As the digital world becomes more interconnected, cyber threats evolve and become more sophisticated, putting businesses and individuals at risk. On February 14, 2023, Microsoft announced a critical vulnerability in the Windows Common Log File System (CLFS) driver, known as CVE-2023-23376.
This vulnerability allows attackers to elevate privileges and gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, potentially resulting in severe consequences for affected systems. In this article, we’ll provide an overview of CVE-2023-23376, including its associated risks, the latest security patch, and how to identify devices exposed to this vulnerability.
If you are concerned about the security of your devices and want to learn more about CVE-2023-23376, keep reading!
About CVE-2023-23376
CVE-2023-23376 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability that affects the Common Log File System (CLFS) driver in Windows operating systems.
The CLFS driver is responsible for providing support for transaction logs in Windows. This vulnerability allows an attacker to gain elevated privileges on a Windows system by exploiting a flaw in the CLFS driver. Specifically, the vulnerability exists due to improper handling of objects in memory by the CLFS driver, which can allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code in kernel mode.
If this vulnerability is exploited, an attacker can take control of the affected system and execute code with elevated privileges. This permission can allow the attacker to steal sensitive data, install malware, or perform other malicious activities on the compromised system. In the worst-case scenario, an attacker can gain complete control of the affected system, compromising the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the system and its data.
Microsoft has released a security patch to fix this vulnerability. It was included in the April 2023 Security Updates, which were released on April 11, 2023. Windows users who have enabled automatic updates will receive the patch automatically. However, users who have disabled automatic updates or who have not installed the latest security updates should install the patch immediately to protect their systems.
How to find devices exposed to CVE-2023-23376
If you suspect your Windows operating system may be vulnerable, taking immediate action to protect it is vital. You can do it with InvGate Asset Management, which can help you quickly identify any devices affected by the CVE-2023-23376 vulnerability and take the necessary steps to patch it. Here are the steps to follow to use InvGate Asset Management to manage this vulnerability on your Windows system:
- Open InvGate Asset Management and go to the Explorer tab.
- Type in the Search bar “Software name, is:Windows” to filter all Windows devices.
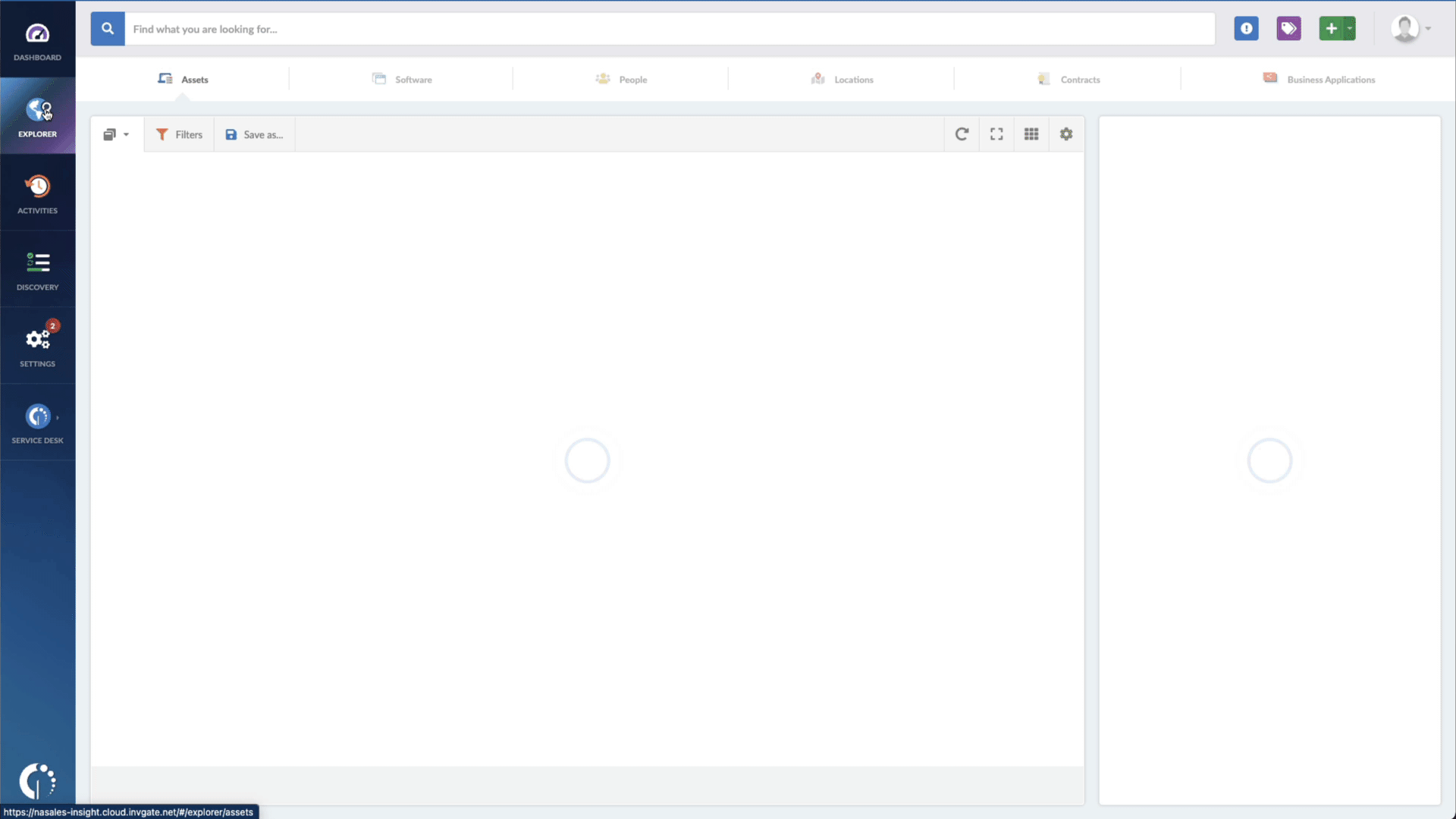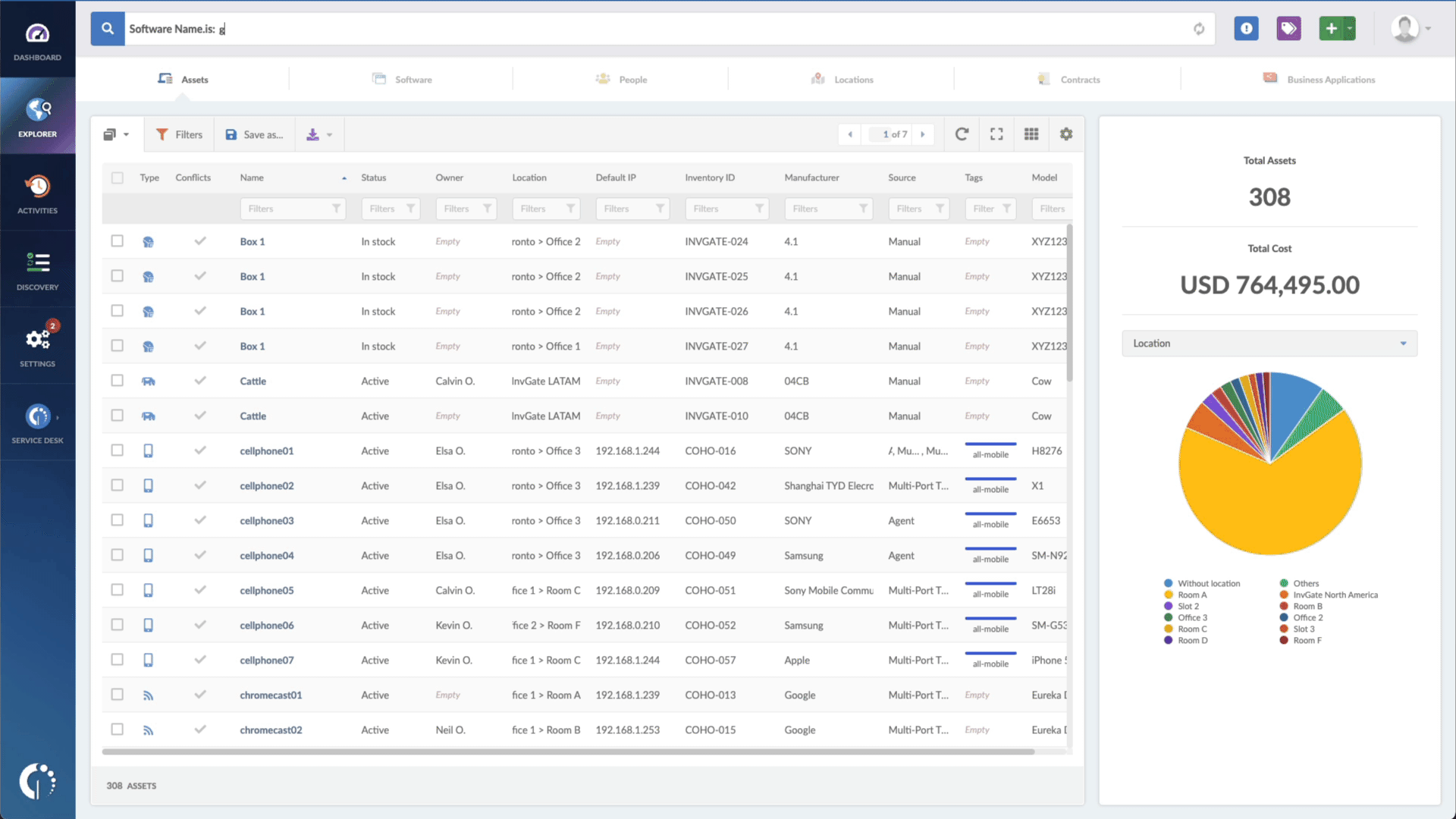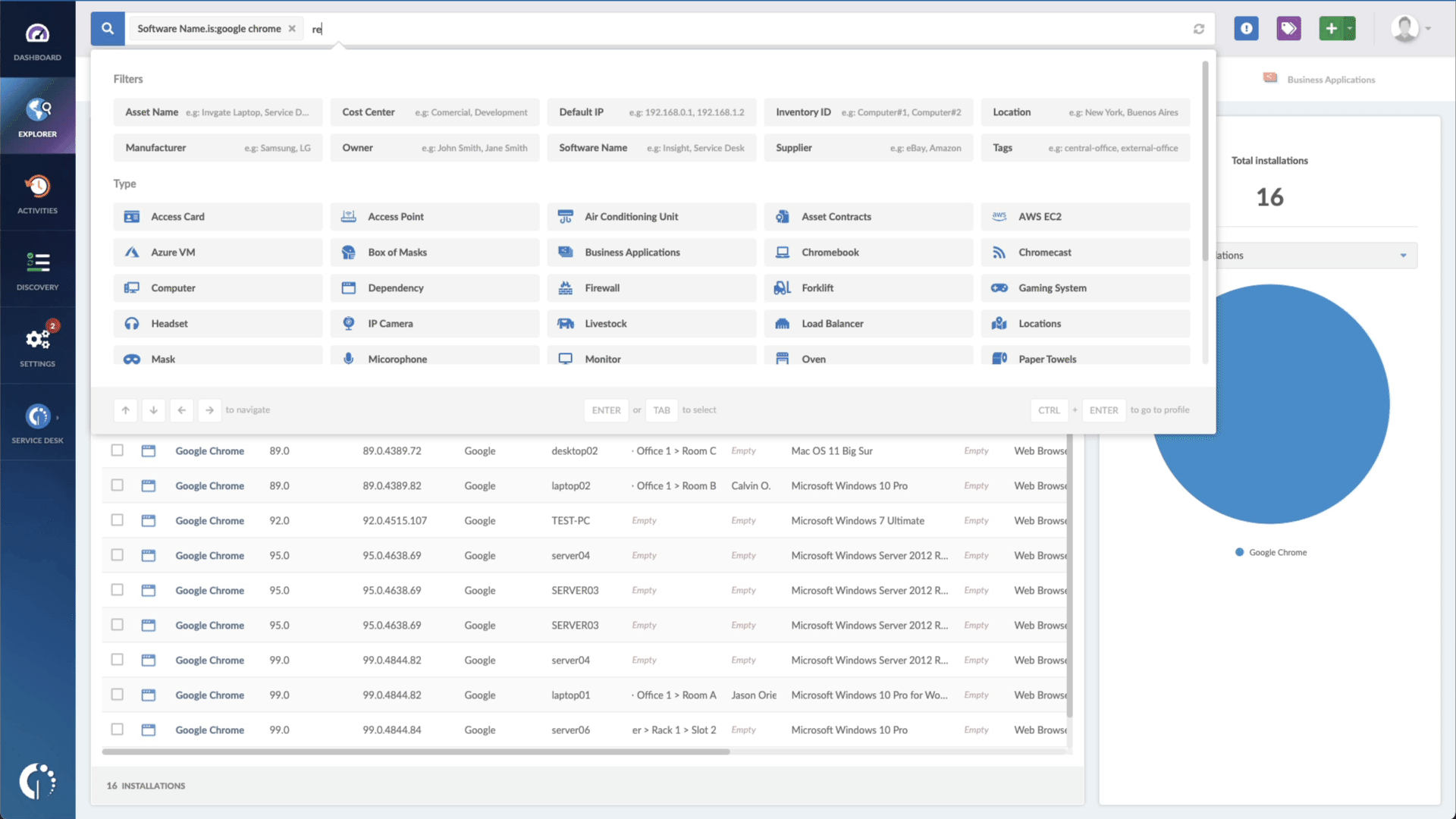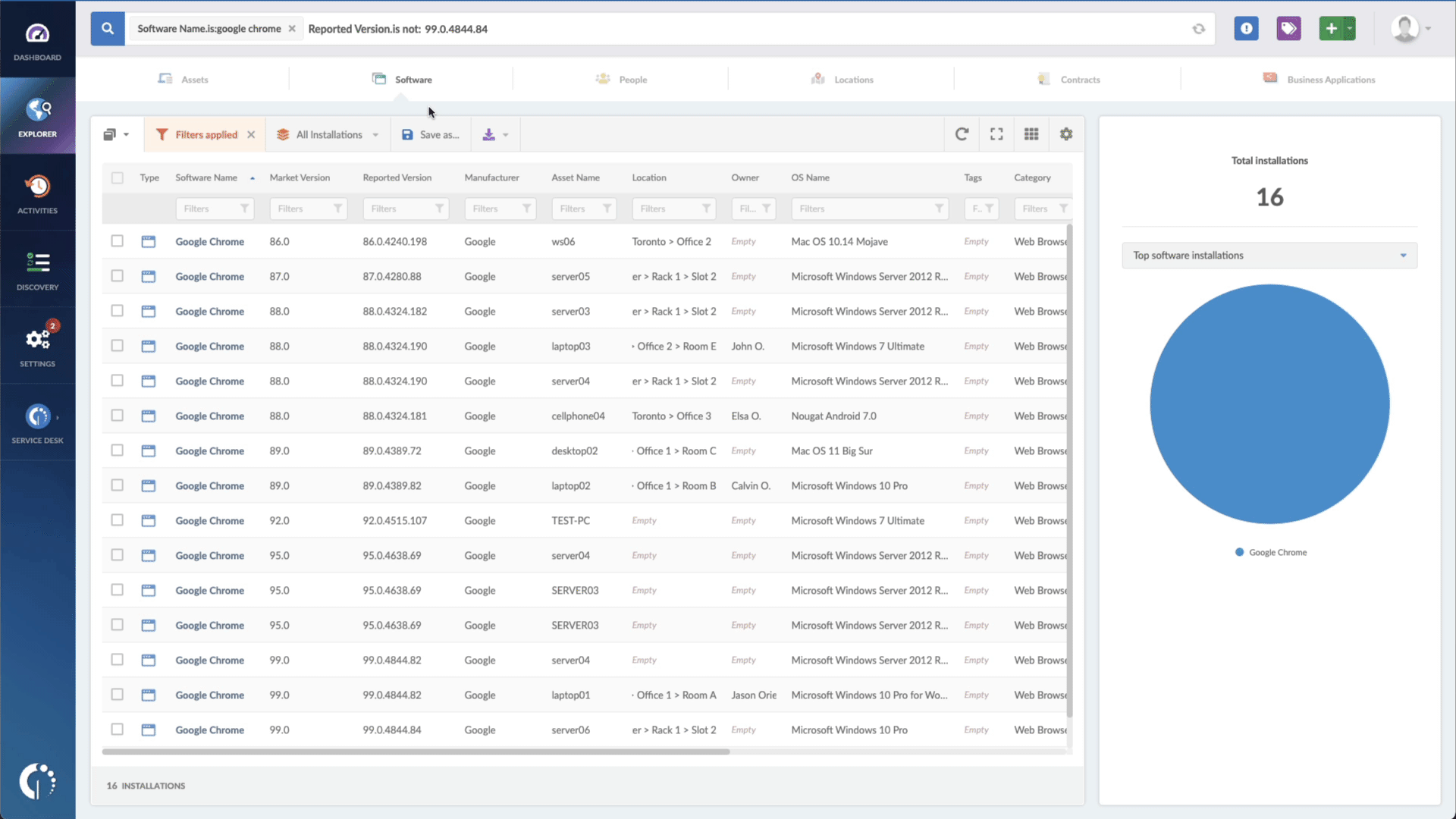
- Add another filter to the Search bar to see all devices missing the security patch. To do that, add the following filter: “Reported version, is not:” and paste Microsoft’s patched version (depending on your operating system, you’ll find the security update number on Microsoft’s webpage).
That’s all! Now you have a list of all the Windows devices vulnerable to CVE-2023-23376. You can then export this list in CSV format and give it to one of your agents to patch or create a ticket so they can be manually updated.
The bottom line
The CVE-2023-23376 elevation of privilege vulnerability in the Common Log File System (CLFS) driver is a critical security threat to Windows systems. Exploiting this vulnerability can result in an attacker gaining control of a compromised system and executing malicious code with elevated privileges. The risk of not patching it is significant, and Windows users are advised to update their systems with the latest security patch as soon as possible.
With InvGate Asset Management, you can effortlessly search for the devices in your network that may be affected by the CVE-2023-23376 vulnerability and take the necessary steps to patch it.
Request a 30-day free trial of InvGate Asset Management today to see how it can help simplify your patch management process and improve your organization's security posture.