Patch Management is the process of acquiring and applying updates to software—essentially keeping your systems secure and running like clockwork. It's a fundamental part of IT Asset Management, ensuring your network's operating systems and applications are protected against vulnerabilities.And it's not just important—it’s a top priority for businesses worldwide. According to a 2024 study by Alexandra Borgeaud on Statista, 56% of companies already use Patch Management solutions, with 32% planning to adopt them this year. That means nearly 90% of organizations recognize how vital it is to safeguard their IT environments against cyber threats and ensure operational stability.
In this article, we’ll delve into:
- The Patch Management definition.
- The benefits it brings to organizations of all sizes.
- How InvGate Asset Management simplifies the process.
If you’re ready to discover how Patch Management can elevate your IT security and operations, you’re in the right place.

What is Patch Management?
Patch Management is the process of distributing and applying software updates—commonly known as "patches"— to fix bugs, close security vulnerabilities, or improve performance. It plays a crucial role in cybersecurity by addressing vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals.
According to ITIL, Patch Management falls under Release Management and focuses on three key areas:
- Security patches – These patches fix vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
- Bug fixes – These patches resolve software malfunctions, preventing data loss and improving system reliability.
- Feature updates – These updates enhance software functionality, adding new tools or improving user experience.
Patch Management vs. Vulnerability Management
While Patch Management and Vulnerability Management are closely related, they’re not the same thing.
Patch Management focuses specifically on identifying and applying software patches to fix bugs and address security gaps. It’s more about action—getting those updates deployed quickly and efficiently.
On the other hand, Vulnerability Management involves the broader task of identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing potential weaknesses across an IT environment. It includes the discovery of vulnerabilities that may or may not have patches available, as well as decisions about how to mitigate them.
If you’re curious to dive deeper, check out our blog post on Patch Management vs. Vulnerability Management for a detailed comparison.
Why is Patch Management important?
Patch Management is crucial for maintaining secure, efficient, and compliant IT operations. It protects your organization, drives innovation, and keeps systems running smoothly. Here’s why it matters:
- Ensuring compliance: Helps meet regulatory standards, reducing the risk of fines and reputational damage.
- Strengthening security: Patches vulnerabilities to protect systems from cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Maximizing system uptime: Keeps systems updated and functional, reducing downtime and performance issues.
- Unlocking feature improvements: Patches often introduce new features and enhancements to improve productivity and efficiency.
- Preventing costly incidents: Proactive patching avoids financial losses from breaches, downtime, and compliance failures.
- Enhancing customer trust and business reputation: Demonstrates commitment to security and reliability, fostering customer loyalty.
How does Patch Management work?
In a nutshell, Patch Management involves discovering vulnerabilities in your software and systems and applying updates (patches) to fix them. The process is carried out by IT teams who ensure everything stays secure, efficient, and up-to-date.
It starts with identifying which assets need patching and continues with a series of steps to minimize risks and disruptions:
- Inventory your assets: Identify all hardware and software assets within your organization to understand what needs patching.
- Monitor for patches: Regularly check for available patches from vendors and assess their relevance to your systems.
- Prioritize patches: Evaluate the criticality of each patch based on factors like security impact and system importance.
- Test patches: Before widespread deployment, test patches in a controlled environment to ensure they don't introduce new issues.
- Deploy patches: Roll out patches systematically, starting with the most critical systems, to minimize potential disruptions.
- Verify and document: After deployment, confirm that patches have been applied successfully and maintain detailed records for compliance and auditing purposes.
For a comprehensive guide on establishing a robust Patch Management process, check out our detailed article: Patch Management Process: A Step-by-step Guide.

Patch Management best practices
Now that we’ve covered what Patch Management is and how to implement it, it’s time to focus on best practices. Following these principles will ensure that your Patch Management program is not only effective but also aligned with your organization's broader IT and security goals.
Here are the key best practices to follow:
- Create an inventory of all IT assets.
- Establish a patching policy.
- Prioritize patches based on criticality.
- Test patches before deployment.
- Automate the patching process.
- Maintain detailed documentation and reporting.
- Regularly review and refine your process.
#1: Create an inventory of all IT assets
An accurate inventory is the foundation of successful Patch Management. Identify and catalog all hardware, software, and virtual assets in your organization. This step ensures you know exactly what needs patching and prevents any devices from being overlooked. With InvGate Asset Management, you can create a complete IT inventory within minutes.
#2: Establish a patching policy
Define a clear patching policy that outlines how and when patches should be applied. Include parameters for urgency levels, roles and responsibilities, and escalation procedures for critical vulnerabilities. A well-defined policy ensures consistency and accountability across the organization.
#3: Prioritize patches based on criticality
Not all patches are created equal. Focus first on high-priority updates, such as those addressing critical security vulnerabilities or affecting key systems. Use a risk-based approach to determine which patches should be applied immediately and which can wait.
#4: Test patches before deployment
Testing patches in a controlled environment prevents unintended disruptions to your systems. By simulating the update on non-production machines, you can identify potential compatibility issues or unexpected side effects before rolling it out organization-wide.
#5: Maintain detailed documentation and reporting
We know this can be challenging, but it’s essential. Keep comprehensive records of all patching activities, including what was patched, when, and by whom. This not only ensures compliance with regulatory standards but also provides valuable insights for auditing and process improvement.
#6: Regularly review and refine your process
Patch Management is an ongoing process. Regularly evaluate its effectiveness by reviewing metrics such as patching timelines, system uptime, and vulnerability reduction. Use these insights to refine your strategies and adapt to evolving threats.
How to simplify Patch Management with InvGate Asset Management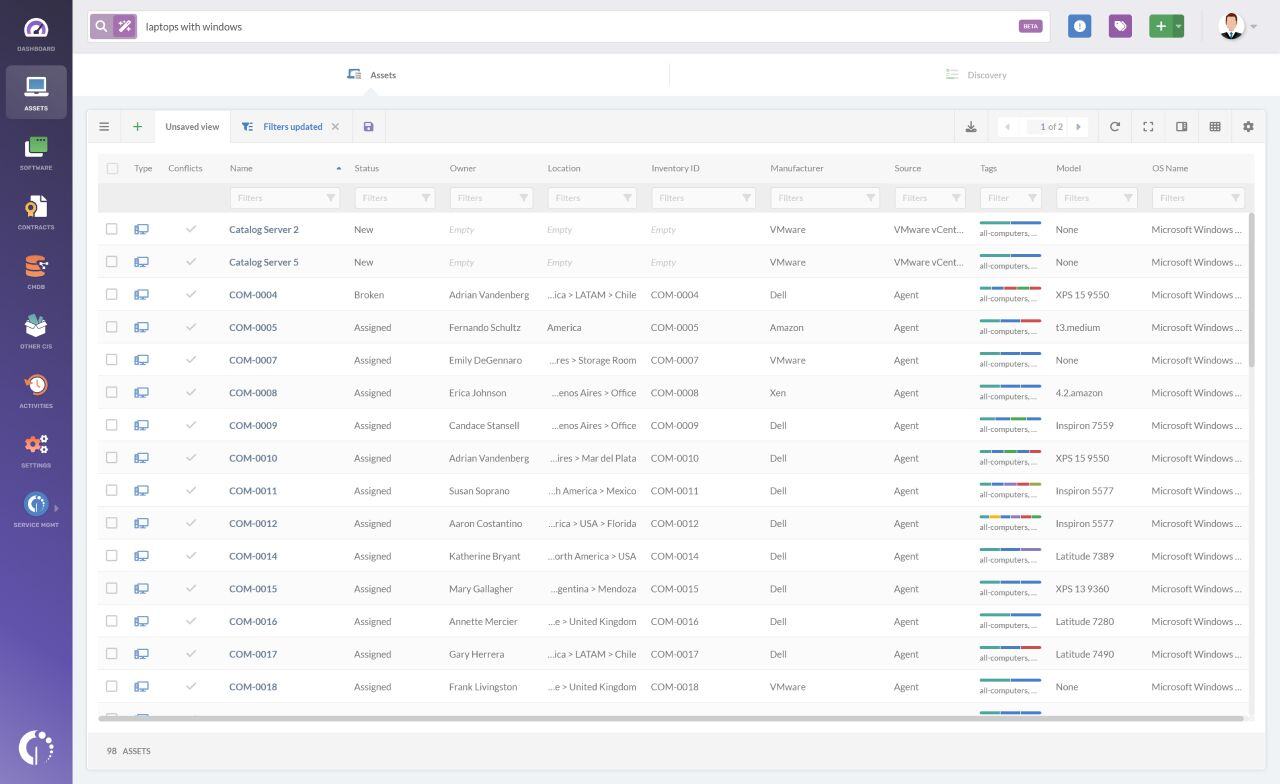
If you don't have a dedicated tool for automated Patch Management software, you can leverage InvGate Asset Management to simplify the process.
Since it centralizes all information about physical, virtual, and cloud assets in one platform, it makes it easier to manage Patch Management tasks and deploy patches effectively.
With InvGate Asset Management's smart tags, you can identify which devices need updates, develop a script to update them, and deploy the changes remotely. Here's how it works:
- As soon as a new vulnerability is out in the wild, go to InvGate Asset Management and create a Smart Tag to identify all vulnerable devices.
- Go to the Software Deployment module and create a script (or pick one from our library) to update the devices.
- Build a deployment plan to update all devices that match the Smart Tag criteria.
If you prefer, you can export the information of the outdated devices in a CSV file and give it to the agent in charge of the patching process.
Smart Search for simplified asset searches
Since InvGate Asset Management is a no-code software that requires minimal technical knowledge, we’ve recently added a new feature, Smart Search, powered by AI.
This feature simplifies searches by allowing you to use natural language in the search bar, so you no longer need to memorize complex filters or SQL commands. You can simply type queries like "laptops with Windows" or "all servers in the New York office," and Smart Search will handle the rest. This makes finding and managing assets even easier, enhancing your workflow without adding complexity.
Key takeaways
Patch Management is not just an IT responsibility—it’s a business imperative. As we’ve seen, it plays a pivotal role in maintaining security, ensuring compliance, minimizing downtime, and driving innovation. By addressing vulnerabilities proactively and keeping systems up-to-date, organizations can reduce the risk of cyberattacks, avoid costly fines, and deliver a seamless user experience.
With tools like InvGate Asset Management, Patch Management becomes more manageable, efficient, and strategic. It enables IT teams to identify, prioritize, and deploy patches effectively. Start implementing these strategies today with our 30-day free trial!















