A proper Patch Management process is crucial as it helps prevent data breaches by fixing security vulnerabilities and bugs. It is also the way to make sure all your devices run the latest software versions, which implies having access to updated functions and characteristics.
Just so we are all on the same page, Patch Management consists of acquiring, testing, distributing, and installing updates or software patches. It is an essential part of an organization's IT Asset Management (ITAM), and it requires following Patch Management best practices and selecting a top patching software to ensure the task is done effectively and efficiently.
In this article, we'll dive into its definition and the instructions needed to implement the whole process. We'll also introduce you to InvGate Asset Management, our solution to complete the entire Patch Management process.
Ready? Let's go!

What exactly is Patch Management?
Patch Management is the process of identifying, acquiring, testing, and installing systems or software updates—or patches—to fix vulnerabilities, improve performance, and ensure compliance. It’s a crucial component of maintaining the health and security of an organization's IT infrastructure.
In essence, Patch Management is about keeping systems up-to-date. By regularly applying patches, organizations can protect against known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. This proactive approach helps in reducing the attack surface, ensuring that all systems are fortified against potential threats.
Patch Management in IT Asset Management
Patch Management is deeply intertwined with IT Asset Management. ITAM involves tracking and managing the lifecycle of IT assets within an organization, from acquisition to disposal. Effective Patch Management ensures that all IT assets, including hardware and software, are up-to-date, secure, and functioning as intended.
By integrating Patch Management with ITAM, organizations can gain better visibility into their assets, ensuring that all are accounted for and maintained properly. This approach not only improves security but also optimizes the performance and compliance of IT assets, leading to a more resilient IT environment.
Patch Management for security vulnerabilities
Patch Management plays a critical role in safeguarding an organization’s IT infrastructure against security vulnerabilities. Security patches are specifically designed to address flaws or weaknesses in software that could be exploited by malicious actors.
By promptly applying these patches, organizations can protect their systems from a wide range of threats, including malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access.
Neglecting to apply security patches can leave systems exposed, creating an entry point for cyberattacks. In today's threat landscape, where attackers constantly search for unpatched vulnerabilities to exploit, a robust Patch Management process is essential.
Regularly updating and securing systems not only mitigates risks but also ensures that the organization complies with industry regulations and best practices, thereby reinforcing overall cybersecurity.

Step-by-step instructions for implementing a Patch Management process
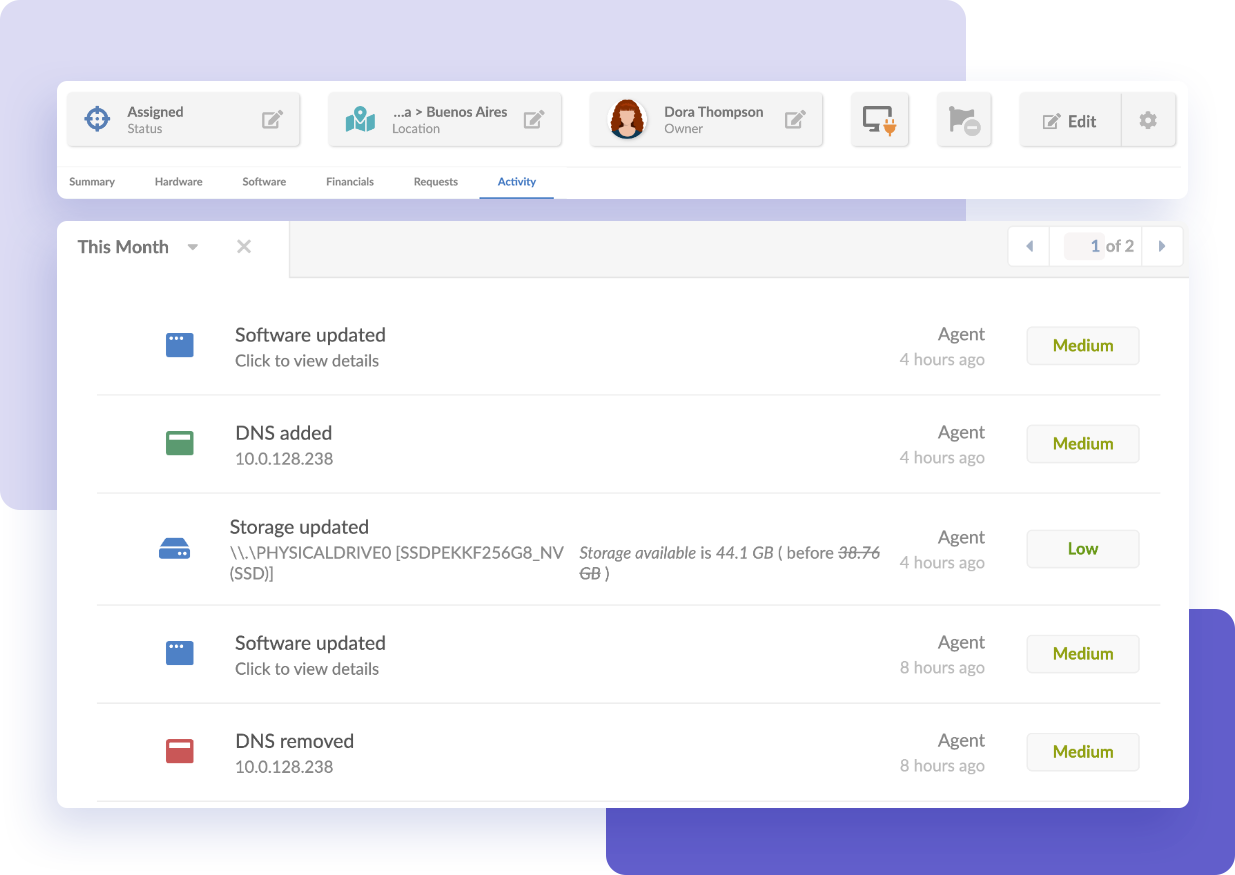
Organizations generally try to maintain software consistency across the different devices connected to the network, and resort to centralized Patch Management rather than letting each computer download its updates.
Centralized Patch Management usually implies an ITAM software solution that checks missing patches, downloads, and distributes them to the related equipment according to the Patch Management workflow defined by the company.
Here are the necessary steps to illustrate this process, as well as some tips to accomplish them with InvGate Asset Management.
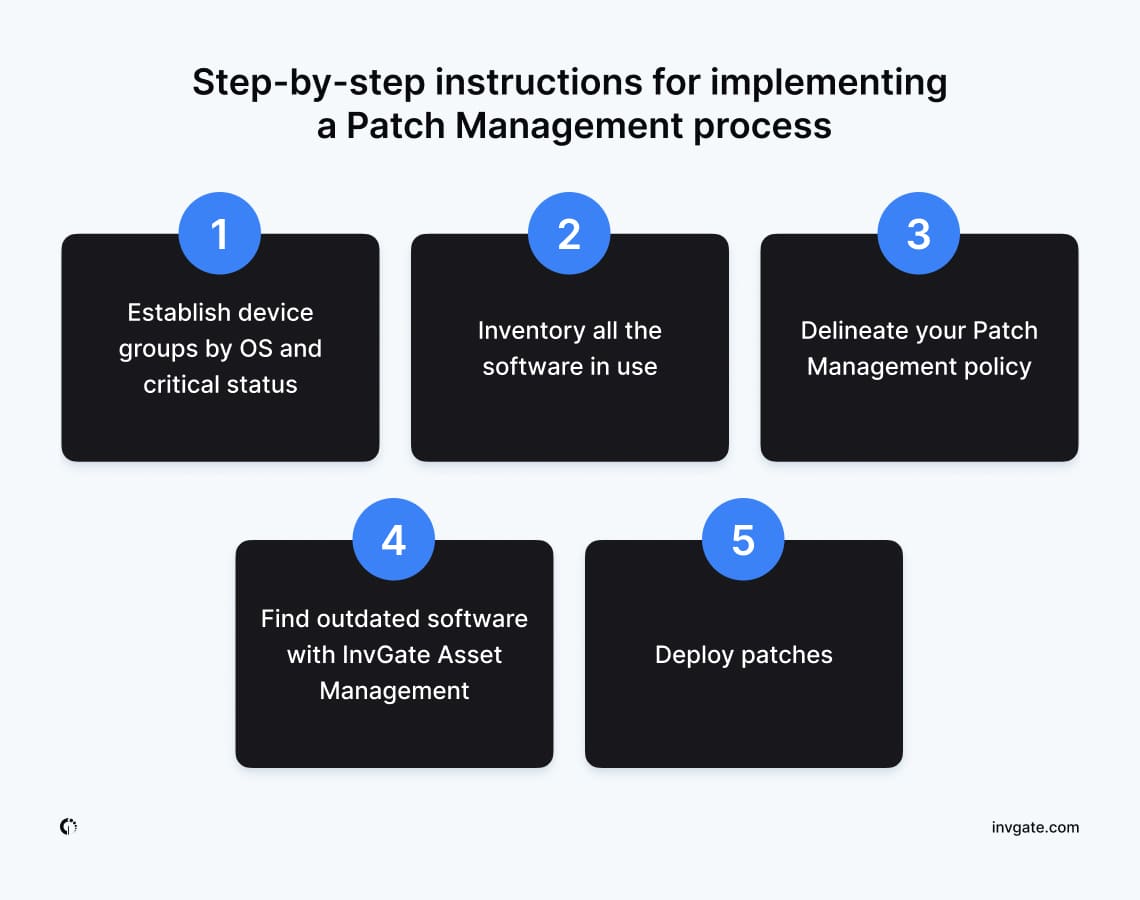
1. Establish device groups by OS and critical status
Applications and devices should be categorized according to their risk factor. How critical is that system or device to the organization? What data and processes will be affected? These questions will help determine priorities. Preserving security is crucial.
Servers or computers with confidential data should be considered a high priority, and thus should receive patches first. In contrast, less relevant, offline, and rarely used devices should be deemed a low priority.
It is crucial to have a multi-staged approach to streamline the patching process. In this sense, the chief information security officer might also want to establish device groups based on their operating system, as this will facilitate the patching process.
2. Inventory all the software in use
Organizations should build a complete IT inventory, including all the operating systems and applications, as the first step to assessing what patches have been installed and which ones might be missing. Knowing the current state of patching will help outline the strategy to be carried out.
In addition to inventorying assets, patch scanning should be performed to identify outdated or vulnerable software versions that require immediate updates. Patch scanning tools can automatically detect missing patches and highlight critical vulnerabilities, ensuring no risks are overlooked.
The inventory can be done manually or automatically through Asset Management software. In this sense, InvGate Asset Management provides you with a quick and easy unified view of your entire asset inventory, including their details and status. Plus, by installing InvGate’s Agent on your computers, it will also report all their data to your instance (including all the installed software), notify you when something is wrong, and help streamline patch scanning to uncover potential security gaps.
3. Delineate your Patch Management policy
Once priorities have been established based on the critical status of all the devices analyzed, it is time to outline a Patch Management policy that will determine how and when security patches should be deployed.
The policy will specify the procedures to be carried out based on the criticality of devices, the mitigation capabilities, and the risk imposed by the type of security vulnerability identified in each case. This is part of the Vulnerability Management organizations should carry out.
4. Find outdated software with InvGate Asset Management
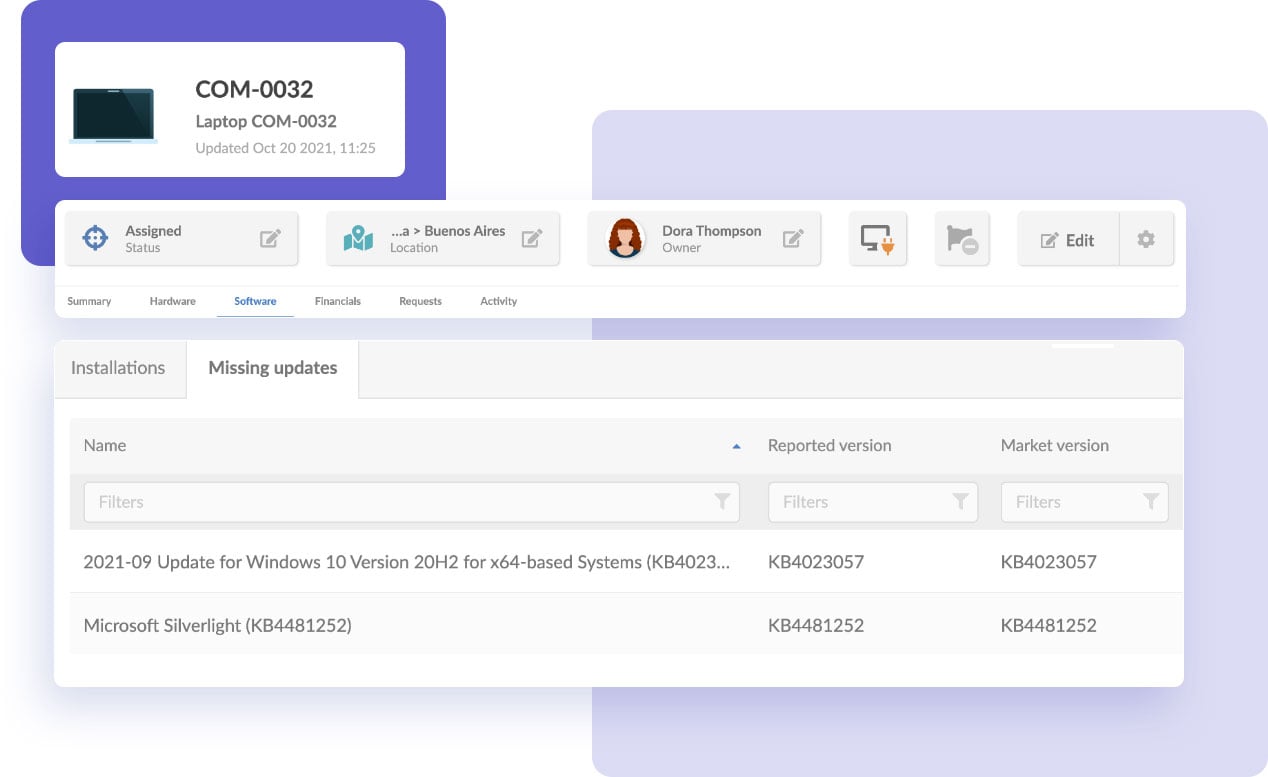
Up until now, you have put together an inventory outlined the rules to patching. Now, it’s time to take action. A crucial part of the Patch Management process is to effectively monitor your network to spot outdated devices that might pose a risk to the organization.
InvGate Asset Management offers two options to do it:
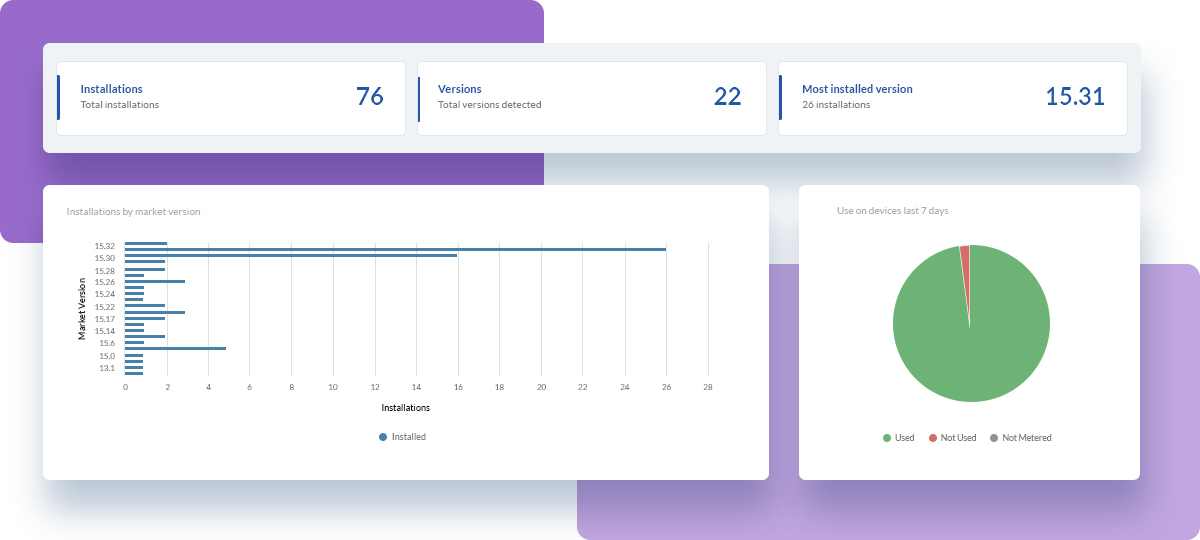
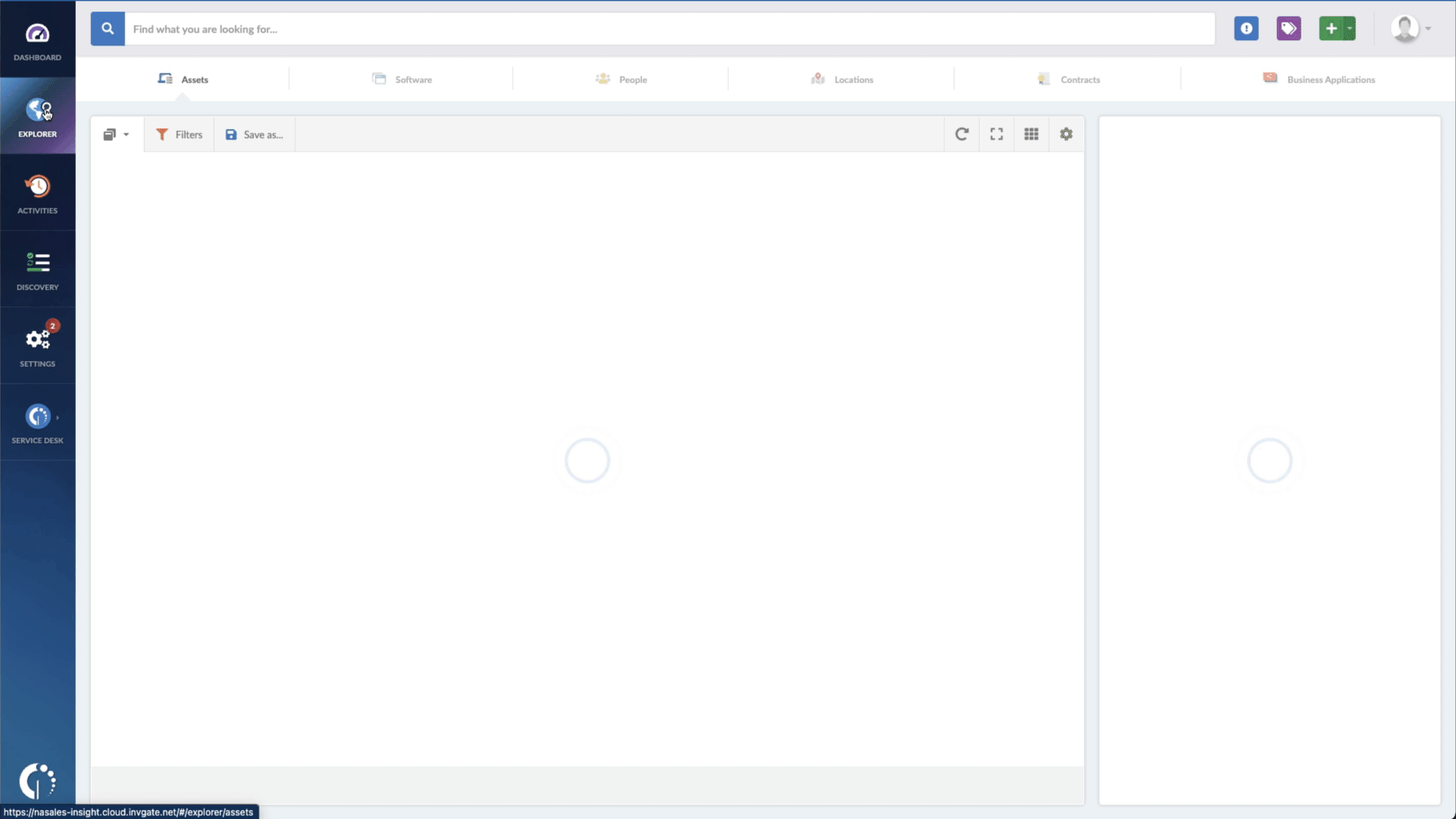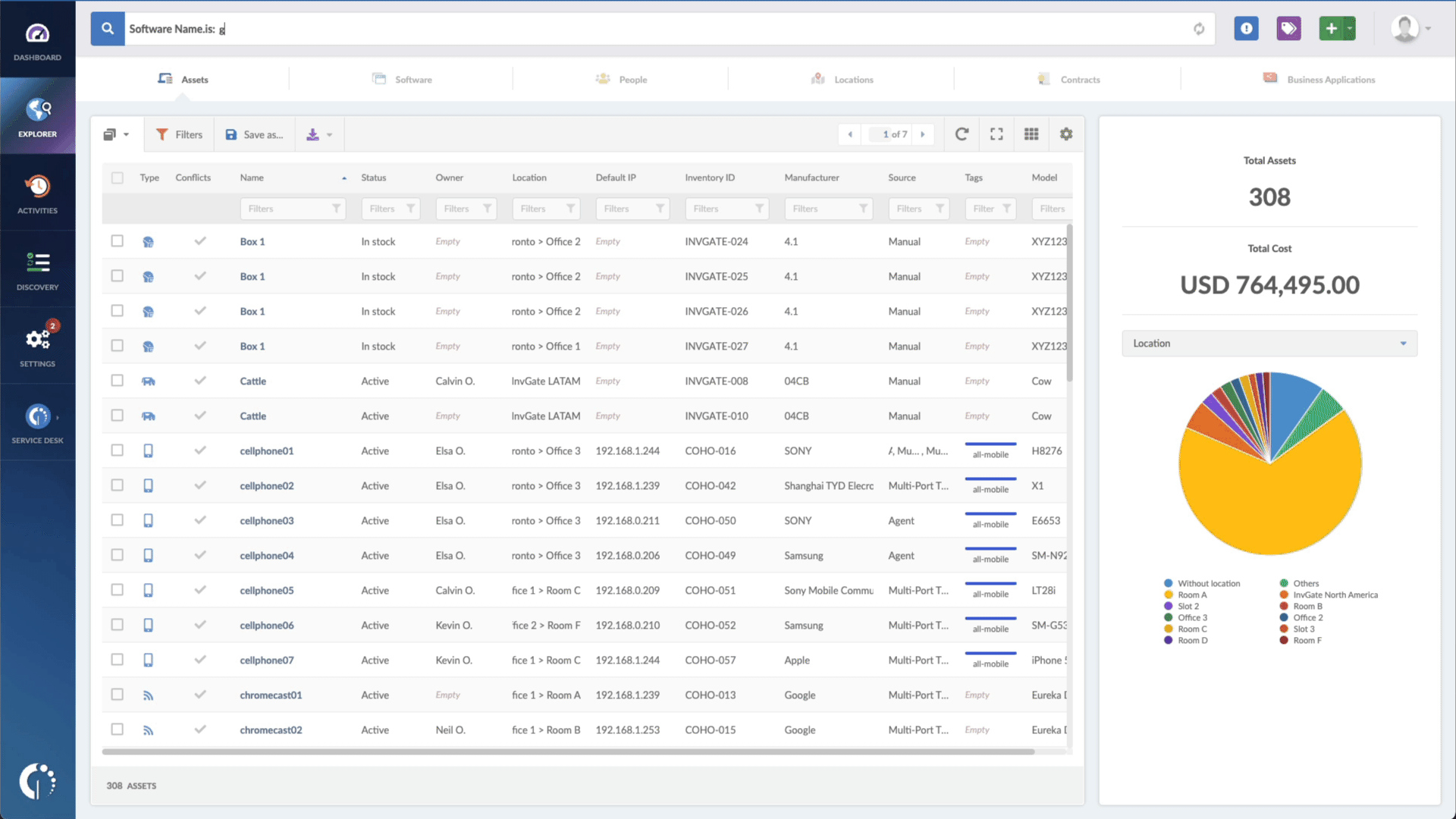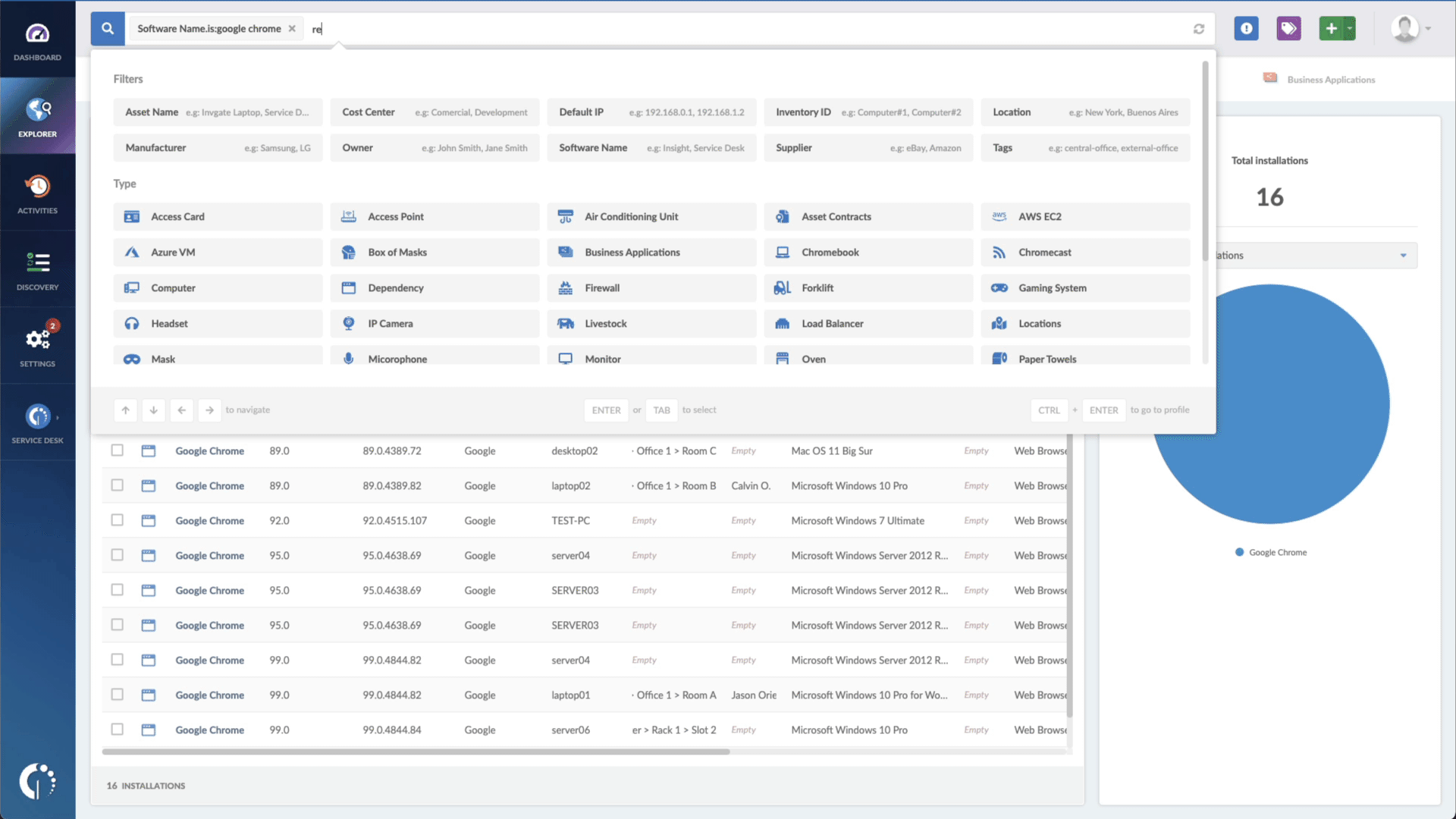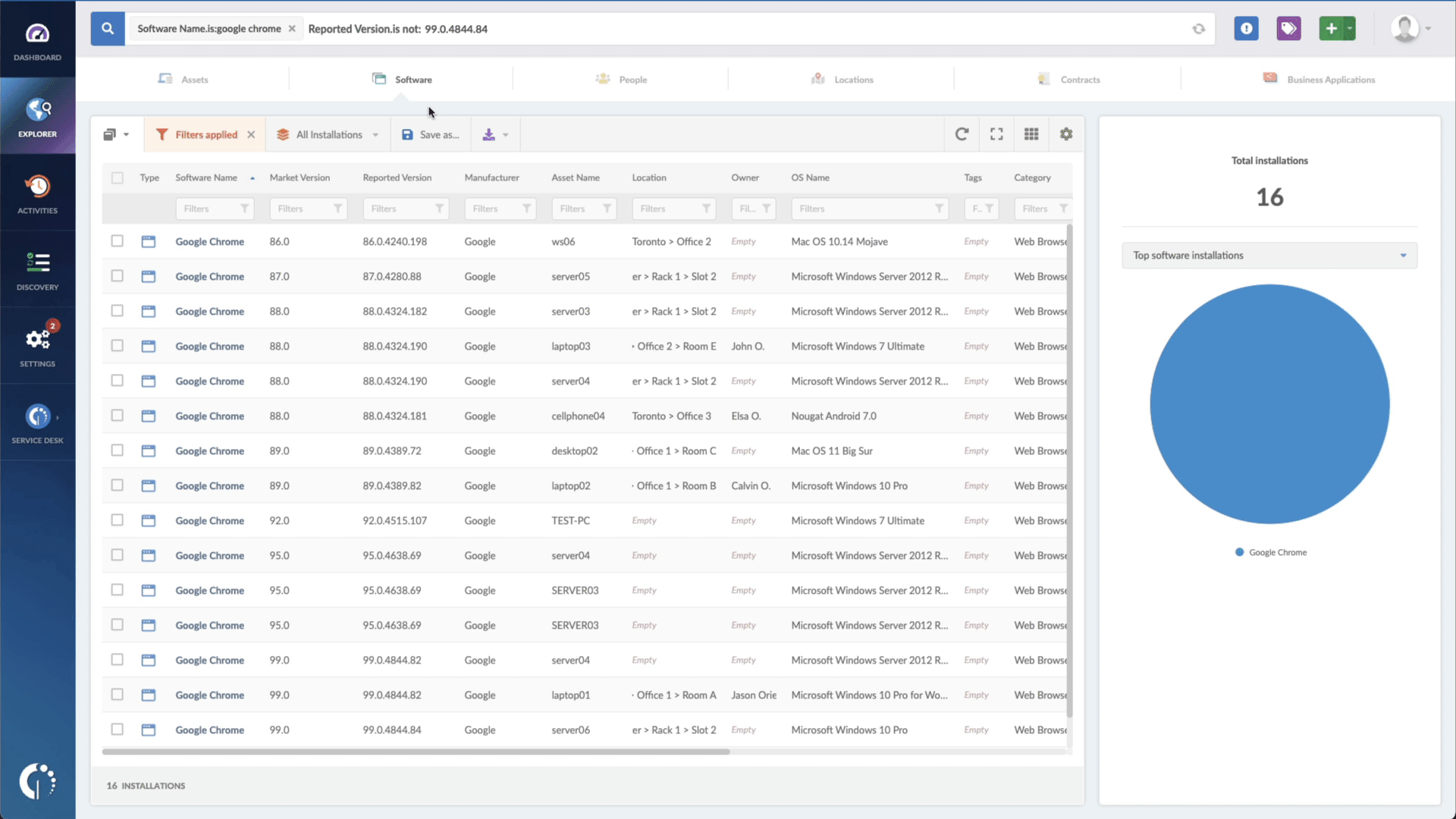
- Use its searching capabilities to find software that matches a specific manufacturer and version. The ones that match stand as the targets to be patched.
- Go to the software’s profile and check the “Installations by market version” dashboard to spot installations from previous versions.
Once you have identified the devices, prioritize the work based on usage or risk. If it’s a simple patch method, you can apply the patches to all machines at once. However, keep in mind that outdated software might be in place for a reason – be it because of old operating systems, lack of technical capabilities, or other. Part of the asset manager’s job is to determine whether updates are the right move for each scenario.
5. Deploy patches
Finally, it’s time to perform the patch deployment. Here, InvGate Asset Management also provides you with two alternatives:
- The first one is manual. Once you identify the device in need of patching, open its profile on InvGate Asset Management and use the remote desktop integration to fix it.
- The second one is using a software deployment tool to automate and streamline the process across various systems.
What are the goals of a Patch Management process?
Patch Management aims to keep all the operating systems in your network updated and, therefore, as secure as possible against malware and other vulnerabilities that may result in data losses and significant risks.
An effective patching process requires attaining the following goals.
1. Reduce interruptions and rollbacks
Careful planning is essential to minimize interruptions and prevent rollbacks during the patch deployment process. A well-executed Patch Management strategy involves scheduling updates during times when devices are not in active use, ensuring that the workflow is not disrupted.
This approach not only reduces the likelihood of interruptions but also minimizes the chances of encountering issues that could lead to rollbacks, which can be time-consuming and disruptive to business operations.
Moreover, by strategically planning patch deployments, IT teams can test patches in controlled environments before rolling them out to the entire organization. This step helps in identifying potential compatibility issues or conflicts, allowing the team to address them proactively.
A robust Patch Management process should also include contingency plans for dealing with unexpected issues, ensuring that rollbacks are a last resort rather than a frequent occurrence.
2. Create predictability and routine around patching
Establishing predictability in the Patch Management process is crucial for maintaining a secure and efficient IT environment. By developing a consistent routine, IT teams can ensure that all devices and software are regularly updated with the necessary patches.
This routine involves categorizing devices and software based on their criticality and scheduling periodic updates to maintain information security and system integrity.
A predictable patching routine also helps in building user trust and reducing resistance to updates. When users are aware of when and how updates will occur, they are less likely to experience disruptions and more likely to support the Patch Management process.
Additionally, a well-defined schedule allows IT teams to allocate resources effectively, ensuring that patches are applied promptly and without unnecessary delays.

3. Empower IT with emergency powers (rollback and distribution) when needed
While automation is a vital component of an effective Patch Management process, it’s equally important to empower the IT team with the ability to intervene manually when necessary. In cases where automated patching fails or unforeseen issues arise, IT professionals should have the authority and tools to perform emergency rollbacks or manually distribute patches.
This capability ensures that the organization can quickly respond to critical issues, minimizing downtime and maintaining system security.
Implementing a well-designed workflow for these emergency procedures is crucial. Such a workflow should outline the steps to be taken, the roles and responsibilities of team members, and the documentation required for future analysis.
By having a clear plan in place, the IT team can respond swiftly and efficiently to emergencies, ensuring that the entire Patch Management process remains smooth and effective even under challenging circumstances.
4. Ensure complete visibility into patch status
Maintaining full visibility into the status of patches across all devices and software is a fundamental aspect of effective Patch Management. It’s essential to know precisely how and when each system has been updated and to track which patch versions have been applied. This level of visibility allows IT teams to ensure that all systems are secure and up-to-date, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities being exploited.
An IT Asset Management (ITAM) tool with IT compliance monitoring capabilities can provide detailed historical reports of applied patches and the current software versions on each device. This data is invaluable for designing comprehensive IT asset reports, tracking potential issues, and proving compliance with internal policies and external regulations.
Furthermore, complete visibility enables the IT department to proactively address any emerging problems, ensuring that all assets remain secure and functional.
Patch Management tools
Selecting the right Patch Management software is a critical part of an effective Patch Management strategy.
These solutions should provide comprehensive features that help streamline Patch Management process making it more neat and efficient. Our pick -obviously- is InvGate Asset Management. Let's see why.
Although it’s not a dedicated Patch Management solution, with InvGate Asset Management, you get access to complete visibility of your IT assets within IT inventory, and you can monitor your network, identifying software that needs patching. This enables IT teams to track, manage, and patch devices across the organization efficiently.
Plus, its advanced reporting capabilities and customizable dashboards, ensures that IT teams can asses and continually improve their Patch Management process. The tool also integrates seamlessly with other systems (you can check out the full list here!), making it a versatile solution for comprehensive IT Asset Management.
Key takeaways
An effective Patch Management process should keep your company network safe against multiple vulnerabilities that have the potential to impact its performance.
The easiest way to do it is to add the workflow to your IT Asset Management practice. ITAM is well-known for its ability to contribute to reducing risks, and this is no exception. With such a solution, you’ll be able to map your entire IT infrastructure, spot outdated software, and update it.
If you want to try out InvGate Asset Management’s capabilities related to patching, ask for a 30-day free trial!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Patch Management process?
A Patch Management process is a procedure that involves acquiring, testing, deploying, and monitoring updates (patches) to software systems to address security vulnerabilities, improve functionality, and maintain system health.
How to audit the Patch Management process?
To audit Patch Management, review documentation for update policies, assess patch testing procedures, examine deployment records, validate monitoring practices, and ensure alignment with security standards.
What are some common problems with Patch Management?
One of the most common difficulties is the lack of visibility into the patches deployed and on what devices. Another problem is that the patch may fail, which opens the system to vulnerabilities and attacks. Manual patching is another common obstacle because it is time-consuming and can lead to errors. Finally, there's the problem of lack of mobile control. It is crucial that organizations implement updates on mobile devices to keep the corporate data secure.
What are the three types of Patch Management?
The 3 most common types of patches are:
- Security patches - Involves patching newly discovered security holes in the system.
- Bug fixes - Involves patching newly discovered security holes in the system.
- Performance patches - Enhance overall performance by lowering resource requirements, making apps run faster, or getting new functionalities.
What are Patch Management procedures?
Patch Management procedures involve identifying, acquiring, testing, and installing patches or making code changes to solve security vulnerabilities, fix bugs, or add features to a network's software or operating systems.
What is a security risk?
A security risk refers to the potential for loss, damage, or disruption to an organization's data, systems, or operations due to vulnerabilities that can be exploited by threats, such as cyberattacks, unauthorized access, or system failures. Managing these risks involves identifying vulnerabilities, implementing safeguards, and regularly updating systems to protect against potential threats.