You’ve heard about artificial intelligence everywhere. It’s been represented and discussed in popular media like films and television, as well as in extensive and potentially fearmongering think-pieces saying that its sentience could spell the end of our times.
But one thing is for certain: artificial intelligence is very real and — despite what certain sci-fi films might tell you — a really helpful tool for us humans.
In this piece, we’ll dive deep into what artificial intelligence is, its different iterations, and how its integration into ITSM is steadily becoming an industry standard in both startups and established companies. Take off that Matrix trench coat and follow us as we explore the world of artificial Intelligence.
What exactly is artificial intelligence?
When reduced to its bare essentials, artificial intelligence (AI) is a field that merges computer science and solid datasets to aid in problem-solving. Its genesis could be traced back to the question posed by Alan Turing's seminal work Computing Machinery and Intelligence (1950): “Can machines think?”.
In recent years, AI has become synonymous with workflow optimization and efficient data processing and analysis in many businesses.
In other words, artificial intelligence can be understood as a simulation of human intelligence. In this context, a simulation of human intelligence means that any task performed by a program or a machine will be carried out in the same way in which a human being would have done it.
Deep learning and machine learning all stem from AI.
How does artificial intelligence work?
The core part of artificial intelligence is the algorithms. AI demonstrates some of the behavior that is linked with human intelligence such as planning, reasoning, learning, manipulation, and creativity.
These disciplines are comprised of the aforementioned AI algorithms that seek to create expert systems that make predictions or classifications based on input data and supervised training. It also encompasses sub-fields of machine learning and deep learning, which are frequently mentioned in conjunction with artificial intelligence.
In general, AI systems work by ingesting large amounts of labeled training data, analyzing the data for correlations and patterns, and using these patterns to make predictions about future states.
In this way, a chatbot that is fed examples of text chats can learn to produce lifelike exchanges with people (through Natural Language Processing or NPL), or an image recognition tool can learn to identify and describe objects in images by reviewing millions of examples.
What are the different types of artificial intelligence?
In broad terms, there are two types of artificial intelligence: strong AI and narrow AI.
Strong AI, also known as artificial general intelligence (AGI), describes programming that can replicate the cognitive abilities of the human brain. In theory, a strong AI program should be able to pass a Turing Test.
Narrow AI is an AI system that is designed and trained to complete a specific task. Industrial robots and virtual personal assistants, such as Apple's Siri, use weak AI.
There are, however more specific types of artificial intelligence that we’ll put under the scope.
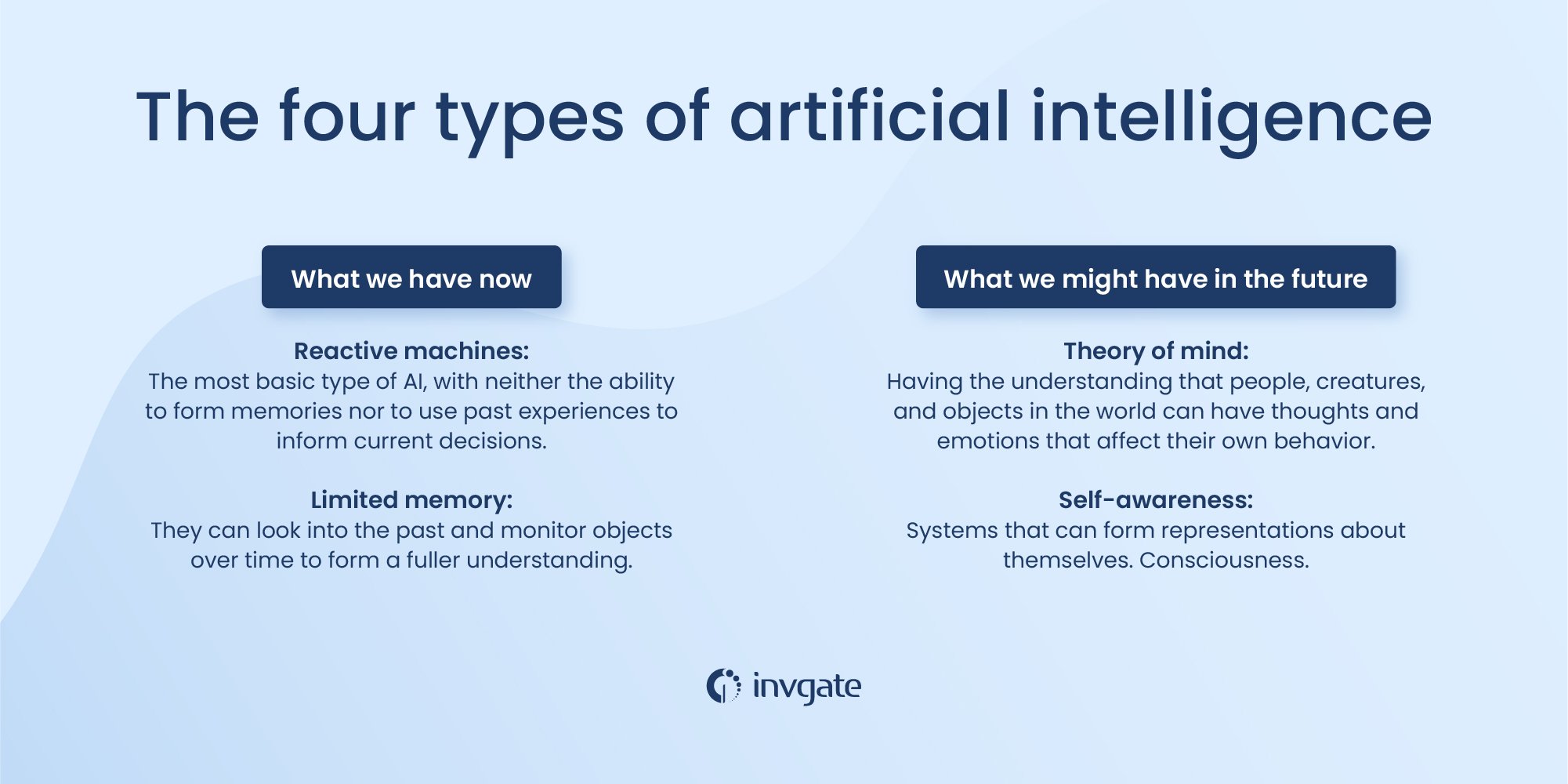
Reactive machines
Reactive machines follow the most basic of AI principles and, as their name implies, are capable of only using their intelligence to perceive and react to the world in front of it. A reactive machine cannot store memory and as a result, cannot rely on past experiences to inform decision-making in real-time.
Limited memory
Limited memory artificial intelligence has the ability to store previous data and predictions when gathering information and weighing potential decisions — essentially looking into the past for clues on what may come next. Limited memory artificial intelligence is more complex and presents greater possibilities than reactive machines.
Theory of mind
Theory of mind is just that — theoretical. We have not yet achieved the technological and scientific capabilities necessary to reach this next level of artificial intelligence. According to researchers and AI experts, the concept is based on the psychological premise of understanding that other living things have thoughts and emotions that affect the behavior of one’s self.
In terms of AI machines, this would mean that AI capabilities would include comprehending how humans, animals, and other machines feel and make decisions through self-reflection and determination, and then will utilize that information to make decisions of their own.
Self-awareness
Once Theory of mind can be established in artificial intelligence, at some point well into the future, the final step will be for new AI to become self-aware. This kind of artificial intelligence possesses human-level consciousness and understands its own existence in the world, as well as the presence and emotional state of others. It would be able to understand what others may need based on not just what they communicate to them but how they communicate it. We're far, far away from achieving this.
Examples of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence can take many forms, here are some of the most common AI examples:
- Chatbots
- Smart assistants
- Robo-advisors
- Email smap filters
- Netflix's recommendations
Let's take a quick look at each of them.
Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots understand free language, but also have a predefined flow to make sure they solve users’ problems. They can remember the context of the conversation and the user’s preferences.
These chatbots can jump from one point of conversation scenario to another when needed, and address random user requests at any moment. Well-known brands are Slush, Vainu, and HDFC Bank’s chatbot.
Siri, Alexa, and other smart assistants
Smart assistants are devices loaded with software that you use to access information, perform tasks, or control other devices. You can have a smart assistant on your computer or your phone, but most people use them through a smart speaker. Speech is then processed through NLP. Well-known brands include Alexa, Siri, Cortana, and Google Assistant.
Self-driving cars
Self-driving cars use technology to replace driver assistance with automated safety features to navigate roads. A mixture of sensors, software, radar, GPS, laser beams, and cameras monitor road conditions to operate and navigate an autonomous vehicle. All the information gathered is then assessed through AI machine learning.
Robo-advisors
Robo-advisors are digital platforms that provide automated, algorithm-driven financial planning services with little to no human supervision. A typical robo-advisor asks questions about your financial situation and future goals through an online survey; it then uses the data to offer advice and automatically invests for you. This is often referred to as responsible AI.
Email spam filters
Blacklist email spam filters work by blocking emails from senders that have been put on a list of spammers. Blacklist filters are updated on a regular basis because spammers can change their email addresses relatively easily.
Netflix's recommendations
Netflix, a leading OTT platform, uses AI for its recommendations system that estimates the probability of a user watching a particular title based on the following factors:
- Viewer interactions with Netflix services like viewer ratings, viewing history, etc.
- Information about the categories, year of release, title, genres, and more.
- Other viewers with similar watching preferences and tastes.
- Time duration of a viewer watching a show.
- The device on which a viewer is watching.
Machine learning & deep learning
Machine learning (ML) is a type of AI that allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms use historical data as input to predict new output values.
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning, which is essentially a neural network with three or more layers. These neural networks attempt to simulate the behavior of the human brain — albeit far from matching its ability — allowing it to “learn” from large amounts of data.
How can AI be used in ITSM?
As systems generate increasing data volumes, service desk and an ITSM automation tool are absolutely key to helping IT improve how it delivers services. Artificial intelligence and machine learning help automate and improve services for end-users, while providing context-based recommendations, improved correlation, anomaly detection, root-cause analysis, and much more. An example of this could be intelligent agents (powered by AI).
A large part of an ITSM platform is its ability to proactively learn about and deal with issues: server concerns, application updates, forgotten passwords — whatever arises. Now, as AI application automates processes and determines root causes, it is reducing all the noise an environment produces not only at the help desk but throughout the organization.
Mauricio Corona, from BP Gurus, expanded on the meaning (and difficulties) of adding artificial intelligence to service management when featured on the 10th episode of Ticket Volume, InvGate's podcast for Service Management professionals:
On the IT Service Management space, what we have seen is one of the main issues is to get the right strategy on the multichannel and omnichannel strategies within the organizations.
And when we are enabling robots, [...] this is going to be an additional channel of communications for you. So, you will consider it into your omnichannel strategy. This robot, it will be connected into your ticketing system, it will go through Incidents, through Requests, through Change, through Configurations. They are going to be into your CMDB, the CI, everything.- Mauricio Corona, BP Gurus.
InvGate Service Management, for instance, features machine learning capabilities in a feature named Support Assist. Support Assist is powered by Artificial Intelligence with some functionalities based on Natural Language Processing, and others built on Neural Networks, to suggest actions that could positively impact the performance of IT support agents.
The main goal of these tools is to speed up first response times significantly while also improving the accuracy of data for better routing and reporting. As each client is different, the assistant relies on a tight collaboration between these machine learning techniques to learn from each of all company environments.
Key takeaways
We’ve learned that AI is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems, and that it works through algorithms that seek to create expert systems that make predictions or classifications based on input data.
It’s important to remember how AI technology is classified into four categories and how they increase in complexity. Additionally, we’ve seen several examples of AI-powered services such as chatbots and smart assistants. But perhaps the biggest takeaway is how AI technology can improve a company’s efficiency with AI integration in a service desk platform like InvGate Service Management does.
We hope to have shed a little more light on the matter of artificial intelligence so as to demystify this powerful technology and see just how useful it can be in the current IT landscape. We’ll take a look at machine learning and deep learning soon!
Frequently asked questions
Will AI steal your job?
According to the World Economic Forum's "The Future of Jobs Report 2020", AI is expected to replace 85 million jobs worldwide by 2025. Though that sounds scary, the report goes on to say that it will also create 97 million new jobs in that same timeframe.
Can AI take over the world?
No, AI will not take over the world. Movies like "I, Robot" are science fiction, with an emphasis on the word fiction. All that said, AI is a powerful business tool that is supporting companies and their customer service strategies. Plus, AI policy makes sure that these potential outcomes are prevented.
What are the pros of AI?
- Increased efficiency.
- Improved workflows.
- Lower human error rates.
- Deeper data analysis.
- More informed decision making.
- 24/7 availability.
What are the cons of AI?
- High costs.
- No creativity.
- Potential increase in unemployment.
- Ethics are still in question.
















