Vulnerability Management is a proactive and continuous process that seeks to keep networks, systems, and general applications as safe as possible from cyberattacks.This practice is also a crucial aspect of IT security, and it's essential because it can help prevent data breaches that could result in severe damage to organizations.
In this article, we'll explore the definition of Vulnerability Management, its process, its importance, and some solutions for performing this task. If you want to learn how to keep your organization safe from hackers, this is the article for you.
What is Vulnerability Management?
Vulnerability Management identifies, categorizes, prioritizes, and solves operating systems and software vulnerabilities. Patch Management, which consists of distributing and applying updates or software patches, is part of Vulnerability Management.
It should be noted that Vulnerability Management is part of a proactive cybersecurity culture that requires patching vulnerabilities and being aware of possible threats and solutions.
This and other cybersecurity measures seek to make the company more secure by reducing the attack surface's known and potential vulnerabilities, which is a great idea since attackers are always looking for security holes and vulnerabilities to carry out cyberattacks.

Differences between a vulnerability, a risk, and a threat
Let's start by understanding the differences between vulnerability, risk, and threat. Each term represents a distinct aspect of cybersecurity that, when understood correctly, allows for more precise and effective strategies to protect an organization's assets.
Vulnerability
A vulnerability represents a weakness or flaw in your system that can be exploited. Identifying vulnerabilities is the first step in protecting your system. Without knowing where the weaknesses lie, it’s impossible to secure your assets adequately.
Understanding vulnerabilities helps prioritize which issues need immediate attention based on their potential impact and exploitability.
Definition (ISO 27005:2018): "A weakness of an asset or control that can be exploited by one or more threats."
Risk
Risk quantifies the potential impact that a vulnerability could have if exploited. It’s the bridge between identifying a vulnerability and understanding its real-world implications. Recognizing risks enables organizations to allocate resources effectively, ensuring that the most critical issues are addressed first.
Definition (ISO 31000:2018): "The effect of uncertainty on objectives." In the context of information security, it's often defined as the combination of the probability of an event and its consequence.
Example: If a company uses outdated software (vulnerability) and there is a possibility of a cyberattack (threat), the risk might be the loss of sensitive data, financial loss, and reputational damage.

Threat
Threat awareness involves understanding the potential sources of harm that could exploit vulnerabilities. Knowing what threats exist and their capabilities allows organizations to develop targeted defenses.
This knowledge helps in anticipating potential attacks and preparing appropriate responses. It’s about being proactive rather than reactive, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers.
Definition (ISO 27005:2018): "A potential cause of an unwanted incident, which may result in harm to a system or organization."
Example: A threat can be a hacker attempting to breach a network, a natural disaster that could destroy data centers, or a disgruntled employee misusing access rights.
How are vulnerabilities categorized?
In order to fully understand Vulnerability Management, we first need to establish how vulnerabilities are defined and categorized.
So, a vulnerability is a weakness in a system that can affect the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of data. A hacker may exploit vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to an organization's network, deploy malware, and steal, damage, or destroy information and other critical assets.
Vulnerabilities are described by taking into account the following systems or methods:
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) system
This system lists publicly known vulnerabilities and exposures. It is maintained by the United States National Cybersecurity FFRDC, operated by The Mitre organization.
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
A free and open industry standard for assessing the severity of vulnerabilities. Scores range from 0 to 10, with 10 being the most severe.
Common Platform Enumeration (CPE)
A method for identifying systems, applications, and hardware devices that are part of an organization's assets. CPEs are relevant in this context because they describe what a CVE or CCE applies to.
Common Configuration Enumeration (CCE)
list of system security configurations that allow “people to quickly and accurately correlate configuration data across multiple information sources and tools,” defined by the Mitre organization.
Why is Vulnerability Management critical?
Cybercriminals constantly look for new vulnerabilities and security holes to access company networks. They usually exploit software vulnerabilities to get into user accounts or computer systems and deploy malware that might result in data loss or damage. This could be especially dangerous if they find a critical vulnerability that could compromise the whole network.
In this sense, a strong Vulnerability Management program is crucial because it seeks to identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited. It also implies thinking ahead and addressing weaknesses that might not have been reported or found before. It is an overall strategy to reduce surface attacks and improve security, and you can put it into practice with initiatives such as red teaming.
Vulnerability Management is relevant for companies because:
-
It helps them protect sensitive data that might hamper or stop their businesses.
-
It is an effective way of protecting assets.
-
It prevents money costs associated with data loss.
-
It avoids or reduces the reputation damage caused by a major cyberattack.
-
It helps design and adapt the best strategy to reduce the attack surface and improve overall security.
The vulnerability management process
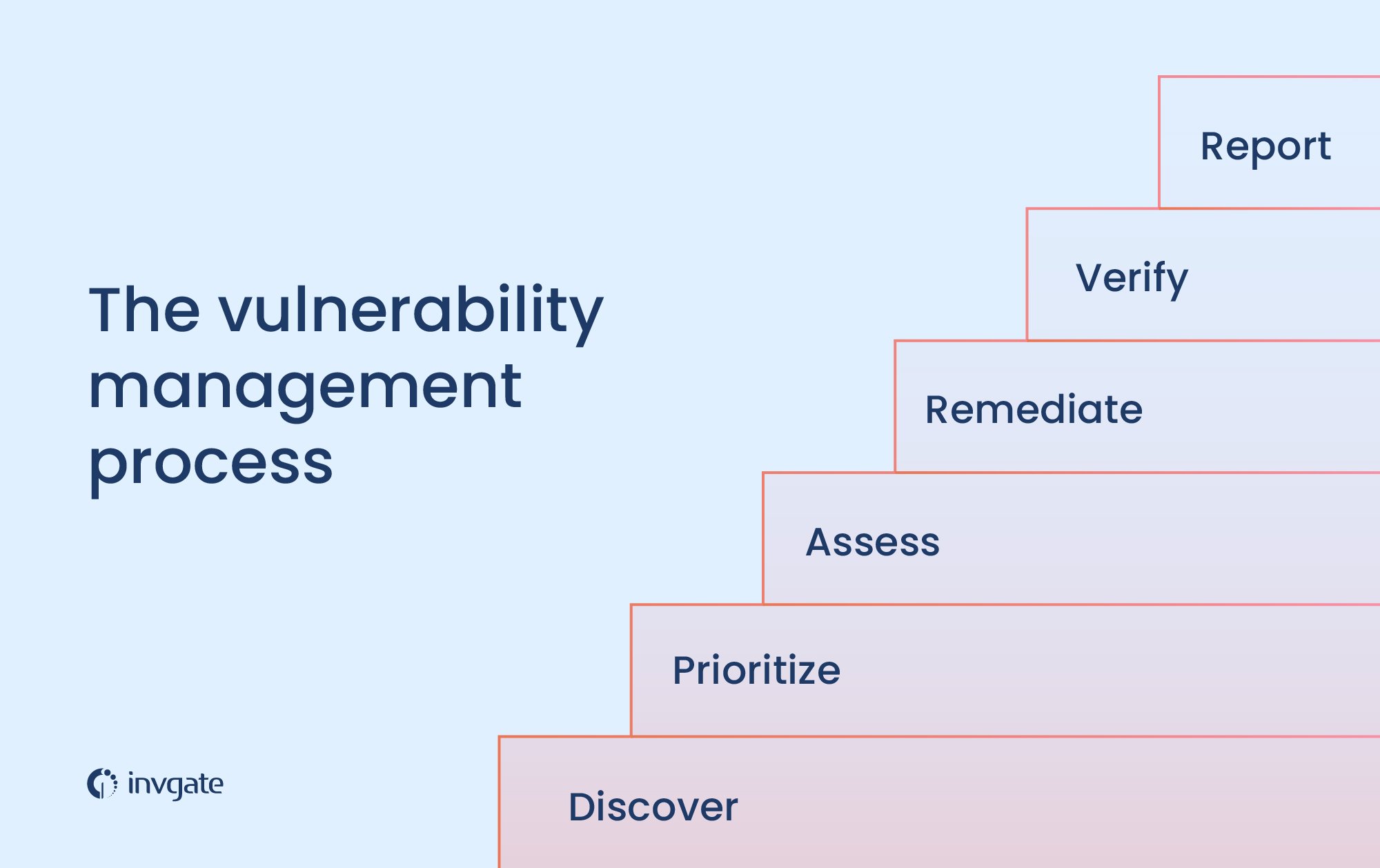
The Vulnerability Management process can be conducted according to different criteria.
Here, we are going to describe the six-step process that is mainly used to allow organizations to identify and address computer system security risks and weaknesses effectively.
1. Discover
The first step requires an inventory of all network assets, including operating systems, software, and hardware. Once all that data is gathered, security holes and vulnerabilities can be identified.
Just a quick side note before we move on to the next step: don't forget that you can automate discovery with an ITAM tool like InvGate Asset Management. Besides always having an up-to-date inventory of assets, you'll be preventing shadow IT and getting ready for software audits.
2. Prioritize
It implies categorizing assets into groups and assigning them a value based on how critical they are to your company. The more relevant they are, the higher their priority should be given. This step is crucial because it will help the IT security department know what to tackle and how to do it.
3. Assess
At this point, you should establish a risk baseline as a reference. It will indicate which risks need to be eliminated based on risk ratings on asset classification and type of vulnerability threat.
4. Remediate
This is the moment to fix vulnerabilities identified based on previously established risk prioritization. Once the remediation process is complete, the information gathered should be documented for the following stages.
5. Verify
You should ensure each vulnerability remediation has been appropriately done through an auditing process, including scans and cross-examinations.
6. Report
Finally, a thorough report should be delivered to the management. It is necessary to specify the state of affairs in terms of identified and fixed vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability Management tools
Vulnerability management programs scan for vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the network to provide solutions and remediation recommendations. These tools help adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity so that your organization can be a step ahead of cybercriminals.
These programs can automatically download and apply patches to software and operating systems. But there is more to it: these tools offer solutions to potential security threats. They can also identify different threat levels to help the IT security team know what to address first.
There are different kinds of Vulnerability Management programs. Some are more complete than others. The idea is to choose solutions that have these features:
-
IT Asset Management (ITAM) is an essential part of Vulnerability Management. ITAM covers the first step in the vulnerability management process: identifying all the assets the company has. Knowing what must be protected is crucial before any cybersecurity strategy is designed.
-
Vulnerability scanners to identify risks such as software vulnerability, security holes, and missing patches. This process should be repeated regularly to detect new vulnerabilities in time.
-
Visualization of the attack surface and risk scoring of any security vulnerabilities identified. This can be done through security incident and event management (SIEM) software, which gives real-time visibility of everything in the IT infrastructure.
-
Configuration Management to make sure that endpoints are configured securely.
-
A vulnerability assessment to analyze the organization's overall approach to security and help the security IT department plan and adopt remediation strategies.
-
Automated remediation to address potential threats.
-
Patch management to automatically apply patches and fixes.
-
Penetration testing is a tool used by IT security teams for simulating attacks and identifying vulnerabilities in the system.
-
Threat protection software analyzes potential threats based on information collected from various sources. This can help a company plan future security technology strategies in advance.
Not all vulnerability management tools have these features. Therefore, you might need to acquire different products to address all these aspects.
Other aspects to take into account when choosing a vulnerability management solution:
-
Assets covered: some tools work on all devices, while others cover only servers or computers, for instance.
-
Compatibility: it is important to know if the tools work only on some operating systems or all of them. Some only work on Windows or Linux, while others can work on different operating systems.
Key takeaways
All Vulnerability Management efforts should work towards identifying, assessing, managing, and remediating known vulnerabilities across the network.
It's a continuous and regular process that helps you address vulnerabilities in a timely manner, reduce the attack surface, and improve your company's overall security. It is essential because it allows system administrators to be a step ahead of cyber threats.
Many organizations learn the hard way how damaging a cyberattack might be in terms of reputation, money, and data loss. They find out too late that they need a proactive security posture and a better vulnerability management program to protect their enterprise network.
To perform this task, the IT security department should follow a procedure with the following requirements:
-
Know the assets at stake (There are asset discovery tools for this)
-
Prioritize risks
-
Establish a risk baseline
-
Remediate the problems found
-
Verify the remediation processes have been completed
-
Report on what you’ve done
But luckily, you're not alone in this. There are several Vulnerability Management solutions that can assist you in completing this task.
If you want to see what InvGate Asset Management can do for your security strategy, ask for your 30 day free trial and see for yourself!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Vulnerability Management and vulnerability assessment?
Vulnerability assessment is only a part of Vulnerability Management. Vulnerability assessment is a one-time examination of the systems or network, whereas vulnerability management involves many layers and steps.
How to manage vulnerabilities?
Vulnerability Management should be a continuous process to protect organizations from present and future threats. The idea is to address vulnerabilities as soon as possible and mitigate as many as possible.
To manage vulnerabilities is vital to have a well-prepared security IT department and reliable management tools to automate and control the whole process.
What is the cycle for vulnerability management?
A continuous Vulnerability Management cycle is a pre-defined process for examining all assets, detecting security weaknesses in the network, and prioritizing the actions to be taken.
Then, the remediations are performed, assessed, and informed through reports.
What are the 4 main types of vulnerability?
-
System misconfigurations: This opens the door to cyber criminals who probe to see if the systems are well protected or if there are security holes they can exploit.
-
Outdated software: This means that patches of known vulnerabilities are not installed. Therefore, criminals can easily exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to steal or destroy data.
-
Weak authorization credentials: Strong passwords and multifactor authentication are key to avoiding security incidents.
-
Insider threats: Employees with access to critical information could accidentally or intentionally give key information to hackers and cause a data breach.
What are standard methods for managing vulnerabilities?
There are different methods, but most of them require:
-
Using vulnerability scanners, firewalls, and other security tools.
-
The regular update of software and operating systems.
-
The implementation of the least privilege principle. This means restricting access to critical data only to those employees who need it to do their jobs.