When IT support teams have a great ticket management process, users get faster resolutions, and organizations minimize downtime. However, if you’re not following best practices for ticket handling, the process often comes with challenges: backlogs, miscommunication, or delays in prioritizing issues.
Research shows that 90% of users expect support teams to resolve their requests immediately — and by immediately, they mean 10 minutes or less — an ambitious goal that requires a well-oiled ticketing system.
Let’s break down some ticket-handling best practices that can make your IT support faster, smoother, and more effective.
6 steps in the service desk ticket handling process
Managing tickets involves more than logging an issue and assigning it to a technician. A clear, consistent help desk ticketing process ensures that requests are addressed promptly and according to their priority. Here's an overview:
- Logging and capturing requests
Tickets begin with detailed information—who submitted the request, what the issue is, and any relevant attachments or data. A comprehensive intake system ensures no key detail is missed. - Categorization and prioritization
Assigning categories and urgency levels allows teams to organize requests effectively. For instance, a system outage typically takes priority over a non-critical software update. - Assignment and triage
Tickets are routed to the right technician or team based on expertise and workload. Automated routing systems often make this step faster and more accurate. - Escalation (if needed)
Complex tickets that can't be resolved at the first-level support are escalated to higher-tier IT support or specialists. This step ensures critical issues don’t get stuck. - Resolution and updates
Once resolved, technicians communicate the solution to the user and log it for future reference. Frequent updates during the process help maintain transparency. - Closure and feedback collection
After confirmation from the user that their issue is resolved, tickets are closed. Feedback gathered during this step is critical for identifying improvement areas.
9 ticket handling best practices to streamline IT support
Managing tickets effectively is essential for delivering timely resolutions and maintaining user satisfaction. Below are detailed best practices, each designed to optimize different aspects of the ticket-handling process.
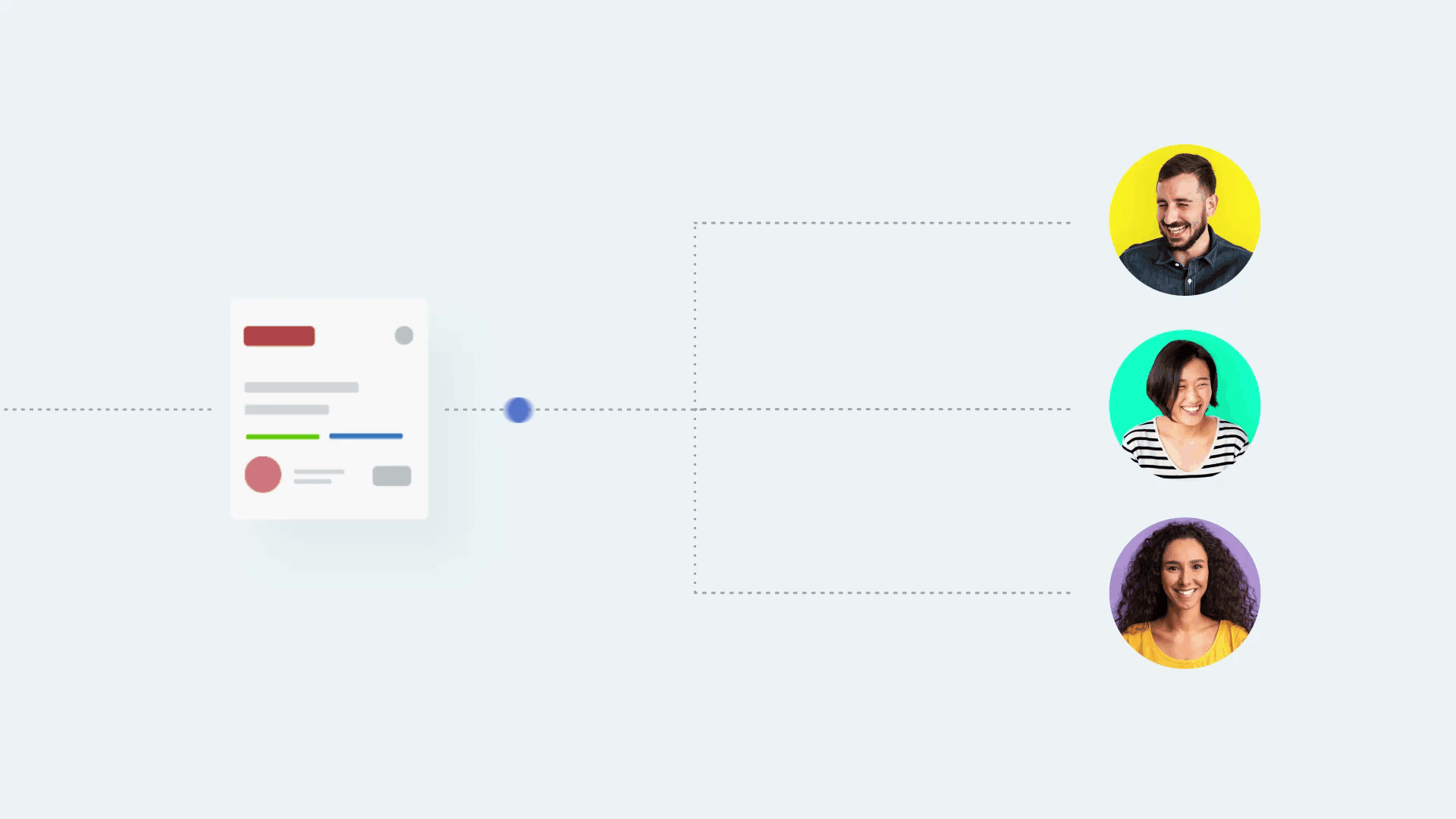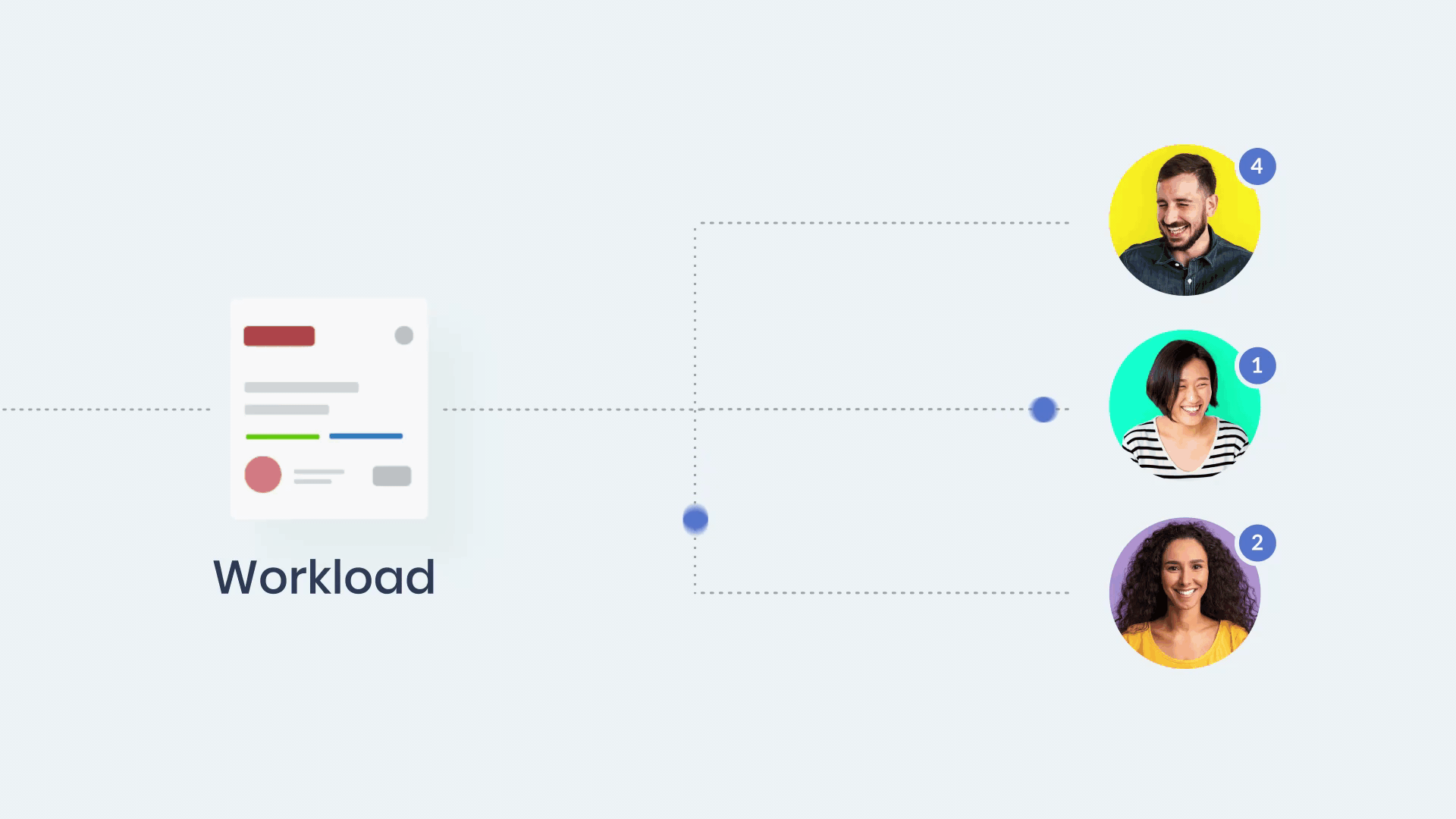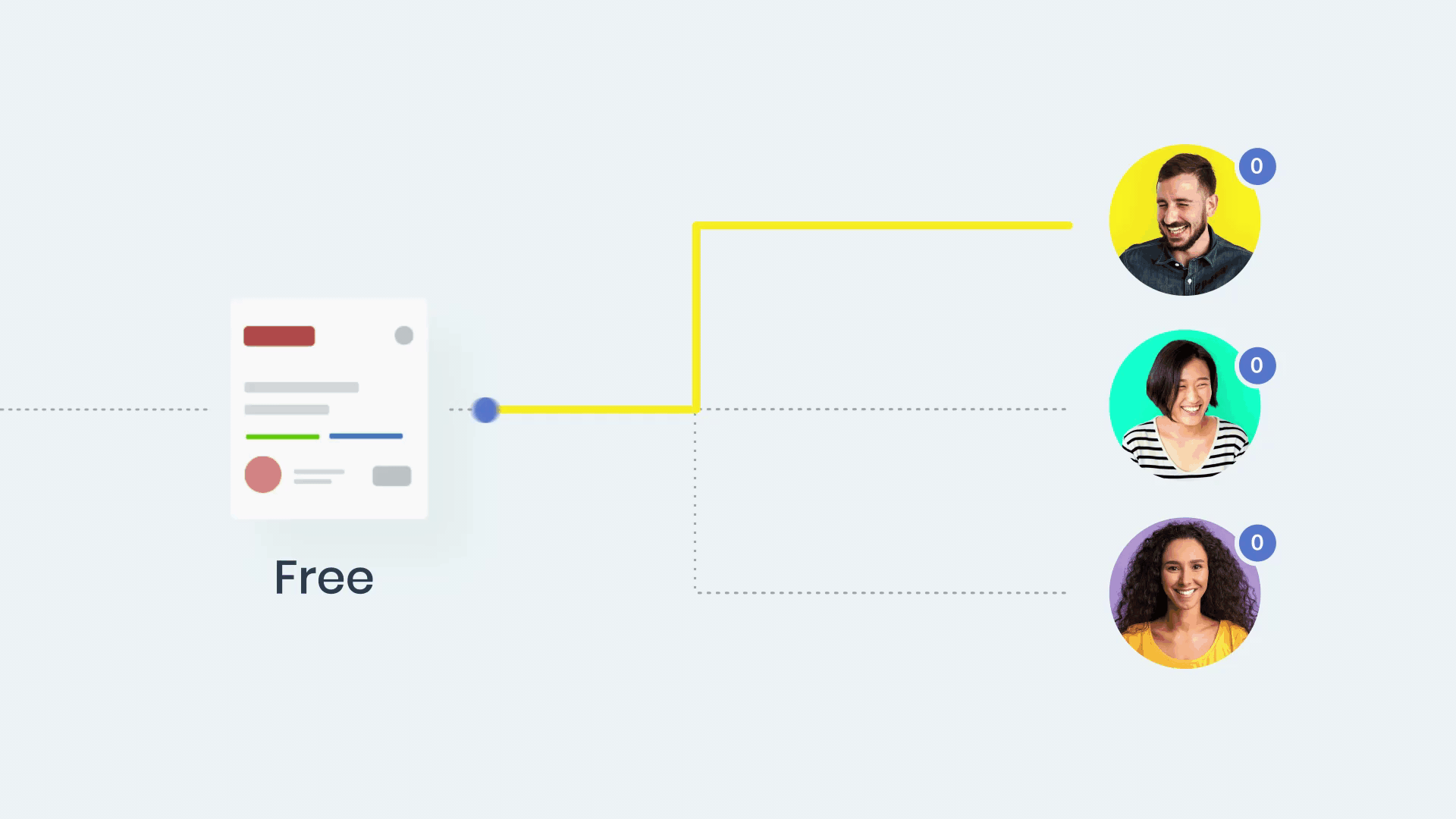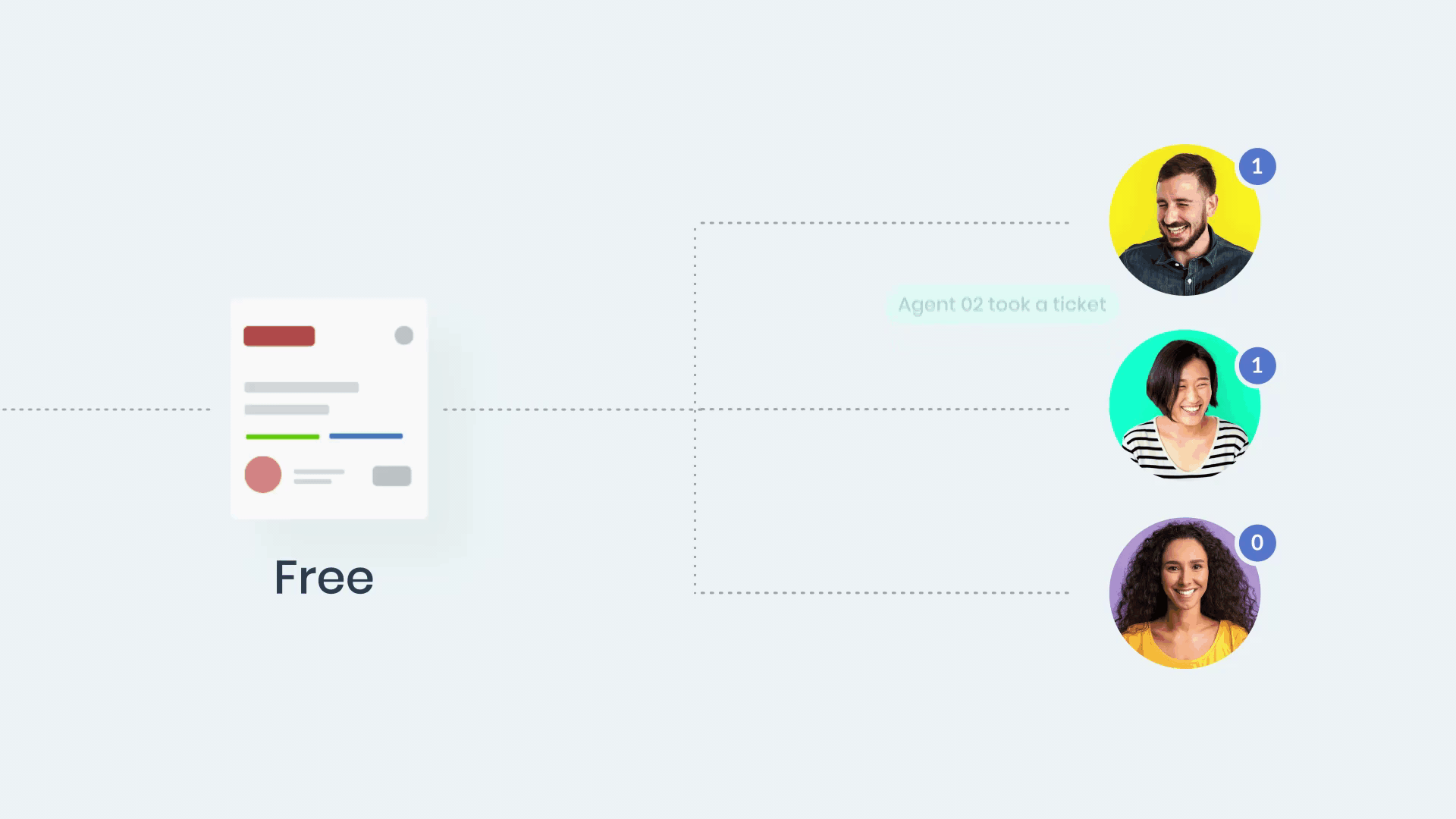
1- Automate ticket assignment
Manually assigning tickets can be time-consuming and error-prone, especially for larger IT teams managing a high volume of requests. Automation ensures that tickets are routed to the right technician or team based on predefined criteria like:
- Expertise: Assign tickets to staff skilled in specific software or hardware.
- Workload: Distribute tickets evenly to avoid overburdening individuals.
- Ticket urgency: Prioritize high-severity issues for quicker resolution.
For example, if your IT support team uses a tool like InvGate Service Management, automation rules can assign network-related issues directly to the network operations team. This reduces response times and ensures specialized attention.
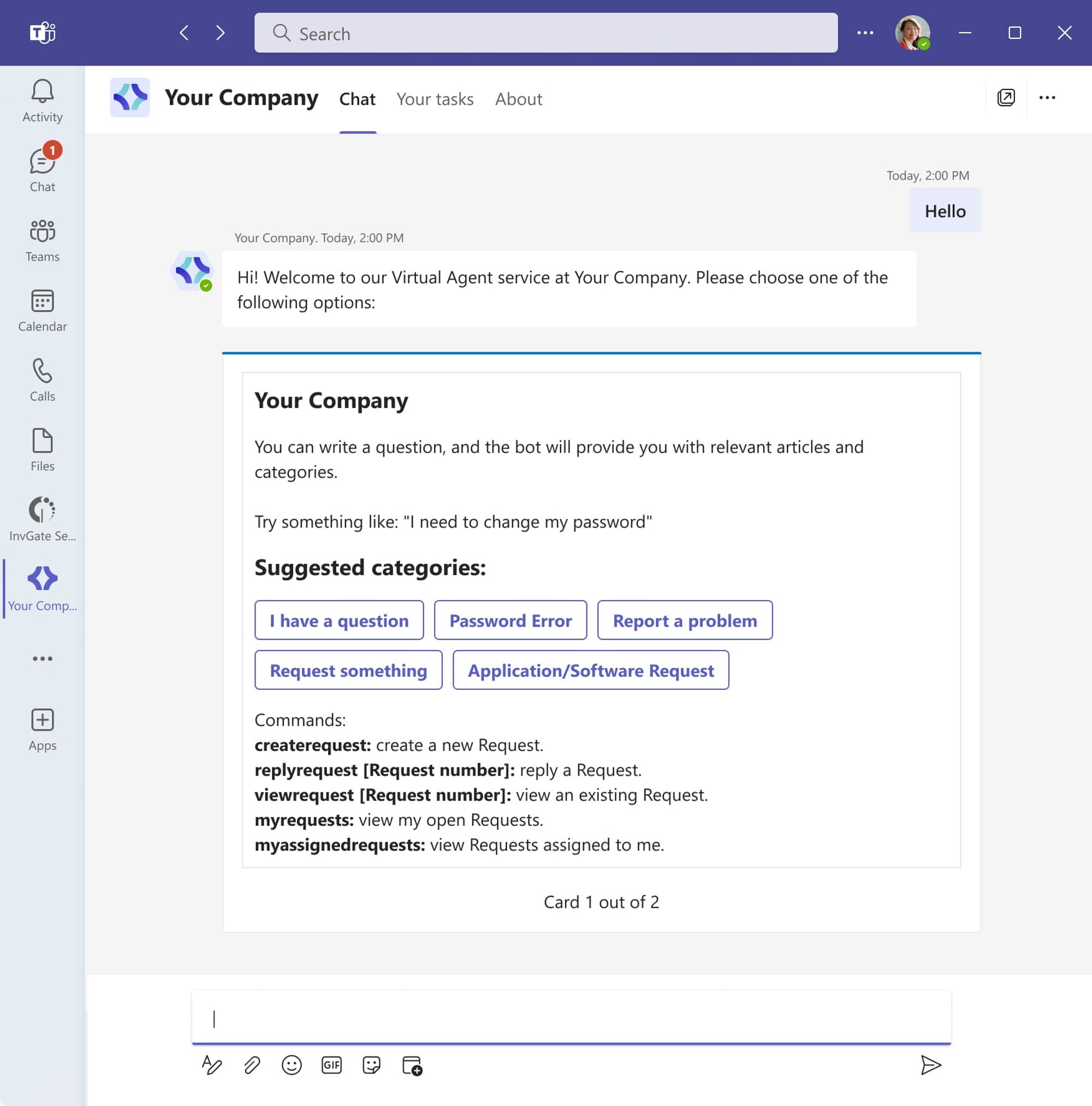
2- Leverage AI to speed up replies
Artificial intelligence has transformed ticket handling by enabling faster and more accurate responses. AI-powered tools can:
- Provide response templates: Based on historical data, AI suggests answers to common queries, allowing technicians to reply quickly.
- Automate routine queries: Chatbots can resolve straightforward issues, such as password resets, without human intervention.
- Assist with troubleshooting: AI identifies patterns in previous tickets to recommend solutions.
For an added layer of support, consider implementing a chatbot to handle initial inquiries. For example, if a user reports an issue like "unable to access the company VPN," the bot can walk them through troubleshooting steps before escalating to a human technician. With InvGate Service Management, users can access the Virtual Agent directly within Microsoft Teams, making it easy to get help without interrupting their work.
3- Define and monitor SLAs
Service level agreements (SLAs) establish clear expectations for ticket resolution. They help prioritize tasks, manage user expectations, and track performance. Here’s how to make SLAs effective:
- Set realistic timelines: For example, resolve critical issues within 4 hours, while minor requests can have a 72-hour window.
- Create multiple SLA tiers: Different departments or users may require varying levels of support. VIP clients or departments with mission-critical functions may have stricter SLAs.
- Monitor compliance regularly: Use dashboards to track SLA adherence and identify where improvements are needed.

4- Escalate and triage effectively
Ticket escalation and triage prevent bottlenecks by ensuring that tickets are routed correctly based on complexity or priority. A clear escalation process includes:
- Defining escalation paths: Specify when tickets should move from Tier 1 to Tier 2 support, or directly to a subject matter expert.
- Using ticket triage categories: Label tickets based on urgency (e.g., low, medium, high) or impact (e.g., affecting one user vs. the entire system).
- Training teams on procedures: Ensure technicians understand when and how to escalate issues to avoid delays.
For example, a system-wide outage might skip Tier 1 entirely and go directly to senior IT engineers, ensuring the fastest possible resolution.

5- Monitor performance with dashboards
ITSM dashboards give teams a real-time view of support operations. They can track metrics like:
- Number of open and closed tickets.
- Average resolution time.
- SLA compliance rates.
Dashboards help IT managers and team leaders visualize data and identify trends and bottlenecks. For instance, a spike in unresolved tickets may indicate a need for more resources or an adjustment of workflows.
InvGate provides this at-a-glance ticket status and metrics paired with customizable views. You can prioritize and focus on specific ticket types, such as high-priority incidents or tickets nearing SLA deadlines.

6- Set up periodic automated reports
Periodic reports provide a detailed, retrospective view of your IT support performance. Generated on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis, these reports can be set to track:
- Commonly reported issues, like printer malfunctions or connectivity problems.
- Performance metrics across different teams.
- SLA breaches and their causes.
For example, a weekly report might show that network connectivity problems consistently account for 30% of tickets, indicating a need for system upgrades or better user training. Such insights are invaluable for identifying patterns, improving workflows, and planning strategically.
The difference between reports and dashboards is that the latter offer real-time data for immediate decision-making, while reports focus on historical analysis. Both tools complement each other, but reports are particularly useful when refining ticket-handling processes over the long term.

7- Offer self-service tools
A well-maintained self-service portal or knowledge base empowers users to resolve straightforward issues without contacting IT support. These tools reduce the number of incoming tickets, free up technicians to focus on more complex tasks and provide users with quick, convenient solutions.
Common resources in a self-service platform include:
- FAQs: Concise answers to frequently asked questions like, “How do I reset my email password?”
- Knowledge base: A centralized repository of detailed articles, guides, and tutorials. For example, troubleshooting tips and step-by-step instructions for common issues, such as "Configuring VPN access.”
- User forums: Collaborative spaces where users can share solutions and advice, often moderated to ensure accuracy.
Using InvGate Service Management, you can create a comprehensive self-service portal tailored to your organization's needs.
For instance, if password reset requests make up a large percentage of your ticket volume, InvGate allows you to build a dedicated page with troubleshooting steps and an automated reset process. It’s a simple way to give users access to solutions, significantly reducing the IT support team’s workload
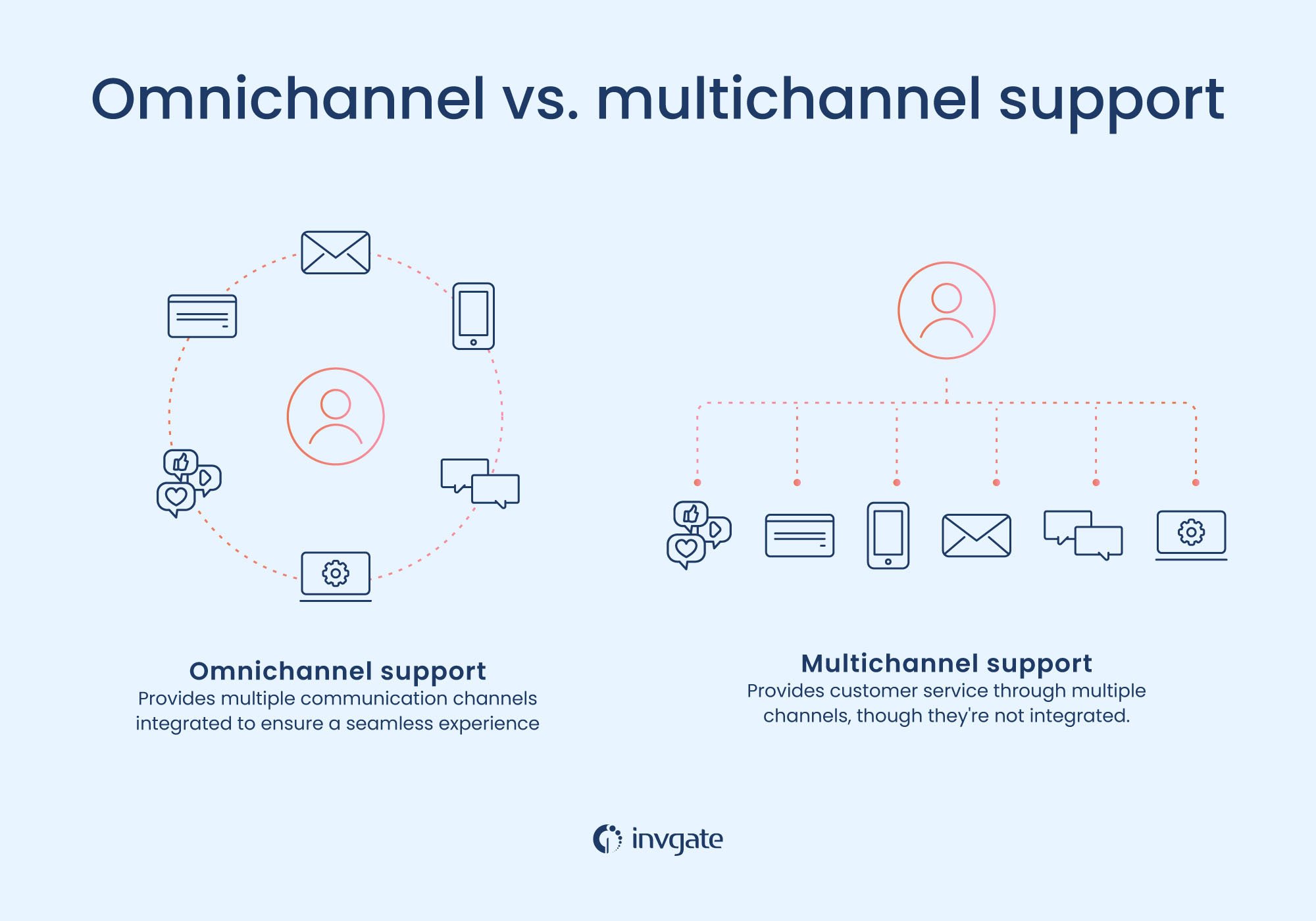
8- Centralize communication channels
Managing tickets across multiple platforms—like email, chat, and phone—can create inefficiencies. Omnichannel support consolidates all communications in a single interface, ensuring that:
- Tickets aren’t lost when users switch between channels.
- Responses remain consistent across platforms.
- Teams can track the entire conversation history.
For example, a user might report an issue via email but follow up with a phone call. A centralized system ensures both interactions are connected to the same ticket, preventing confusion.
9- Keep an eye on the ticket backlog
A growing ticket backlog is a warning sign of inefficiency. It can lead to frustrated users and stressed technicians. Prevent backlog issues by:
- Regularly reviewing pending tickets: Identify stalled or outdated requests.
- Adding resources during peak times: Seasonal surges, like during new employee onboarding, may require additional staff.
- Auditing workflows: Look for bottlenecks that slow down ticket resolutions.
Of course, clearing existing tickets will be your priority at first, but it's equally important to address the underlying issues that led to the backlog. That’s why you should also aim to implement a sustainable process that minimizes the risk of it happening again in the future.

Conclusion
Handling IT support tickets effectively is no small task, but it can make a measurable difference in your team’s productivity and your users’ satisfaction. Throughout this article, we’ve walked through practical approaches — from automating ticket assignment to leveraging periodic reports and self-service portals.
The truth is, there’s no single “perfect” way to manage tickets because every organization has unique challenges and priorities. What matters is building a process that works for your team and constantly refining it based on data and feedback. If you can implement even a few of the practices we’ve covered, you’ll likely notice improvements in how your team operates and how users perceive your support services.
Ultimately, better ticket handling isn’t just about closing tickets faster — it’s about creating an experience where both IT teams and users feel supported and equipped to succeed.
Experience the benefits of integrated ITSM with InvGate Service Management. Register for our 30-day free trial!















