Navigating the complexities of IT Service Management (ITSM) can be challenging, but mastering help desk workflows can make all the difference. They are the backbone of efficient service operations, ensuring that tasks are handled swiftly and consistently.
In this article, we’ll dive into the world of service desk processes, highlighting how workflow automation can revolutionize your operations.
Whether it’s routing tickets, managing incidents, or streamlining change requests, here you will find some practical examples of workflows you can implement immediately to boost efficiency and improve customer satisfaction.
Read on to discover how you can transform your help desk operations with these powerful workflow strategies!
|
|
Table of contents
- What is a help desk workflow?
- Benefits of designing service desk workflow processes
- 10 help desk workflow examples to automate your business processes
- 5 IT help desk workflow best practices
What is a help desk workflow?

A help desk workflow is essentially a roadmap for handling tasks in an IT support environment.
Think of it as a set of rules or a game plan that guides how tickets are routed, incidents are managed, and service requests are fulfilled.
These workflows can help automate routine support tasks, ensuring that every step is executed smoothly and consistently. This not only reduces the chances of human error but also speeds up response times, making your service desk more efficient and reliable.
Your help desk should function as a well-oiled machine. Each part has a specific role, and workflows ensure that all parts work together seamlessly. Whether it’s assigning a ticket to the right technician or escalating a critical incident, workflows help keep everything on track.
And by automating these processes, you free up your team to focus on more complex issues, ultimately improving the overall quality of your service.
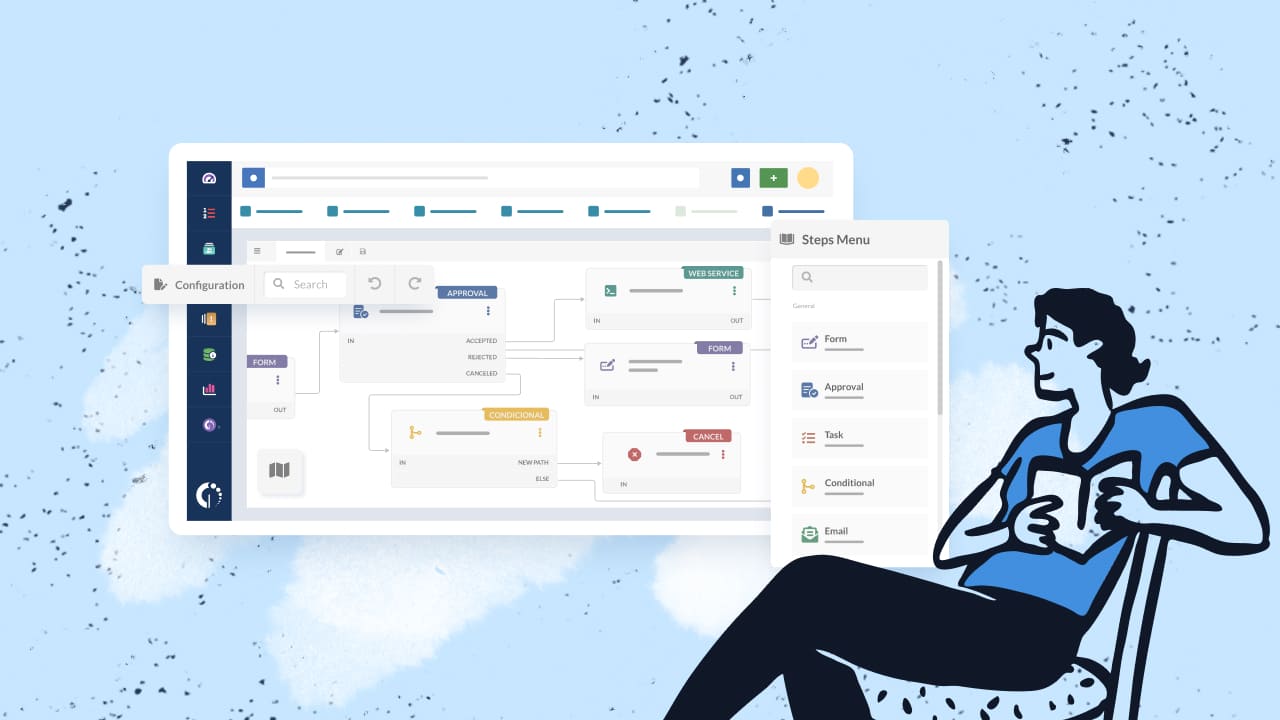
Keep in mind that your chosen help desk software must incorporate workflow capabilities that enable teams to design and customize their flows according to their needs. For this, InvGate Service Management’s no-code workflow builder allows users to drag and drop the different components into a process to define and automate its multiple steps. But stay tuned, there will be more on this when we get into the examples!
What is Workflow Management? Benefits, Templates, And Automation
Benefits of designing service desk workflow processes
Automating service desk workflows can help transform how your team operates on a daily basis. Let’s break down the key benefits:
Increased efficiency
Automation is like having an extra set of hands that never sleep. By streamlining routine tasks, your team can handle requests faster and more consistently. No more juggling or manual sorting – tickets get routed to the right person instantly, so response times are slashed and resolutions come quicker.
Enhanced customer satisfaction
Happy customers are the endgame of any successful service desk. Automated workflows mean less waiting and smoother experiences for your users. When issues are resolved swiftly and efficiently, it leaves a lasting positive impression, boosting overall satisfaction and loyalty.
Improved compliance and accuracy
Staying compliant and accurate is crucial, especially when dealing with sensitive data or complex processes. Automated workflows ensure that every step follows predefined policies and procedures. This reduces the risk of human error and deviations, keeping everything on track and in line with regulations.
Scalability
As your organization grows, so do the demands on your service desk. Automated workflows are your cheat code for scalability. They allow you to manage a higher volume of requests without needing to hire a small army. This means you can scale up your operations smoothly, meeting increased demand without breaking a sweat.

IT Support Automation: Definition, Benefits, and Tools
10 help desk workflow examples to automate your business processes
Now, it’s time to roll up our sleeves and get into some practical help desk workflow examples to implement in your help desk.
1. Knowledge article creation
Overview
This workflow tracks how knowledge is handled from proposal to publication within the IT environment. The workflow ensures that content is appropriately vetted and classified before it becomes part of the knowledge base, enhancing the utility and integrity of the information shared.
Workflow steps
- Proposed article: The process begins with the submission of a proposed knowledge article via a form.
- Content approval: Once an article is proposed, it enters the content approval stage. Here, designated reviewers assess the quality, accuracy, and relevance of the content.
- Accepted: The article is approved for publication.
- Rejected: The article does not meet the required standards or relevance and is therefore not approved for further processing.
- Canceled: The request for publication is withdrawn or terminated for other reasons.
- Publication
- Public: The article is made available to the general public or all users of the knowledge base. Utilizes a web service to publish the article in the designated public section of the knowledge base.
- Private: The article is published but restricted to specific users or groups. Utilizes a web service to place the article in a restricted area that only authorized users can access.
- Continue or cancel request: Following publication, there may be a decision point on whether to continue creating more articles or to stop further requests.
- Email to writer: Generates and sends an email notification to the writer at the conclusion of the workflow. This email could contain feedback, publication status, and any next steps or acknowledgments.
To support the process of this workflow, InvGate Service Management’s knowledge base article generation feature (powered by AI) helps streamline the first steps by automatically turning solved tickets into knowledge base article drafts. This way, writers can save time by working directly from this first draft to improve and adapt it accordingly.

6 Steps For a Solid Knowledge Management Process [+Workflow Template]
2. Change Management control
Overview
This workflow manages the change request approval process, ensuring that all necessary steps, from submission to review, are meticulously followed to mitigate risks. It minimizes the risks associated with changes, ensuring stability and compliance.
Pro tip: You can download a free template to kick off the request for change process here.
Workflow steps
- Change request submission: A change request is submitted detailing the proposed changes.
- Impact analysis (automation): The system performs an impact analysis to evaluate the potential effects of the change.
- Approval workflow (automation): The request goes through multiple automated approval stages, including peer review and CAB (Change Advisory Board) approval.
- Implementation planning: Once approved, a detailed implementation plan is created.
- Change implementation: The change is implemented according to the plan.
- Post-implementation review: A review is conducted to ensure the change has achieved the desired outcomes without negative impacts.
- Documentation and closure: The change is documented, and the request is closed.

Change Request: Definition, Form, And Free Workflow Template
3. Onboarding new employees
Overview
This workflow automates tasks related to new employee onboarding, such as account creation and access provisioning, ensuring a smooth and efficient onboarding process. It speeds up the readiness of new employees and ensures no steps are missed.
Pro tip: You can download a free template to kick off the request for change process here.
Workflow steps
- Onboarding request submission: HR submits a request for onboarding a new employee.
- Account creation: The system automatically creates necessary accounts (email, system access, etc.).
- Access provisioning: Required access and permissions are provisioned based on the employee's role.
- Welcome package: A welcome package, including necessary information and resources, is prepared and sent to the new employee.
- Training schedule: The system schedules mandatory training sessions for the new hire.
- Progress tracking: The progress of the onboarding tasks is tracked and monitored.
- Completion: The onboarding process is completed, and a welcome notification is sent to the new employee.

How to Build a Flawless Onboarding Workflow [+Free Template]
4. Ticket routing and assignment
Overview
This workflow ensures that incoming tickets are automatically routed and assigned to the appropriate technician or department based on predefined criteria such as issue type, priority, or customer category. It ensures quick handling of issues by the most suitable personnel, improving resolution times and customer satisfaction.
Workflow steps
- Ticket creation: A user submits a ticket via the service desk portal.
- Categorization: The system categorizes the ticket based on keywords, issue type, or other metadata.
- Priority assignment: The ticket is assigned a priority level automatically based on predefined rules.
- Routing: The ticket is routed to the appropriate technician or department based on its category and priority.
- Assignment notification: The assigned technician or department receives a notification about the new ticket.
- Resolution: The technician works on resolving the issue and updates the ticket status.
- Closure: Once resolved, the ticket is closed, and the user is notified.
This workflow is already a configuration within InvGate Service Management. Once you have your help desk configured, you can choose from the following assignment rules for the routing process: round robin (goes to the next available agent), workload (assignment based on the agent's current workload), or free (agents pick up the tickets out of a queue).

What is Ticket Routing And How to Automate it
5. Service request fulfillment
Overview
This workflow automates the full lifecycle of service requests, from approval to fulfillment, ensuring efficient and accurate service delivery. It enhances the speed and precision of service delivery.
Workflow steps
- Request submission: A user submits a service request through the portal.
- Approval workflow: The request goes through an automated approval process, which may involve multiple approvers depending on the request type.
- Task assignment: Once approved, tasks are automatically assigned to the relevant departments or personnel.
- Progress tracking: The system tracks the progress of the request fulfillment.
- Notification: Users are notified at each stage of the request fulfillment process.
- Completion: Once all tasks are completed, the request is marked as fulfilled.
- Feedback collection: A feedback request is sent to the user to gather their satisfaction level.
6. Incident Management automation
Overview
This workflow streamlines the Incident Management process, from incident logging to resolution, ensuring that incidents are handled efficiently and effectively. The idea is for it to reduce downtime by ensuring incidents are escalated and resolved promptly.
Workflow steps
- Incident logging: The incident is logged through various channels (e.g., email, service portal, monitoring tools).
- Categorization and prioritization: Based on predefined criteria, the incident is classified and, depending on the impact and urgency, automatically assigned a priority level.
- Ticket routing: The incident is automatically routed to the appropriate support team or individual based on skill set and availability.
- Diagnosis and resolution: The team investigates and diagnoses the root cause of the incident and implements a solution to resolve the incident.
- Incident communication: Automated updates are sent to users and stakeholders about the incident status and progress.
- Incident closure: The resolution is confirmed with the user and the incident is closed.
- Incident review: The incident handling process is reviewed and documented.
7. Regular maintenance schedules
Overview
This workflow schedules and manages regular maintenance and updates for IT systems, ensuring consistent system health and uptime.
Workflow steps
- Maintenance schedule creation: Regular maintenance schedules are created based on system requirements.
- Notification: Notifications are sent to relevant stakeholders about the upcoming maintenance.
- Task assignment: Maintenance tasks are assigned to the appropriate technicians.
- Execution: Technicians perform the scheduled maintenance tasks.
- System checks: Post-maintenance system checks are conducted to ensure everything is functioning correctly.
- Documentation: Maintenance activities are documented for future reference.
- Completion: The maintenance cycle is marked complete, and stakeholders are notified.
8. Customer feedback collection
Overview
This workflow automates the collection and processing of customer feedback after ticket resolution, providing valuable insights into service quality and customer satisfaction. It provides valuable insights into customer satisfaction and service quality.
Workflow steps
- Ticket closure: Upon ticket resolution, the system triggers a feedback request.
- Feedback form: A feedback form is sent to the user, requesting their input on the service received.
- Feedback collection: User feedback is collected and stored in the system.
- Analysis: The feedback is analyzed to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Reporting: Feedback results are compiled into reports for management review.
- Follow-up: If necessary, follow-up actions are initiated based on the feedback received.
- Improvement: Insights from the feedback are used to make continuous improvements to service processes.

How to Obtain Customer Feedback – And What to do With it
9. New asset procurement
Overview
This workflow automates the tracking and management of IT assets from procurement to disposal, ensuring accurate Inventory Management and optimal asset utilization.
Workflow steps
- Asset procurement: New assets are procured and logged into the system.
- Tagging and tracking: Automation: Assets are tagged and tracked throughout their lifecycle.
- Maintenance scheduling: Regular maintenance schedules are created for each asset.
- Usage monitoring: The system monitors asset usage and performance.
- Decommissioning: Assets that reach the end of their lifecycle are decommissioned and disposed of responsibly.
- Inventory updates: The asset inventory is updated to reflect current status and availability.
- Reporting: Asset management reports are generated for review.

The Complete Guide to IT Procurement
10. Compliance auditing
Overview
This workflow regularly audits processes to ensure compliance with internal policies and external regulations, maintaining high standards of governance.
Workflow steps
- Audit schedule creation: Automation: Regular audit schedules are created based on compliance requirements.
- Notification: automation: Notifications are sent to relevant stakeholders about upcoming audits.
- Audit execution: Audits are conducted to evaluate compliance with policies and regulations.
- Findings documentation: Audit findings are documented and stored in the system.
- Review and action: Findings are reviewed, and necessary actions are initiated to address any non-compliance issues.
- Reporting: Compliance reports are generated for management and regulatory review.
- Follow-up audits: Follow-up audits are scheduled to ensure corrective actions have been implemented.

How to Conduct an IT Audit in 2024
5 IT help desk workflow best practices
Creating effective IT help desk workflows is crucial for smooth and efficient service operations. Here are some best practices to help you design workflows that truly make a difference:
1. Define clear objectives
Before diving into the nuts and bolts of creating a workflow, take a step back and think about what you want to achieve. Are you looking to speed up ticket resolution times? Improve customer satisfaction? Reduce the workload on your team? Having clear goals will guide the design of your workflows and ensure they deliver the results you need.
2. Keep it simple
When it comes to workflows, simplicity is key. Aim for straightforward, easy-to-understand processes that your team can follow without a hitch. Overly complex workflows can be confusing and are more likely to lead to errors. Stick to the essentials and make sure every step adds value.
3. Regularly review and update
The world of IT is constantly changing, and your workflows should adapt accordingly. Regularly review your workflows to see what's working and what's not. Be open to feedback from your team and make adjustments as needed. This will help keep your processes relevant and efficient.
4. Automate where possible
Take advantage of automation to handle repetitive tasks. This could include things like routing tickets, sending notifications, or updating statuses. Automation not only speeds up these processes but also reduces the risk of human error, freeing up your team to focus on more complex issues.

Workflow Automation Guide: Definition, Benefits, And Software
5. Focus on user experience
Always keep the end-user in mind when designing your workflows. The easier and more intuitive the process is for your team, the more effective it will be (this will help with user adoption, too). Aim for workflows that not only streamline operations but also enhance the overall user experience, making everyone’s job a little bit easier.
In short
By automating key processes, you can improve the speed, consistency, and quality of your service operations. Here are the main takeaways from our discussion on help desk workflows:
- Automate routine tasks to improve efficiency and accuracy.
- Regularly review and update workflows to keep them relevant.
- Focus on user experience to enhance adoption and satisfaction.
With this information and examples, you're well-equipped to optimize your help desk workflows and drive better outcomes for your service desk team and your customers.
And, if you want to have a try at implementing these workflows with an intuitive and robust solution, ask for InvGate Service Management’s 30 day free trial!