As IT evolves alongside both the physical and – now more common – digital workplace, so too does the IT infrastructure that sustains it.
Basically, the IT infrastructure of an organization includes the whole set of IT assets that keep it operating. And, in recent years, we’ve seen a significant migration from mostly traditional infrastructure (i.e. servers and storage devices) to the more cost-effective cloud infrastructure.
In this article, we’ll first explain what IT infrastructure is and its main components. We’ll then explore the most common types of IT Infrastructure Management practices out there, and how to use InvGate Asset Management as your IT Asset Management (ITAM) software to take it to the next level.
Let’s dive in!

What is IT infrastructure?
IT infrastructure refers to the collection of hardware, software, and networks that maintain the operation and delivery of IT-managed services.
Naturally, a business relies on the efficiency of its IT infrastructure to work properly. Productivity and profit depend on how reliable, fast, and secure it is. This includes both internal operations and the development of external customer IT business solutions.
Some advantages of a well-oiled infrastructure include (but are not limited to) better customer service, greater employee productivity, streamlined organization of data centers, and faster, more seamless delivery of solutions into a market.
An ITAM tool can open the doors to all of those benefits, keeping a full and thorough view of your IT infrastructure. Companies use InvGate Asset Management to keep a unified view of their entire IT asset inventory (with updated information and the status of the infrastructure), build a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) to map out their relationships, and much more.
The 3 main IT infrastructure components
The components of your standard IT infrastructure can be broken down into the following three categories: hardware, software, and networking. While these represent the pillars of more traditional infrastructure, some of the same components are still used in cloud infrastructure.
Hardware
One way to see the components of IT infrastructure is from the ground up. That is, starting with the physical devices that increase and foster the operations of the digital ones. Hardware in your information technology infrastructure is your assortment of computers, servers, routers, data centers, switches, wires, facilities, and any other equipment that takes a corporeal form.
Software
Software, on the other hand, refers to the applications or programs that manage or are otherwise brought to life by the hardware. It can include the Operating System (OS), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Content Management Systems (CMS), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERM), or various web servers. Operating systems are arguably the most important as they connect and manage all physical resources.
Networking
Networking is the practice of connecting and managing computer systems and devices to share system resources and information. It involves the design, implementation, and maintenance of communication systems using various networking components.
Networking components are the building blocks of a network infrastructure. These include routers, switches, hubs, servers, cables, wireless access points, and Network Interface Cards (NICs).
A well-designed network integrates these components to establish reliable internet connectivity and facilitate communication between internal and external systems. Network infrastructure security is a crucial aspect of networking, and it includes measures and protocols to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
3 types of IT infrastructure
Let’s move on from the components to the different IT infrastructure types and what you can expect from each one. They can all involve different types of components.
Traditional
In traditional IT infrastructure, the items listed above are owned and managed by the organization itself. This type of infrastructure is also known as on-premise. Usually, they’re kept on company property and require physical space and power to maintain them.
Traditional IT infrastructure is also the logical starting point for the implementation of edge computing. In light of new third-party cloud services that don’t require the same physical space, the traditional infrastructure, however, is the most expensive option. Despite that, it is chosen by many companies that attempt to have robust security, or have higher compliance requirements.
Cloud
Cloud infrastructure offers a modern approach to delivering computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, over the Internet. Instead of maintaining physical hardware on-site, businesses access these resources through a managed service provider. So long as you have access to the internet, you can access the components of either your own privately built cloud or via a public cloud service like Microsoft Azure.
Unlike the traditional one, cloud-based infrastructure is a modern alternative that allows automatic software updates, better remote support, and access from multiple locations. Through virtualization, it can be easily scaled and is much more cost-effective.
Many organizations choose a hybrid cloud model, combining public and private cloud services with their existing on-premises hardware. This approach allows businesses to enjoy the flexibility and scalability of cloud computing while maintaining control over sensitive data on local servers.
Hyperconverged
Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) combines computing, storage, and networking into a single system managed through one interface. Instead of having separate hardware for each function, HCI integrates everything into a software-driven platform. This usually involves a group of servers, virtualization software, and a management layer.
While hybrid cloud mixes public and private cloud services, hyperconverged infrastructure focuses on unifying key IT components in one hardware system. It simplifies how resources are deployed, managed, and scaled, making IT operations more efficient. Though still a newer approach, HCI is growing in popularity due to its ability to handle modern workloads with less complexity.

Asset Management in IT infrastructure

IT Asset Management practices lay out the guidelines to control and support the costs and well functioning of your IT infrastructure. Of course, to work efficiently, they must be supported by a comprehensive tool.
Consider that an organization’s IT assets, which include the hardware, software, systems, and values of the business, are the infrastructure’s lifeblood. Their correct management facilitates real-time infrastructure monitoring and the distribution of your team’s IT Service Management.
The most common IT infrastructure management types
Having run through the basics of IT infrastructure, let’s now take a look at how the different IT practices contribute to the Infrastructure Management:
- IT Operations Management - It ensures efficient utilization of IT resources and identifies bottlenecks in the IT infrastructure.
- IT Automation - This helps to reduce errors and free up human resources for more strategic and complex tasks in your Infrastructure Management.
- API Management - It facilitates the seamless sharing of data and functionalities between applications in your infrastructure, enabling innovation and collaboration.
- Cloud Management - This enables organizations to effectively utilize cloud resources while maintaining control and governance.
- OS Management - It ensures the smooth operation of an IT environment with a shared operating system.
- Risk Management - It helps in understanding potential threats to the infrastructure, vulnerabilities in it, and their potential impact.
IT Infrastructure Management with InvGate Asset Management
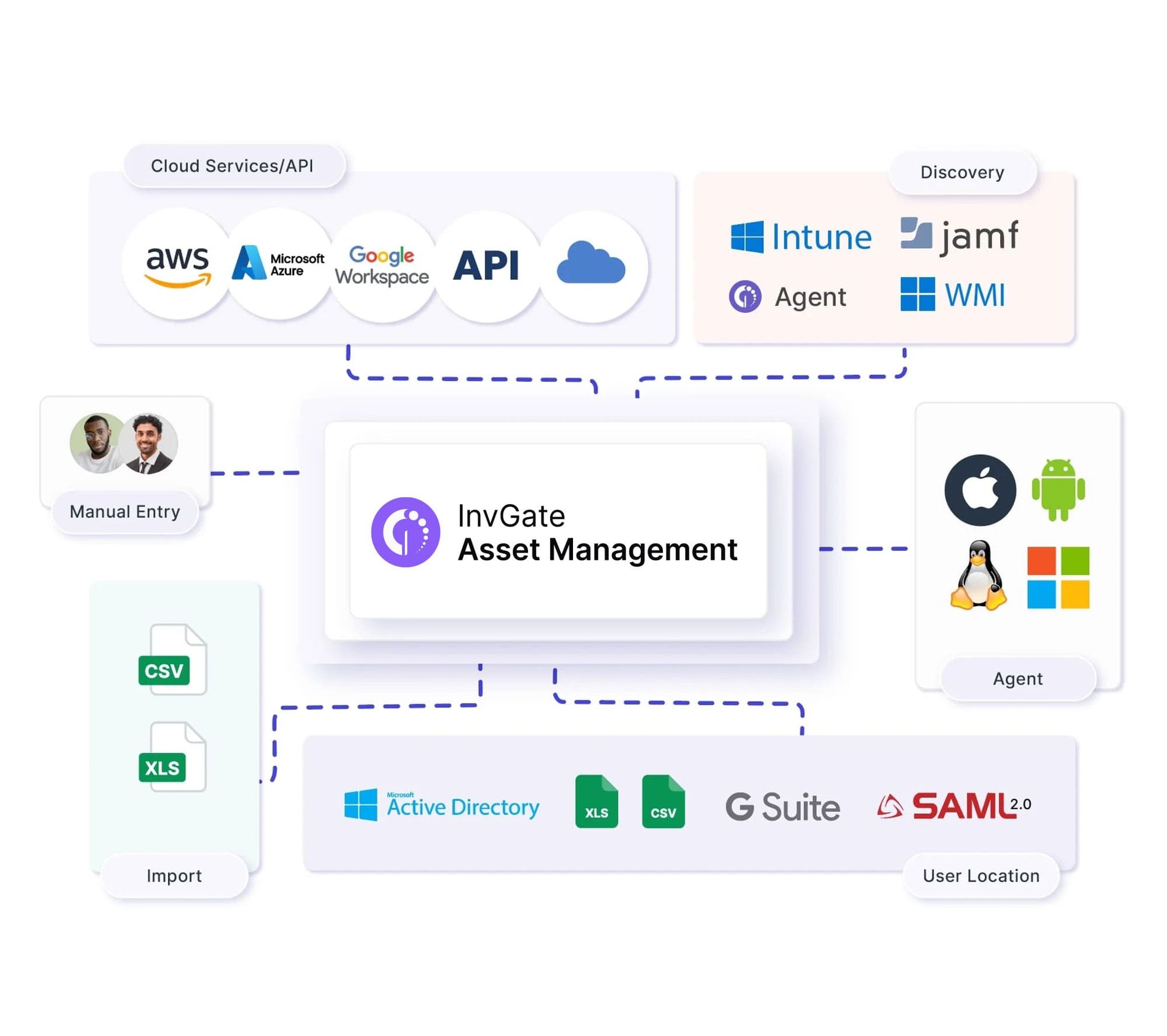
InvGate Asset Management’s set of features work together to create a complete IT inventory, giving you clear access to the information, status, and relationships between all the assets included in it.
An IT asset inventory is the process of documenting and tracking all assets within an organization's IT infrastructure. Basically, it organizes your infrastructure in a clear and practical way.
Let’s see which InvGate Asset Management's features are most helpful to do Infrastructure Management.
Discovery
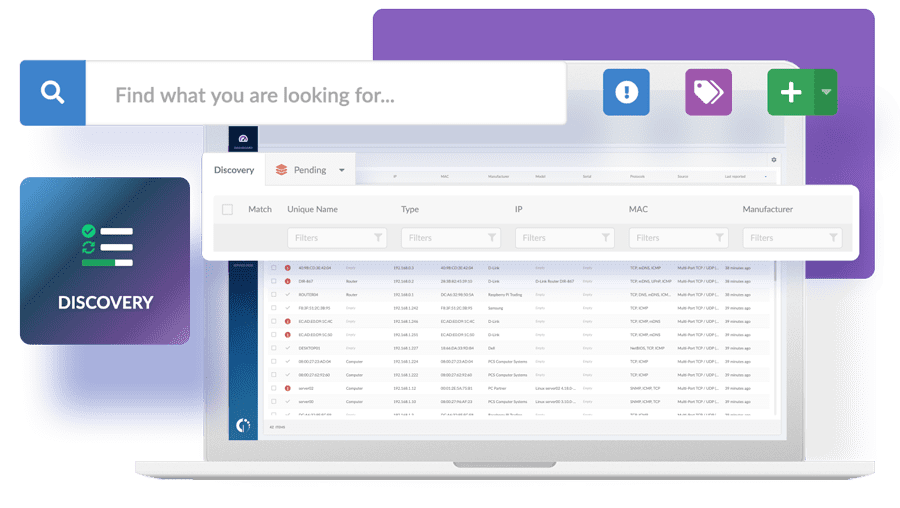
The Discovery feature allows you to scan your entire network to search for unknown devices connected to it. Then, you can choose to add them to your inventory and keep tracking them, ignore them or leave them as pending.
This will give you a complete and reliable picture of your whole IP infrastructure, making sure nothing is missed. It also helps ensure your cyber security against any threats within your network.
Cloud Services integration
It’s quite common that some of the basic and most important data regarding infrastructure is located in cloud services. InvGate Asset Management seamlessly integrates with some of the most commonly used options, such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, to ensure your IT inventory is complete.
CMDB
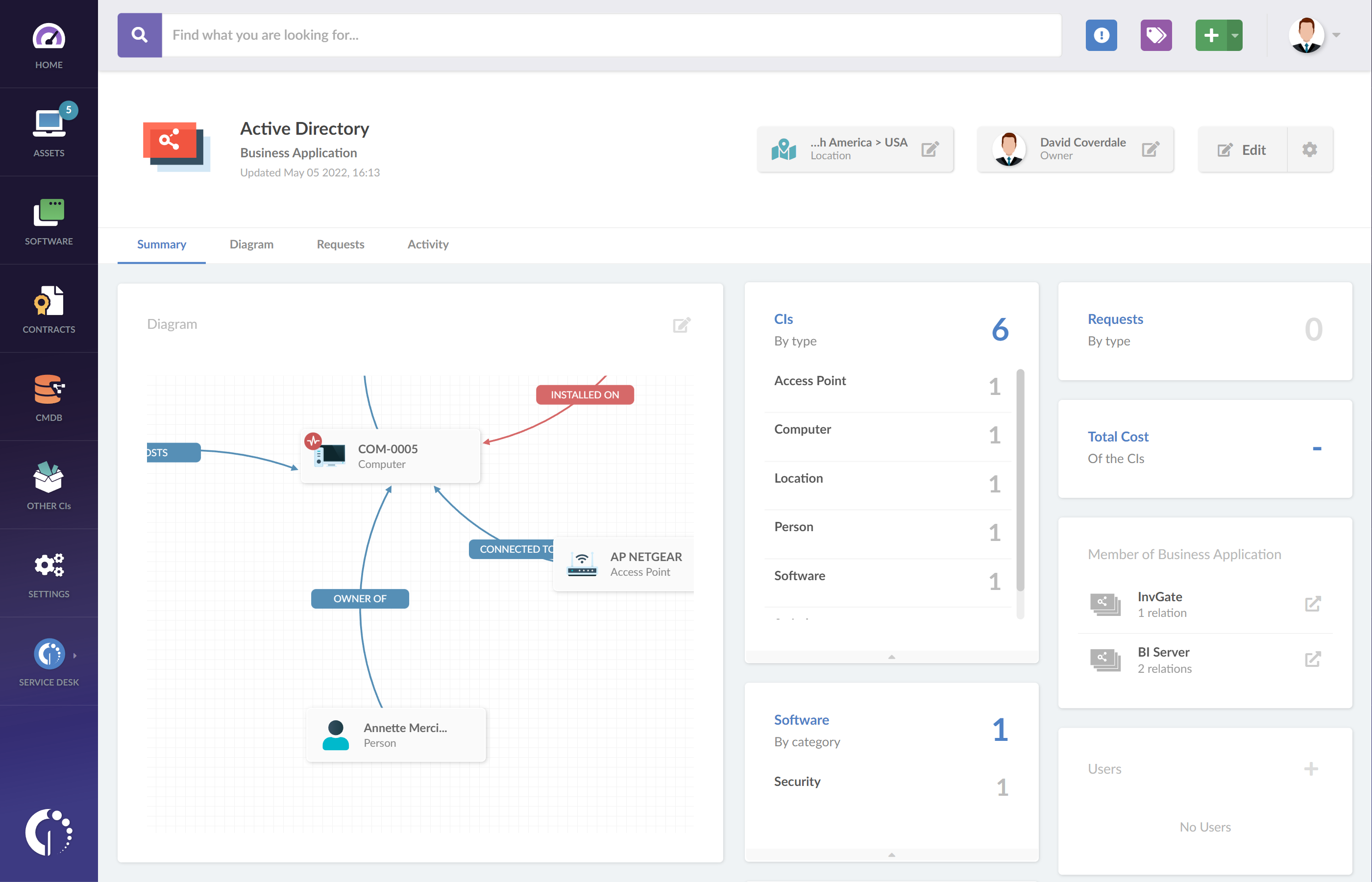
Once you have a unified IT inventory, it is time to map the relationships in your environment. A CMDB creates a bird's eye view of the relationships between networks, applications and the other CIs that populate your IT infrastructure.
Health Rules
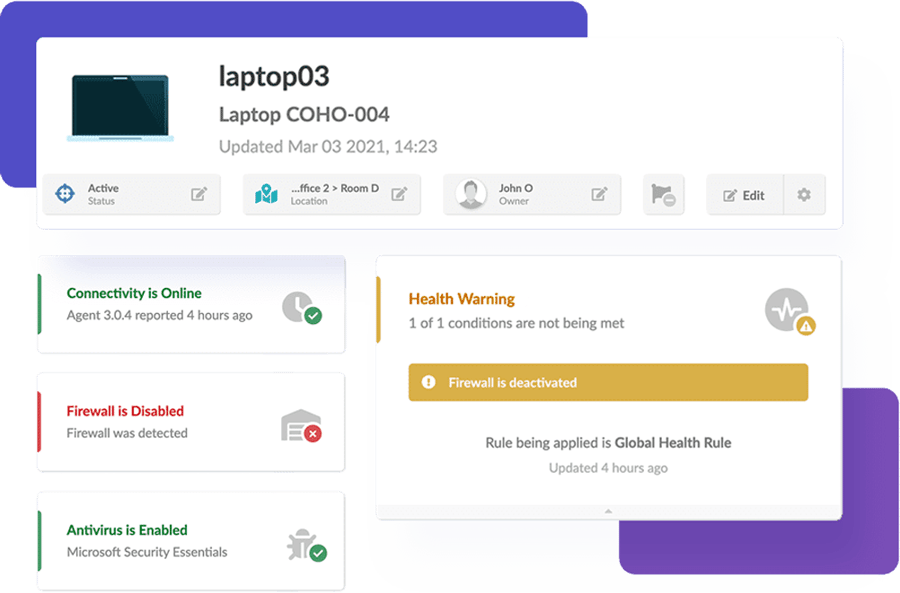
To ensure your IT infrastructure is safe and in compliance, use InvGate Asset Management’s Health Rules to notify when something might be going wrong. They send alerts to your system regarding the health status of your monitored devices. You can set your own predefined conditions to determine if they are safe, warning, or critical.
Smart Tags
Smart Tags are designed to classify and characterize all types of Configuration Items (CIs) on your InvGate Asset Management instance, such as devices, users, and software. So, they will automatically be assigned to those CIs that meet those conditions. You can run reports or set notifications when an asset falls into one of these categories.
In conclusion
The importance of a well-managed IT infrastructure cannot be overstated in any organization, big or small. Whether it's traditional, cloud, or hyperconverged, businesses rely on the efficiency, reliability, and security of their technological infrastructure to drive productivity. And if it isn't complete, reliable, and easy to access, you can’t do the job right.
InvGate Asset Management emerges as a valuable tool for IT Infrastructure Management. Thanks to its robust set of features, you can streamline operations, optimize resource utilization, and mitigate risks, ultimately ensuring the seamless functioning of your IT infrastructure and of your whole organization.
So, ask for a 30-day free trial and see what it can do for you!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the basic IT infrastructure?
The basic IT infrastructure comprises hardware, software, networks, and data centers that enable the functioning of an organization's IT systems.
What is a weakness in the IT infrastructure?
A weakness in the IT infrastructure can be inadequate security measures (i.e. insufficient firewalls, weak authentication mechanisms, or outdated software and hardware components), making it susceptible to cyber attacks and data breaches.
Who should support or maintain the IT infrastructure?
IT infrastructure should be supported and maintained by a dedicated IT team or department within the organization.
What is IT Infrastructure Management?
IT Infrastructure Management refers to the process of overseeing and maintaining the IT infrastructure to ensure its optimal performance, security, and availability.
What are the levels of IT infrastructure?
The levels of IT infrastructure include the physical layer (hardware and cabling), network layer (routers and switches), storage layer (servers and data storage), and application layer (software and applications).
What is an example of IT infrastructure?
An example of IT infrastructure can be a company's network of computers, servers, routers, switches, and data centers that facilitate communication and data storage.
Why upgrade the IT infrastructure?
Upgrading the IT infrastructure is necessary to improve performance, security, scalability, and to leverage new technologies that enhance business processes and productivity.
What's the difference between traditional and cloud infrastructure?
Traditional infrastructure relies on on-premises hardware, requiring manual management and significant upfront investment. On the other hand, cloud infrastructure is hosted remotely by third-party providers, offering scalability, flexibility, and lower upfront costs since resources are accessed and managed over the internet.