CVE-2023-0266, which has recently emerged, joins the expanding roster of vulnerabilities that have been exploited in 2023. This use-after-free vulnerability, discovered in the ALSA PCM package of the Linux Kernel, presents a grave security risk. Local attackers with normal privileges can exploit this flaw, gaining unauthorized access and potentially exposing sensitive kernel memory.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the technical intricacies of CVE-2023-0266, explore its implications, and most importantly, provide you with actionable steps to mitigate the associated risks with InvGate Asset Management.
Effective Patch Management is crucial in combating vulnerabilities like CVE-2023-0266. Keep reading to strengthen your defenses against emerging threats and safeguard your systems.
About CVE-2023-0266
CVE-2023-0266 is a critical use-after-free vulnerability discovered in the ALSA PCM package within the Linux Kernel. This security flaw enables a local attacker with normal privileges to exploit the system, leading to the disclosure of sensitive kernel memory. If successfully leveraged, this vulnerability could result in further privilege escalation, allowing the attacker to gain root access.
The vulnerability specifically resides in the snd_ctl_elem_read function, located in sound/core/control.c, responsible for handling the reading of control elements within the ALSA sound system. The issue arises when the function fails to properly deallocate memory that was previously used to read a control element. Consequently, this lapse in memory management creates a use-after-free condition, enabling the attacker to access freed memory.
To exploit this vulnerability, a local attacker with normal privileges can deliberately trigger the use-after-free condition to leak kernel memory. Subsequently, the attacker can utilize the leaked memory to escalate their privileges, potentially achieving complete control over the compromised system.
To mitigate the risks associated with CVE-2023-0266, it is crucial to promptly update your Linux kernel to the following patched versions:
- 5.18.7
- 5.15.25
How to find devices exposed to CVE-2023-0266
InvGate Asset Management offers a highly efficient remedy for pinpointing devices within your company that demand immediate attention. You can easily follow the process described below:
- Open InvGate Asset Management and go to the Explorer tab.
- Type in the Search bar “Software name, is:Linux”.
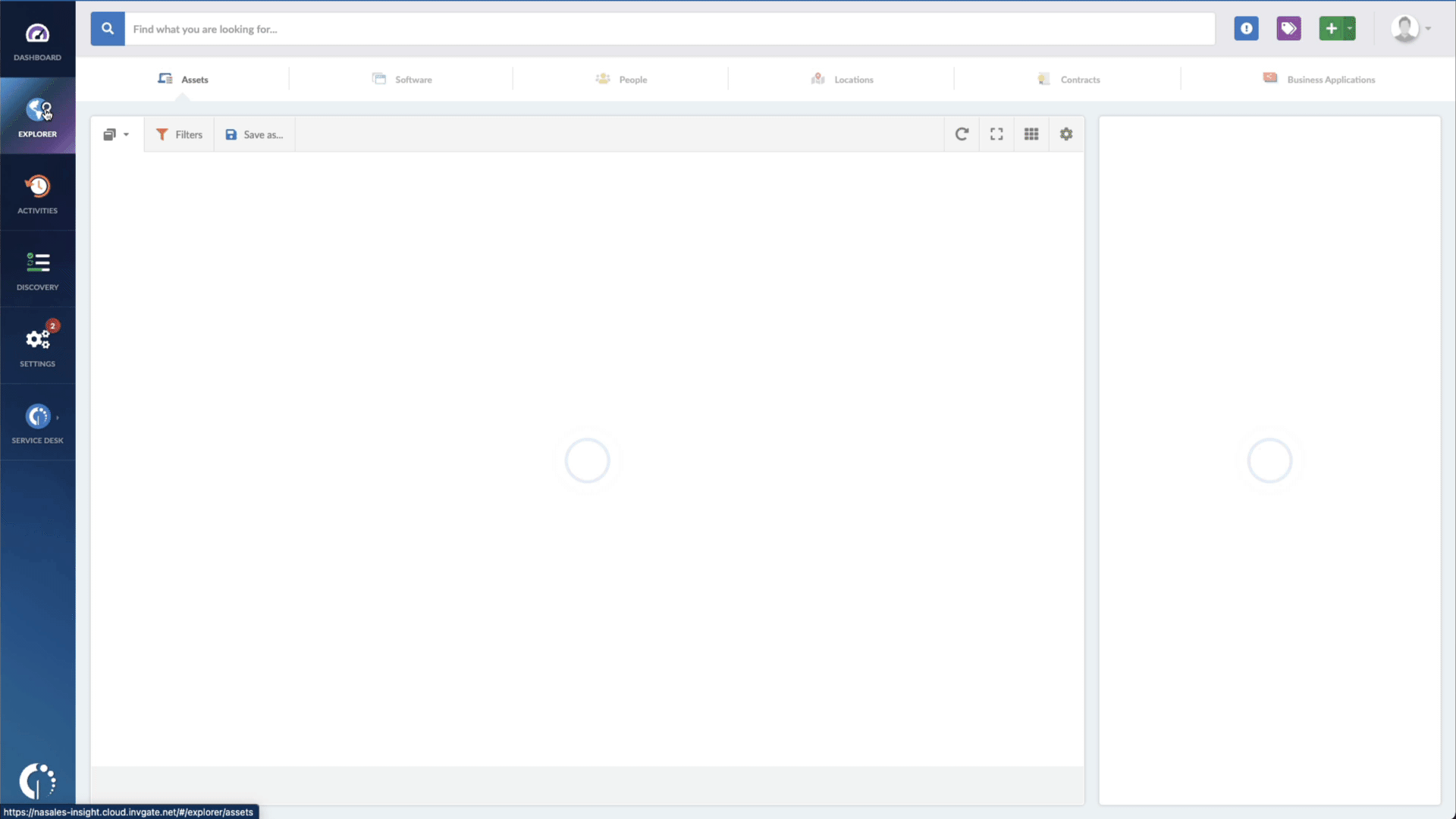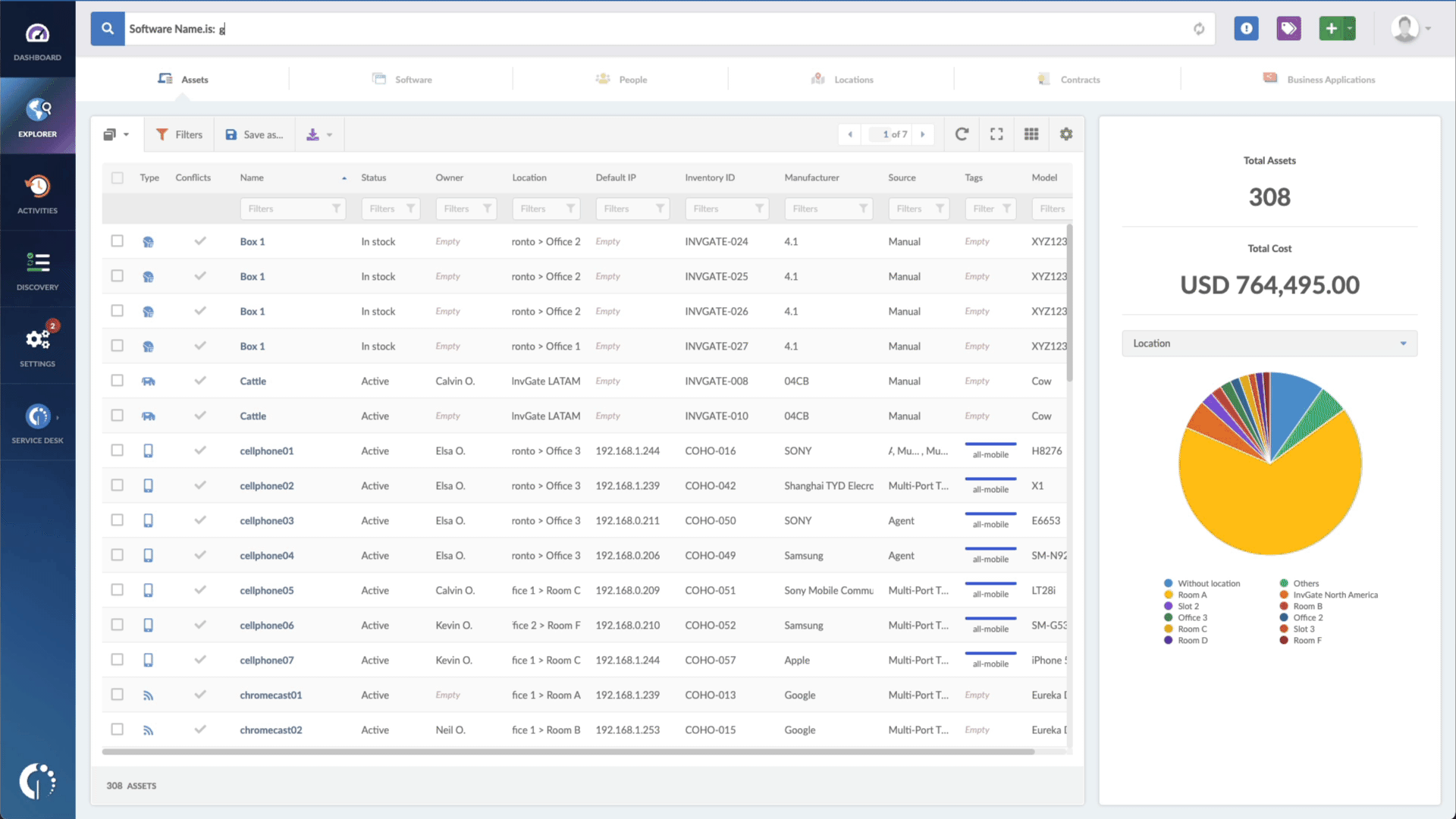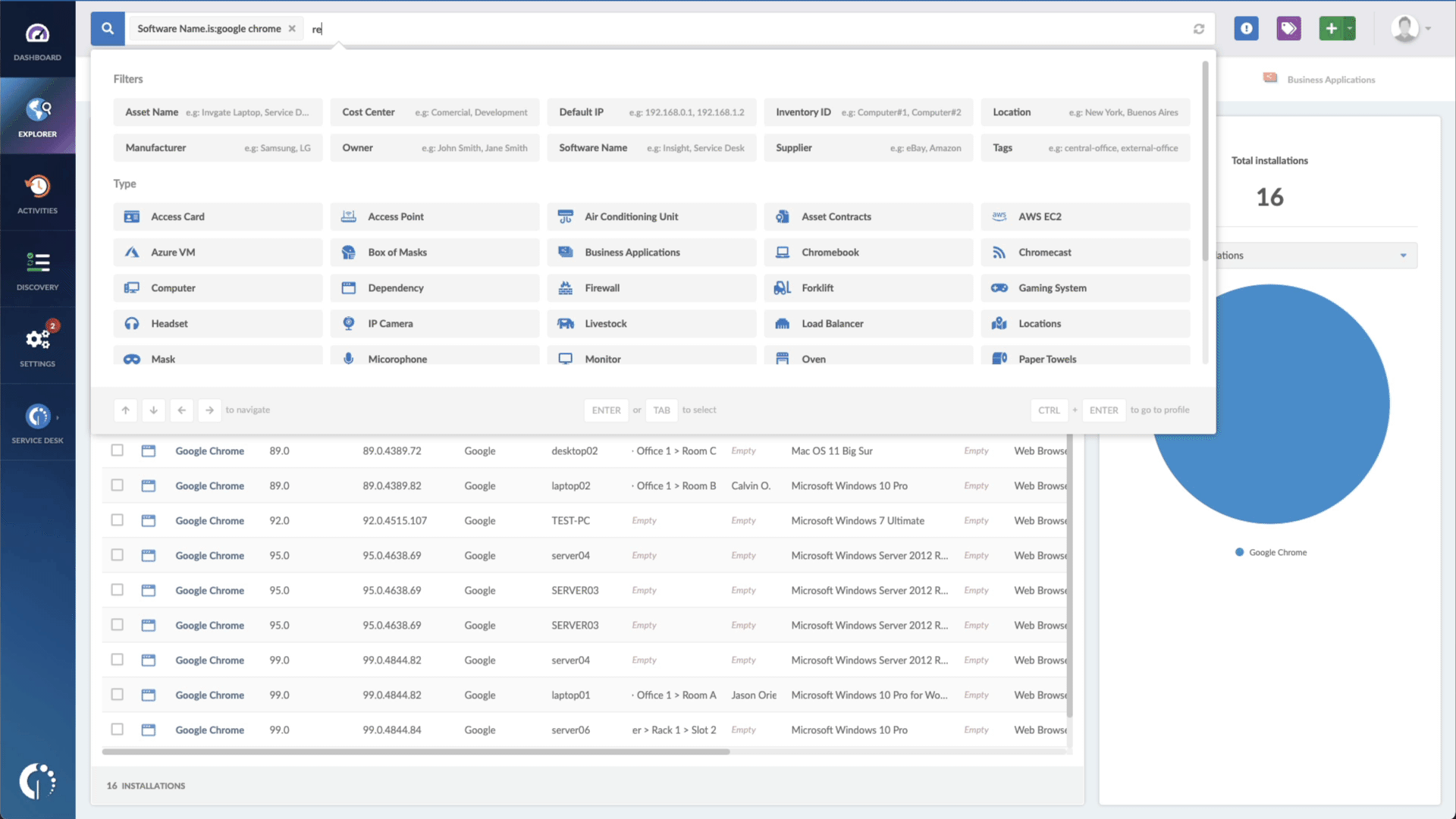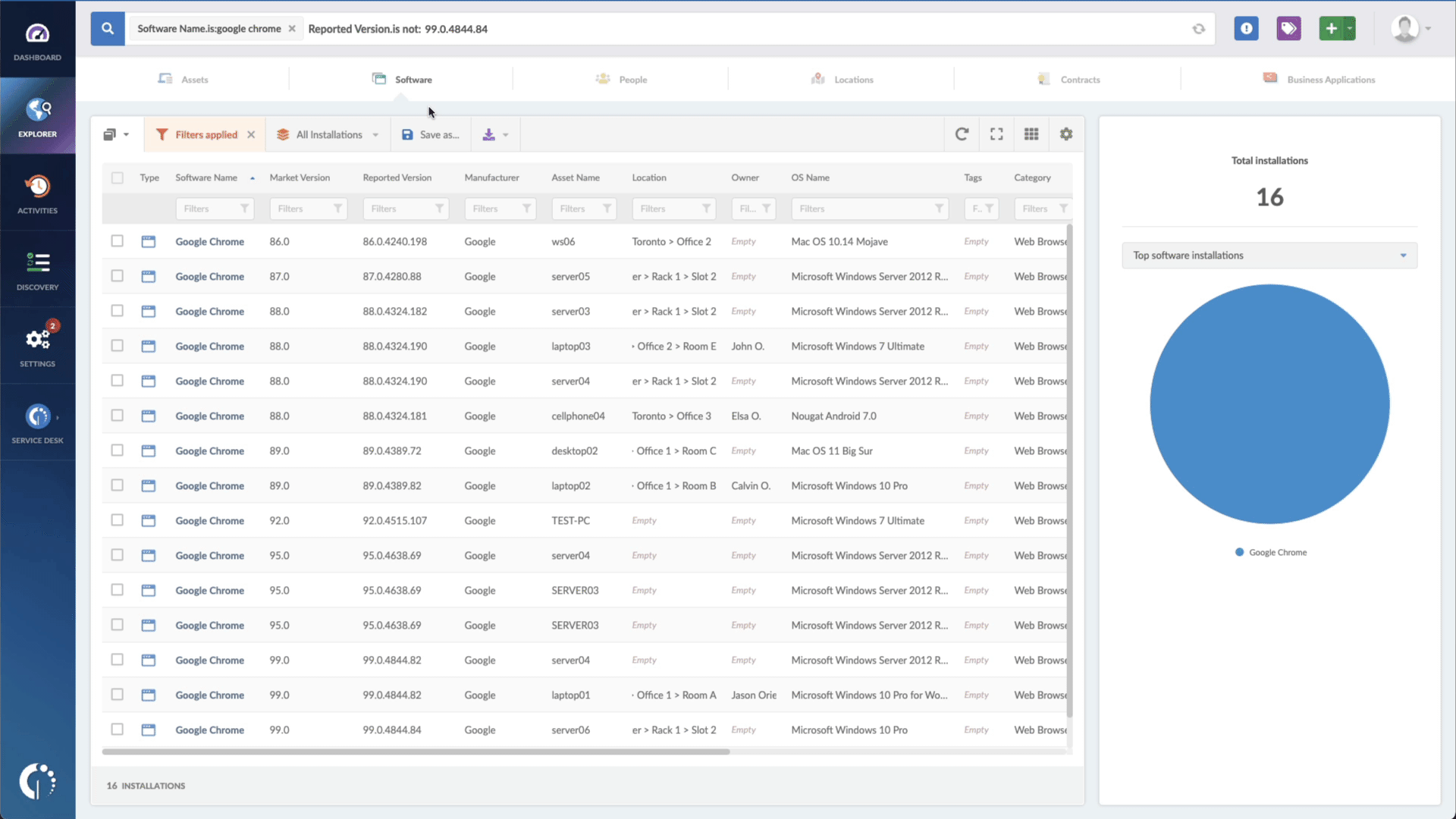
- Add another filter to the Search bar to see all devices missing the security patch. To do that, add the following filter: “Reported version, is not:” and paste the patched version.
That's it! In a matter of seconds, you will have a comprehensive list of vulnerability-prone devices so you can take immediate action. You can download this information in CSV format and distribute it to your agents to keep them informed of the latest updates.
For more information, watch our video that provides valuable insight into identifying vulnerable devices for patching.
The bottom line
CVE-2023-0266 poses a significant security threat to Linux systems, allowing attackers to exploit the use-after-free vulnerability and potentially gain root access. It is essential to prioritize the installation of patched kernel versions to mitigate these risks effectively.
InvGate Asset Management can be part of your Vulnerability Management strategy to streamline the process of identifying vulnerable devices and taking prompt action.
Ready to protect your network? Request our 30-day free trial today and start searching for vulnerable devices within your network.















