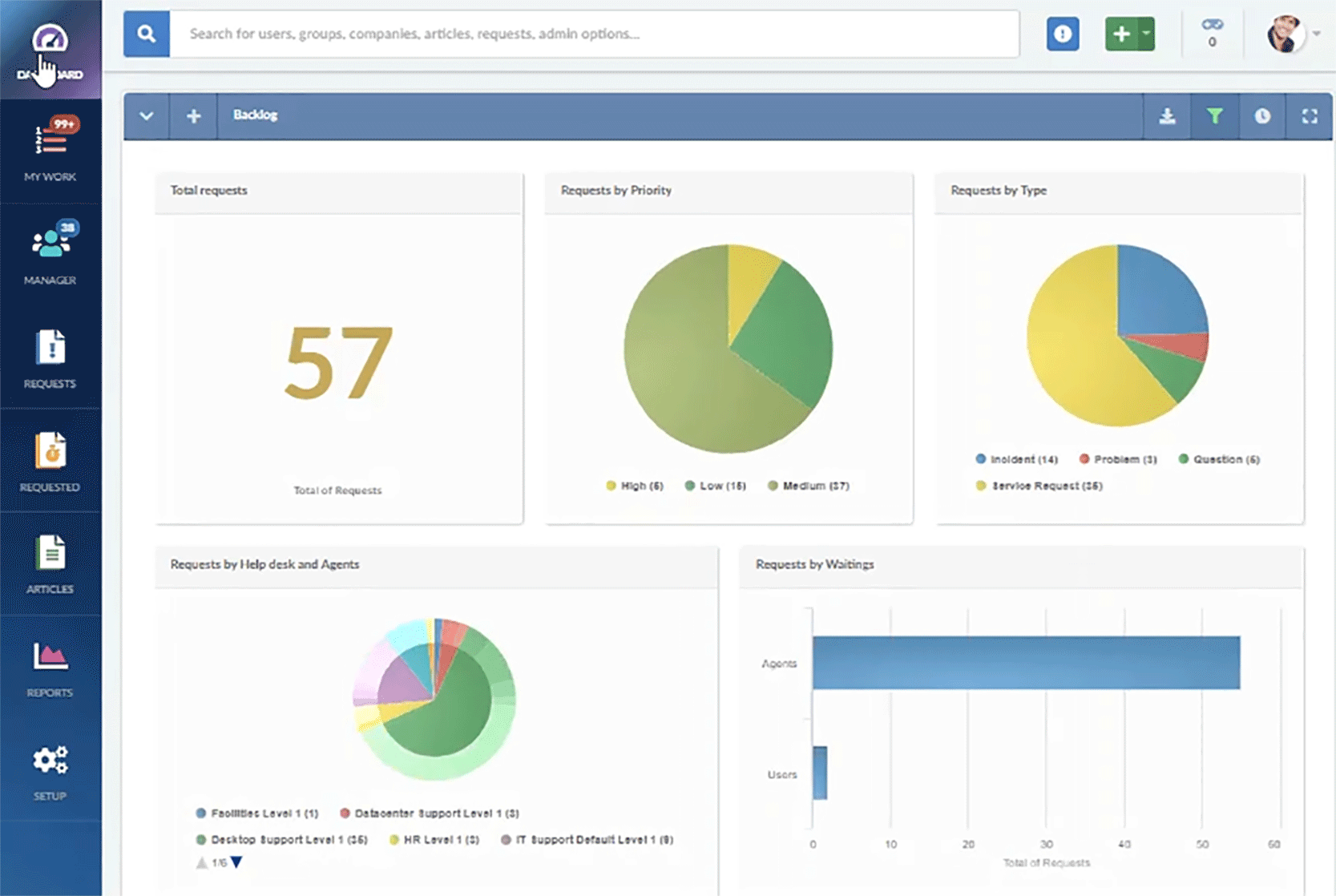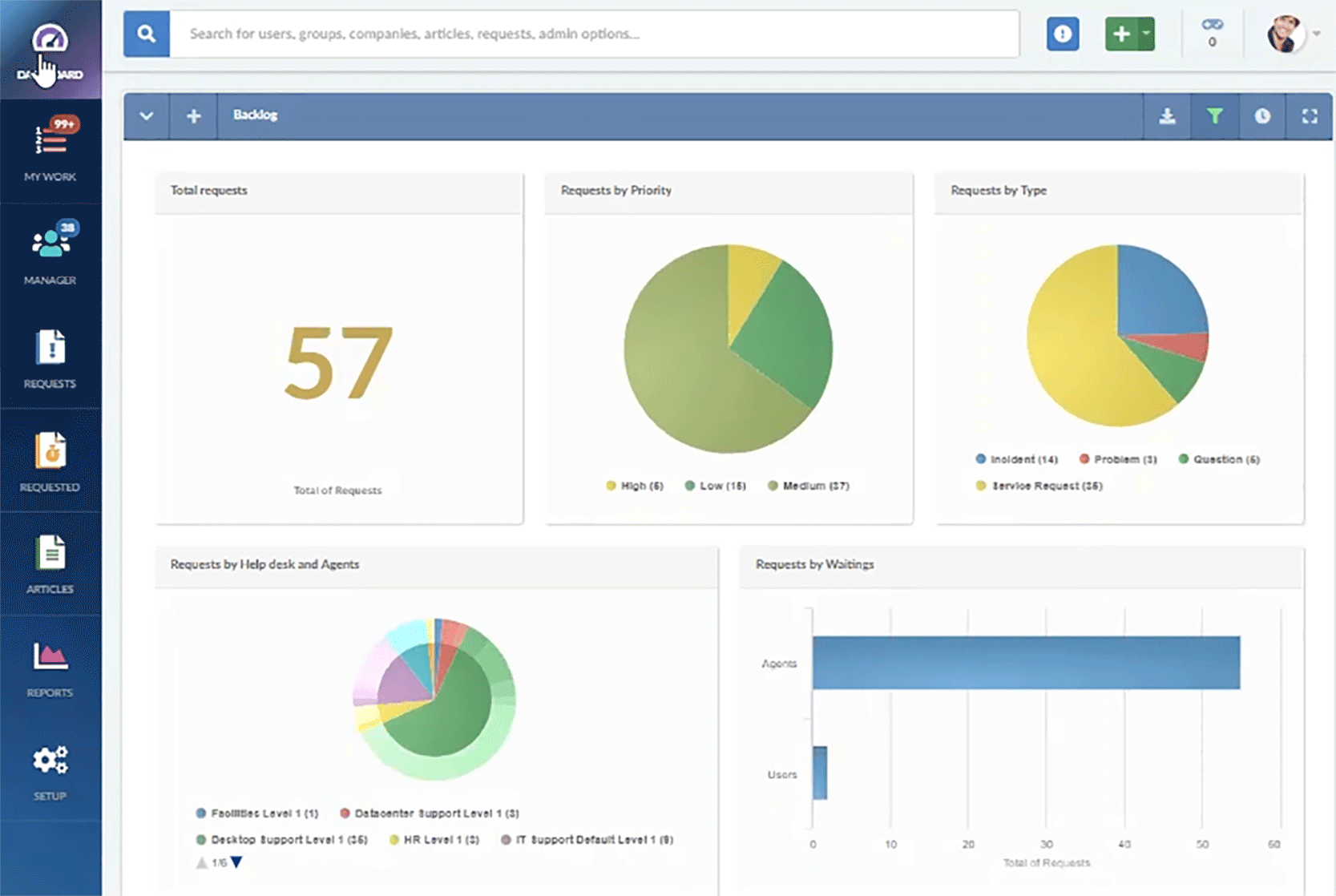
Robust reporting and analytics capabilities to track service performance through relevant help desk metrics, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
Gain valuable insights with InvGate Service Management's powerful and customizable reporting and analytics features. With comprehensive reporting capabilities, you can continuously optimize your operations and deliver exceptional service to your organization.
Customization and scalability
The software should offer customization options to adapt to the specific needs and terminology of different business functions, while also helping to standardize service delivery across the organization. Additionally, it should be scalable to accommodate organizational growth and evolving requirements.
Customize the software to align with your unique business needs and terminology with InvGate Service Management. With its user-friendly interface (a must for successful ESM), you can easily customize various aspects, including fields, forms, workflows, and service catalogs. You can modify and configure these elements to reflect your organization’s terminology, processes, and service offerings, ensuring a personalized and intuitive experience for your users.
Furthermore, InvGate Service Management is designed to be highly scalable. As your organization grows and evolves, the software can effortlessly accommodate increased user demand, expanding service requirements, and changing business dynamics. You can scale up the usage and capabilities of InvGate Service Management to meet the evolving needs of your organization without compromising performance or functionality.
AI for Enterprise Service Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a significant role in enabling ESM to thrive by enhancing Service Management processes' efficiency, accuracy, and user experience.
AI-powered capabilities in for ESM offer intelligent automation, predictive insights, and smart assistance that simplify and streamline Ticket Management, benefiting both agents and end-users.
Some examples of AI-powered features you can't miss that are revolutionizing ESM are the following.
AI-Improved Responses
InvGate Service Management's AI-Improved Responses enhance, condense, or elaborate on ticket replies drafted by help desk agents.
This enhancement not only streamlines your team's workflow but also ensures precision and uniformity in support responses, saving technicians valuable time otherwise spent crafting replies.
Knowledge Article Generation
The Knowledge Article Generation capability converts incident resolutions into knowledge articles. Agents can then use this draft and modify or elaborate on it, saving significant time during the process.
This functionality is particularly beneficial for ESM by streamlining the process of capturing and documenting solutions. It provides the different areas the ability to quickly translate incident resolutions into usable knowledge articles crucial for maintaining efficiency and improving service delivery across the whole organization.
Ticket Summarization
The Ticket Summarization feature provides an automated way to generate a recap of ticket activity to date. Users also have the option to post this summary as an internal comment for future reference.
This functionality is effective for Enterprise Service Management environments, as it expedites the onboarding process for new team members and ensures seamless continuity in managing complex, ongoing incidents with extensive activity.
In conclusion
Enterprise Service Management represents a powerful framework that extends the principles of ITSM to transform and optimize various areas of an organization. It's no surprise that it's on everybody's agenda. Embracing ESM not only empowers organizations to meet the growing demands of the modern workplace but also drives streamlined processes, enhanced collaboration, improved service delivery, and increased customer satisfaction.
With the right technology, such as InvGate Service Management, organizations can unlock the full potential of ESM, enabling them to centralize support, automate workflows, and gain valuable insights through data-driven analytics.
Ask for a 30-day free trial and be at the forefront of this transformative movement with InvGate Service Management!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Enterprise Service Management in ITIL?
Enterprise Service M offers a strategic approach to delivering and supporting services across the organization. ITIL, a best practice framework, helps in this regard, emphasizing service delivery, improvement, and managing services from demand to value.
ITIL 4 introduces a holistic approach through its four dimensions model, addressing organizations and people, information and technology, partners and suppliers, and value streams and processes. The Service Value System (SVS) in ITIL 4 discusses how different components work together for value creation, including guiding principles, governance, service value chain, continual improvement, and practices.
What does an Enterprise Service Manager do?
An Enterprise Service Manager is responsible for overseeing the implementation, operation, and continuous improvement of ESM practices within an organization. The role involves aligning Service Management strategies and practices with the overall business objectives, ensuring efficient and effective service delivery across various departments and functions.
What does ESM do?
ESM aims to improve service delivery, efficiency, and customer satisfaction by applying Service Management concepts to non-IT business functions. Its primary goal is to provide a holistic approach to Service Management, where consistent practices, tools, and governance are applied throughout the organization.
What is an ESM strategy?
An Enterprise Service Management strategy is an organization's comprehensive plan and approach to implement and leverage Service Management principles across various business functions. It outlines the goals, objectives, and key initiatives for integrating Service Management practices beyond the IT department and across the enterprise.
An effective ESM strategy considers the specific needs, objectives, and organizational culture of the business. It provides a roadmap for how Service Management principles, processes, and tools will be extended and applied to non-IT areas such as Human Resources, Facilities Management, Finance, Customer Service, and more.