With vulnerabilities continuously on the rise, staying oblivious to cybersecurity is no longer an option. A strong Vulnerability Management strategy has to be proactive, and in order to help you with that, we've created this list of known exploited vulnerabilities in 2025.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) is at the forefront of safeguarding critical infrastructure and combating cyber threats. It has a complete catalog of Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE), where you can find a brief overview of every discovered security breach that affects a wide range of vendors.
In this article, we'll focus on known vulnerabilities identified by CISA thus far in 2025, focusing on major operating systems and software providers. Specifically, we will delve into vulnerabilities affecting Google, Microsoft, Apple, and Linux, shedding light on their potential risks and emphasizing the significance of Patch Management strategies.
- Google vulnerabilities
- Microsoft vulnerabilities
- Apple vulnerabilities
- Linux vulnerabilities
- How to find outdated software

List of known exploited vulnerabilities in 2025
Google vulnerabilities
Let's start with Google vulnerabilities. So far, the company has addressed the following CVEs:
- CVE-2024-7965: A vulnerability in the V8 JavaScript engine used by Google Chrome and other Chromium-based browsers. This vulnerability is categorized as an inappropriate implementation, which allows remote attackers to exploit heap corruption through specially crafted HTML pages. It has a high CVSS score of 8.8, indicating a significant risk to system confidentiality and integrity.
- CVE- 2023-2033 - Chromium's open-source JavaScript engine V8 in Google Chrome browsers was affected by a type confusion. The vendor patched the issue from version 112.0.5615.121. An attacker could "exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page" if exploited.
- CVE-2023-2136 - A high severity vulnerability in the Skia graphics library that is used by Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. It affects Google Chrome versions prior to 112.0.5615.137 and Microsoft Edge versions prior to 112.0.1722.58.

Microsoft vulnerabilities
As for Microsoft vulnerabilities, CISA has issued the following:
- CVE-2025-21333: A heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability found in the Windows Hyper-V NT Kernel Integration component. This vulnerability allows local attackers to escalate their privileges to SYSTEM level, which grants them full control over the Hyper-V host system.
- CVE-2024-26169: Serious vulnerability in the Windows Error Reporting Service that allows local attackers to gain SYSTEM privileges. It was actively exploited in ransomware campaigns, particularly by the Black Basta group. Microsoft addressed this issue, and users are strongly advised to apply the patch immediately.
- CVE-2023-21674 - Vulnerability that affected the Advanced Local Procedure Call (ALPC) interface of Microsoft Windows operating systems. Classified as an elevation of privilege vulnerability, it was patched along with Windows 10 version 21H1 (May 2021 Update), Windows 10 version 20H2 (October 2020 Update), and Windows Server version 20H2 (October 2020 Update).
- CVE-2023-21715 - A security flaw that affects Microsoft Publisher. It allows attackers to bypass a critical security feature known as Office macro policies. The vulnerability was patched by the vendor.
- CVE-2023-21716 - Remote code execution vulnerability discovered in Microsoft Office. The vendor issued a patch to prevent attackers from tricking users into opening a malicious RTF document.
- CVE-2023-21768 - The Ancillary Function Driver (AFD) of the Windows operating system had a flaw that allowed attackers to elevate their privileges on a targeted system. The vendor released a security update to update the exploit.
- CVE-2023-21823 - Attackers could execute arbitrary code in an elevated context and affect the graphics component of Microsoft Windows. The vendor released a security patch to solve the issue.
- CVE-2023-23376 - Elevation of privilege vulnerability that affected the Common Log File System (CLFS) driver in Windows operating systems. The patch was included in the April 2023 Security Updates, released on April 11, 2023.
- CVE-2023-23397 - Security vulnerability that affected Microsoft Outlook and allowed an attacker to gain elevated privileges on a targeted system. The vendor released a patch to address it.
- CVE-2023-24880 - A critical vulnerability that targets the Windows SmartScreen feature. It allows attackers to craft malicious files that evade the MOTW defenses. Organizations and users must apply the latest security patches released by Microsoft.
- CVE-2023-28252 - Vulnerability that affects the Windows Common Log File System (CLFS) and allows attackers to gain SYSTEM privileges on targeted machines.
- CVE-2023-41080 - High-severity privilege escalation flaw that affected Microsoft Exchange Server 2013, 2016, and 2019. The latest versions that include the patch are CU24, CU15, and CU4.
Apple vulnerabilities
The following are the most recent vulnerabilities that affected Apple products:
- CVE-2025-24085: This is a use-after-free vulnerability identified in Apple's CoreMedia framework, which is utilized across various Apple products, including iOS, macOS, and others. This vulnerability allows a malicious application to potentially elevate privileges on affected devices, enabling attackers to execute arbitrary code within the context of the logged-in user. Apple has addressed this issue.
- CVE-2024-23222: Classified as a high-severity vulnerability, it affects the WebKit engine, which powers Apple’s Safari browser. This vulnerability stems from a type confusion issue in WebKit, where the system incorrectly handles objects. Devices running iOS, iPadOS, macOS, and tvOS are susceptible.
- CVE-2022-42475 - Heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability found in FortiOS SSL-VPN that allowed attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (DoS) condition.
- CVE-2023-23529 - Type of confusion issue in the WebKit browser engine patched by the vendor shortly after its discovery.
- CVE-2023-28204 - It is WebKit zero-day vulnerability attackers that might be able to access sensitive data and is addressed in Apple's Rapid Security Response update.
- CVE-2023-28205 - This zero-day vulnerability affects macOS, iOS, and iPadOS.
- Apple has released security updates for macOS version 13.3.1 iOS and iPadOS version 16.4.1.
- CVE-2023-28206 - Security vulnerability that affects Apple devices, specifically macOS, iOS, and iPadOS. Apple promptly responded by releasing security updates to address the issues.
- CVE-2023-32373 - It is a WebKit vulnerability which can result in the disclosure of sensitive information. Apple has addressed in its recent security updates.
- CVE-2023-32409 - Zero-day vulnerability that can allow a remote attacker to "break out of Web Content sandbox." It was addressed by the vendor in recent updates.
Linux vulnerabilities
And lastly, these are the known vulnerabilities regarding the Linux operating system:
- CVE-2024-1086: A use-after-free vulnerability in the Linux kernel's netfilter component, specifically affecting the nf_tables framework. This flaw allows local attackers to escalate their privileges, potentially gaining root access to the system
- CVE-2023-0266
- CVE-2024-1086 is a serious Linux kernel vulnerability that allows local attackers to escalate privileges to root. As noted in active exploitation reports, it has been used in ransomware campaigns.
- CVE-2014-0196
Patch Management with InvGate Asset Management
If you need help spotting outdated software in your company network, InvGate Asset Management can do that in just a few clicks.
All you need to do is go to the Explorer tab and type "Software name, is:[Name of the software or device]" and "Reported version, is not:[Number of patched version]". And that's it!
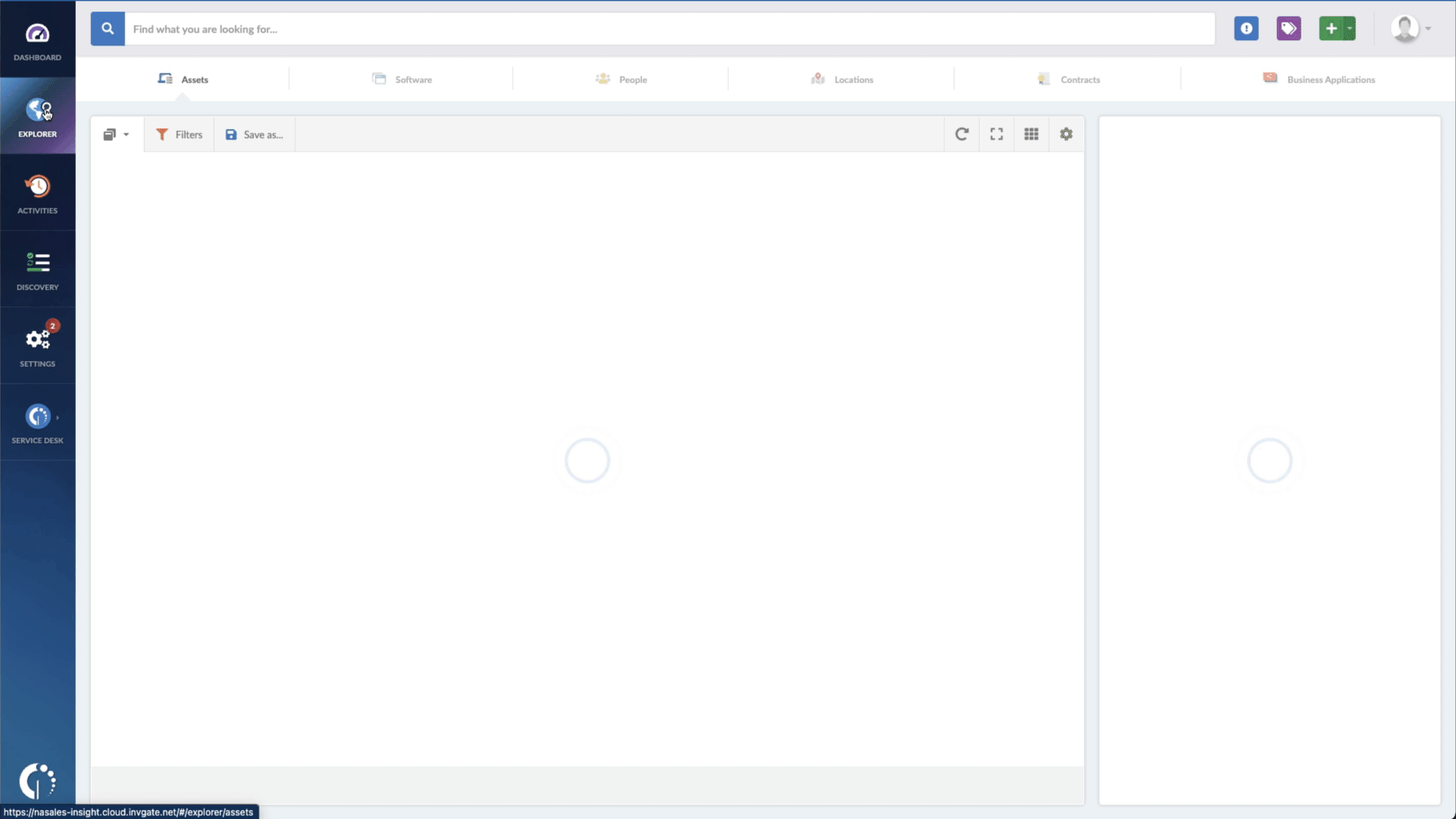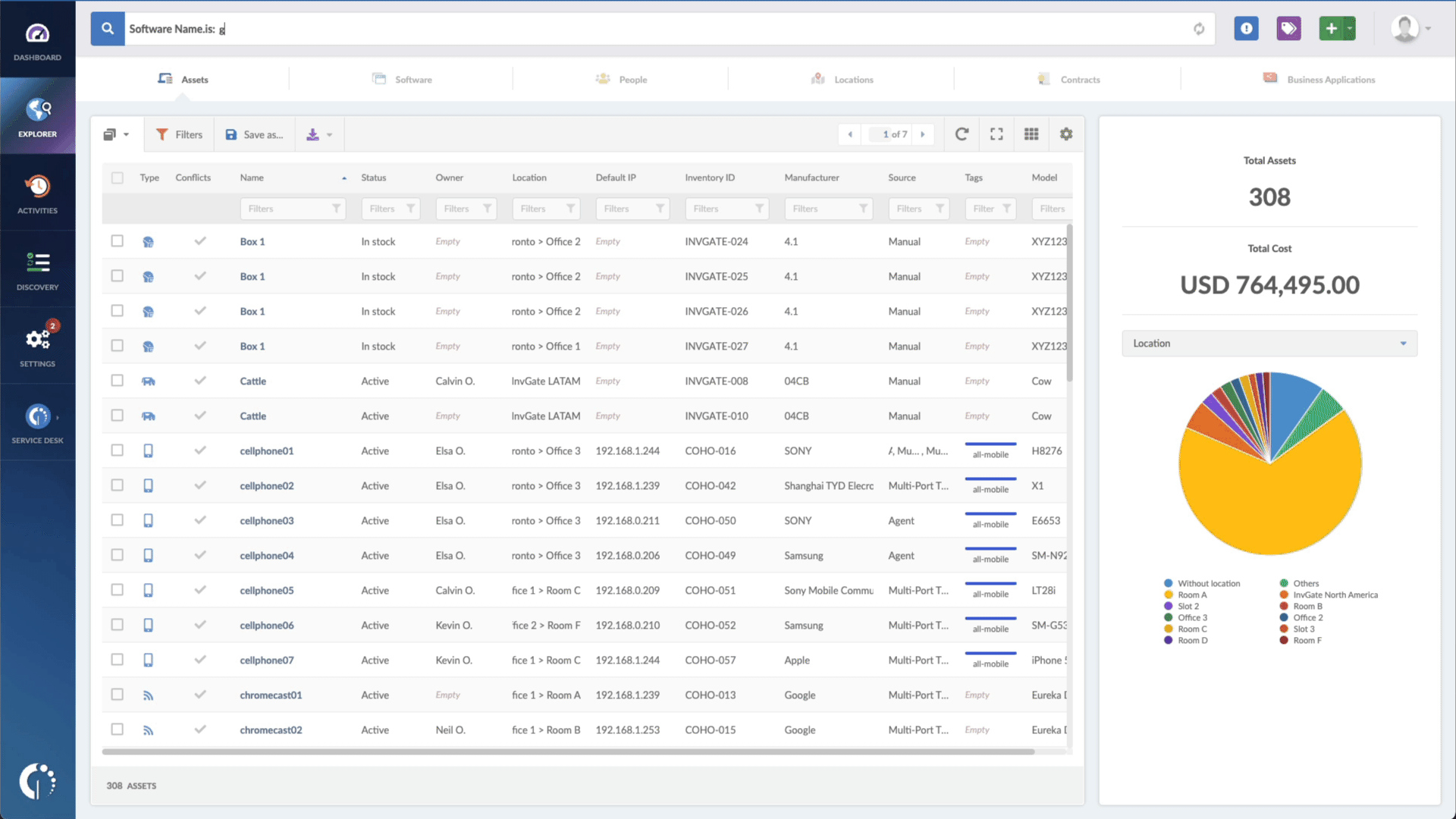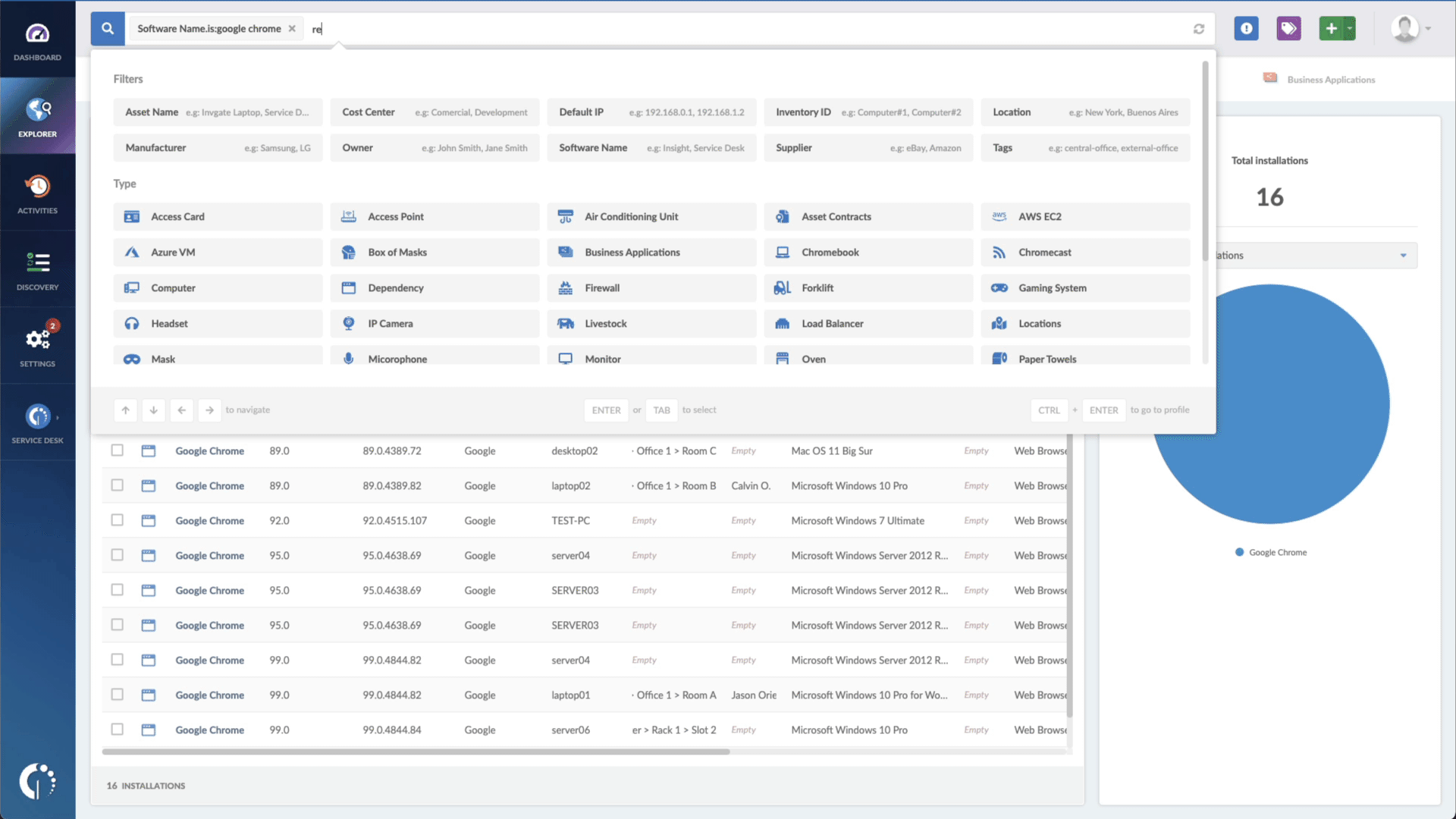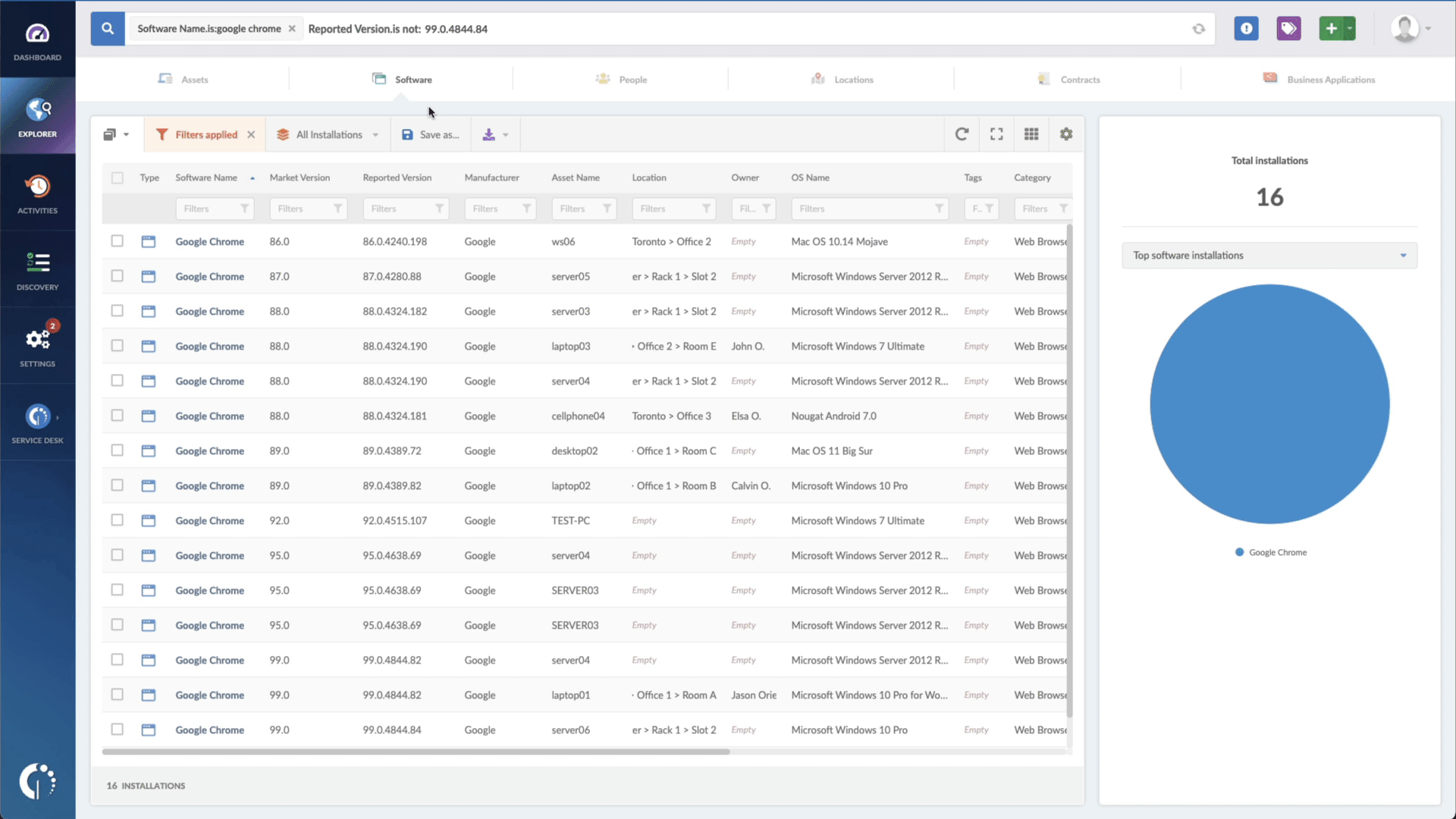
InvGate Asset Management will pull out a report in seconds with all the software that needs to be taken care of. If you like, you can export the information in CSV format and hand it out to an agent to solve it.
Want to try it out? Request InvGate Asset Management's 30-day free trial or explore the live demo!