Ticket triage is a central process of all service desks: when something goes wrong, it must be solved. It is at the heart of every support team's work and is related to what ITIL describes as Incident Management. Well implemented, triage can save time and help deliver consistent IT services, which is one of the main goals of all high-performing organizations.
Complete service desk solutions include different features, such as workflow automation, to triage support tickets simply and quickly. In this article, we will look into how this process works and how to automate it with InvGate Service Management.
Let's get to it!

Ticket triage meaning
Simply put, ticket triage is made up of all the steps you take in order to solve a ticket.
This can go from a simple problem, like a keyboard breaking, to a highly complex environment that has a set of checklist items you need to complete in order to solve and close the ticket.
This operation represents the standard operating procedure to be followed and the individual work instructions on how to solve an incident. So, ticket triage is exactly where the rubber hits the road. In order to be successful, on top of solving the problem, the IT support team should create a satisfactory experience for both the agent and the customer.
Well-functioning IT processes that have been properly adapted to your organization contribute to both the IT and overall business strategy. They can help you achieve the goals defined in the strategy, including Incident Management, for which ticket triage is central.
3 benefits of implementing automated ticket triage
Implementing automated ticket triage over your service desk will help you ensure consistency in your work and manage tickets, guaranteeing that they are in the right hands at the right time. This way, your customers will always receive a high-quality support experience. Some of the main benefits of implementing this process include control over:
- Costs – Selecting who is assigned to the ticket and an agreed time to solve it will help you better manage your resources and consequently control your costs.
- Accuracy – Having a clear protocol for the ticket resolution process can give you precision on the proper steps to take.
- Speed – Automated ticket triage can help you prioritize tickets and assign the proper resources to solve them faster. This will improve response times and customer satisfaction.
Ticket triage process: how to triage support tickets
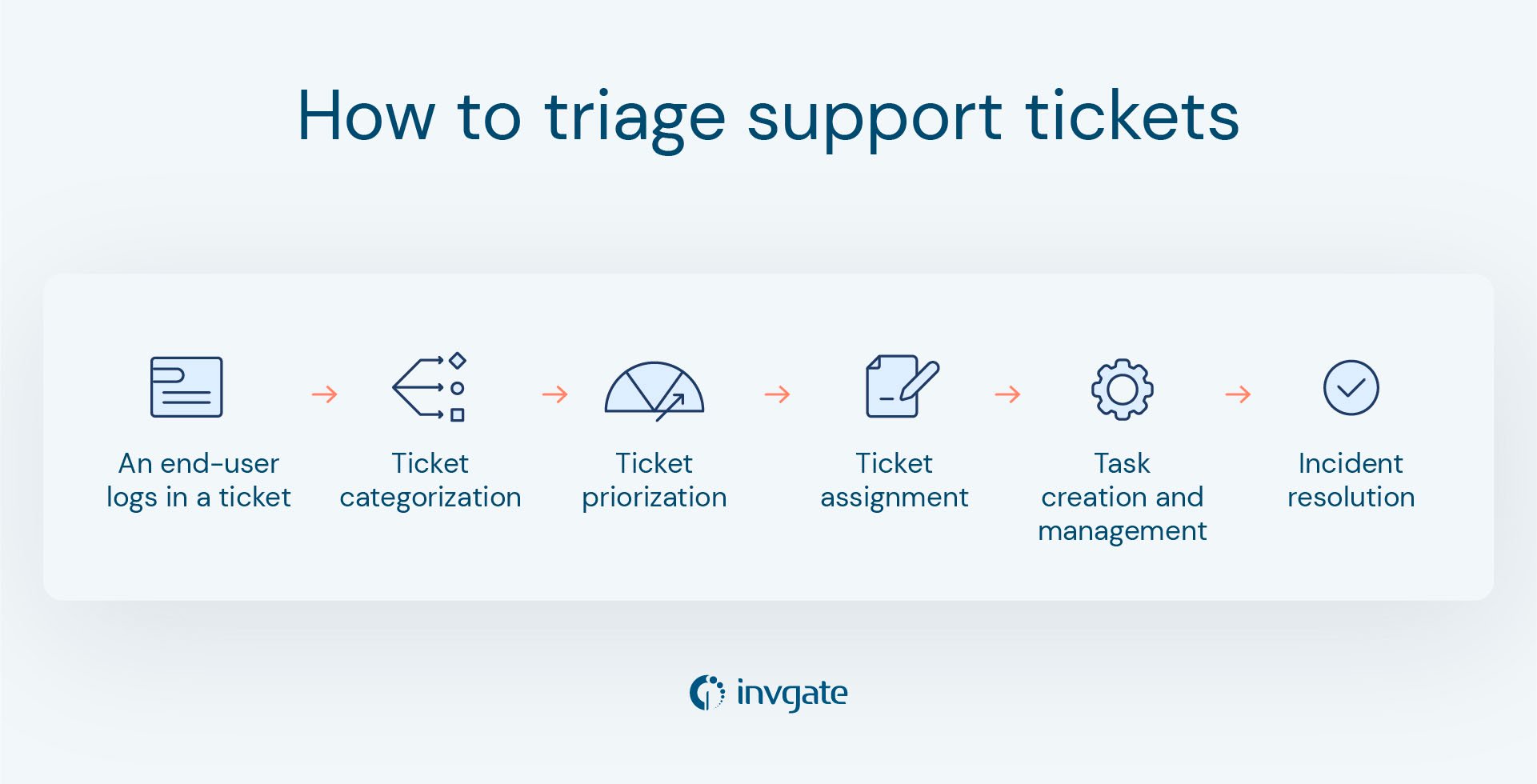
So far, we've looked at what ticket triage is and described some of its main benefits. Now, it's time to explore the process in greater detail and learn how InvGate Service Management can be your best ally for its implementation and automation.
1- Ticket logging
The very first step for triaging a ticket is logging. An end-user can do this on InvGate Service Management's self-service portal, which has a space to fill in all the necessary information about the incident.
They can also do this through an integration with email or Microsoft Teams, or they can have an agent do it. And if you have the ITSM tool connected with our ITAM software, InvGate Asset Management can provide your agents with information on the equipment owned by each user to solve tickets even faster.
2- Categorization and assignment
The ticket will be categorized as soon as it has been logged, but agents and admins can always change it to another category and help desk if they consider it necessary. Depending on its category, the request will be assigned to a specific agent or a group of people.
It's important to consider that the more information you collect, the easier it will be to establish the incident priority. Once you know what's going on, you can determine how business-critical it is, how urgently it must be solved, and how many people it impacts.
Prioritization of tickets is another example where InvGate Asset Management can help. If you have your critical services and primary business applications clearly mapped out on our CMDB, you can quickly identify its impact and correctly assign the ticket.
After prioritizing, it's time for the automatic ticket assignment. This will depend on the help desk to which the request is linked and the assignment rules that you have previously configured. InvGate Service Management offers three options:
- Round Robin: Assigns tickets automatically to the next available agent in a sequence.
- Workload: Assigns tickets automatically based on the agent's current workload.
- Free: Instead of automatically assigning tickets, agents pick up the tickets out of a queue.

However, this is not always a straightforward process. Sometimes, teams have more complex issues that can't be solved by simply assigning them to a category. Perhaps you need specific teams for certain locations, or you may have different groups that support particular employees or customers. For these cases, InvGate Service Management includes "Automation," which responds to a simple if-this-then-that logic.
So, for example, with this feature, you can set all computer replacements to go to the "Field Services" team but include an exception for when a VIP creates the ticket to move the ticket to the right team automatically.
Agents can also receive AI-powered suggestions for expert collaborators based on analysis of similar requests, allowing them to add experienced colleagues to help with ticket resolutions when necessary.
3- Task creation for agents
The next step of triaging is task creation and management. Automation and planning are crucial here. For instance, you can establish a predetermined list of tasks for new agents to complete. Checklists are also very helpful when there are different places to search and multiple steps to follow. Another resource many teams create for this instance is a knowledge base article with some basic steps to solve general tickets.
Apart from describing a basic set of troubleshooting steps, you can also populate your internal knowledge base with articles for specific systems, services, or applications and link both the generic steps and additional ones for that specific system.
These are particularly useful procedures to include during hand-off and other transitional activities. If there is a new service or technology to support, for example, providing specific instructions to triage really pays off, as it helps to create a great experience for customers, colleagues, and support staff alike.
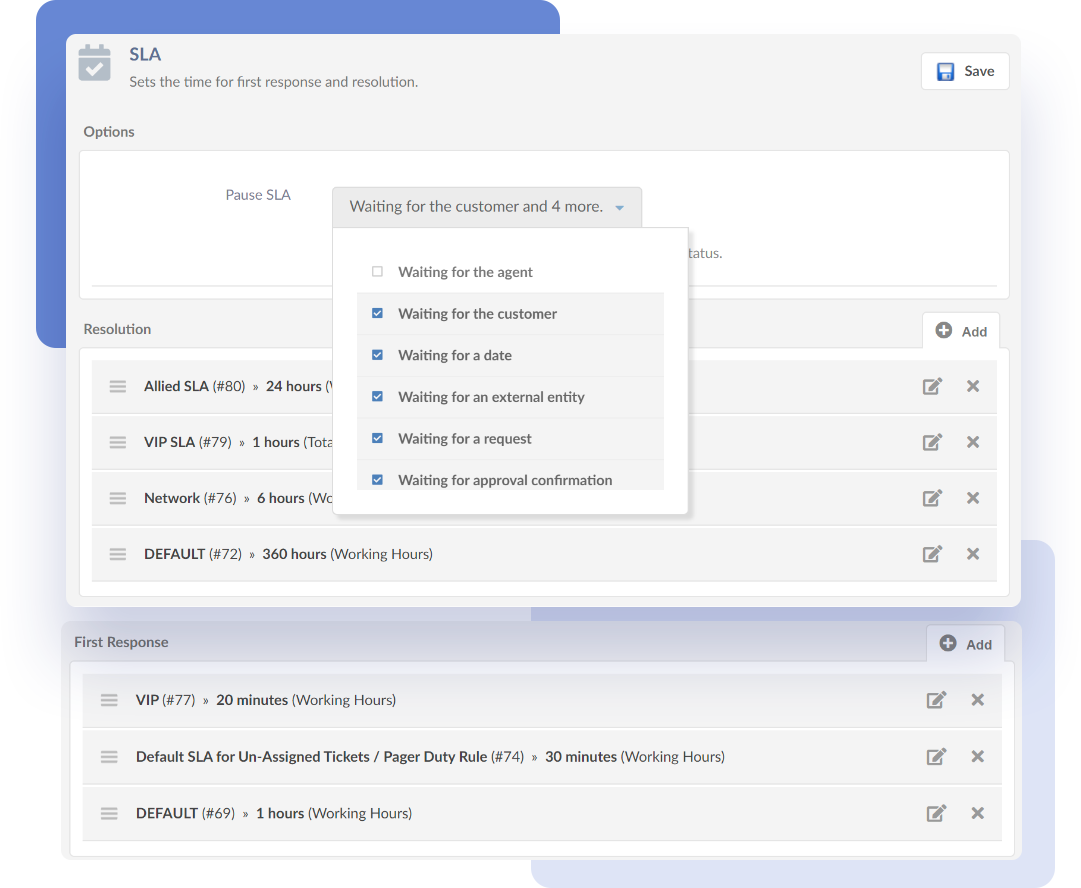
4- Ticket escalation
Not every issue can be resolved by the first assigned agent. Some requests require more specialized expertise or higher-level approval, while others risk breaching SLAs if not handled promptly. Having a structured escalation process ensures that these tickets don’t get stuck or delayed.
InvGate Service Management provides several tools to streamline this step:
- Shortcuts to escalate tickets – Quickly reassign tickets to higher-tier support or specialized teams.
- Predictive suggestions – The system recommends the most suitable escalation path based on similar past cases.
- Add watchers and approvers – Keep key stakeholders in the loop for better visibility and faster decision-making.
It's important to plan SLA calculations and notifications ahead of time. This way, you can automate them when you're building your help desk and service catalog.
For an extra layer of efficiency, AI-powered smart escalation can identify SLA risks before they become a problem. Analyzing historical case data suggests timely escalations, ensuring urgent issues get the attention they need without constant supervision.
4- Resolution and documentation
Finally, the last step is the incident resolution, when the agent or team identifies that the issue, incident, or problem has been solved and notifies the user to validate and confirm the resolution.
With the problem addressed, the ticketing process wraps up — but documentation is just as important as the resolution itself. Keeping records updated helps prevent recurring incidents and improves future response times.
InvGate Service Management makes this step easier by allowing teams to log resolution details and update the knowledge base quickly.
For an even more efficient approach, the AI Knowledge Article Generation feature uses generative AI to create a first draft of a knowledge article in under 30 seconds. It pulls key details from the initial request and resolution steps, giving agents a solid starting point for documentation. Keeping this information updated ensures that common issues can be resolved faster in the future.
4 service desk ticket triage best practices
Although it is at the very base of Service Management, ticket triage can still be a complex process. Each scenario and organization is unique and will have its own requirements. Here, we will explore some general good practices that you can follow to optimize operations.
1. Pre-build a categorization and prioritization system
Throughout the day, requests will accumulate at your service desk, and users will always expect you to solve things as fast as possible. To tackle this, it's important to establish predetermined ticket prioritization criteria based on impact and urgency.
This way, the team will be informed on the appropriate way to respond to each situation. If a ticket is related to an incident that has a large impact and a high urgency, for instance, you will choose a completely different path to resolution than a ticket with a lower impact and urgency.
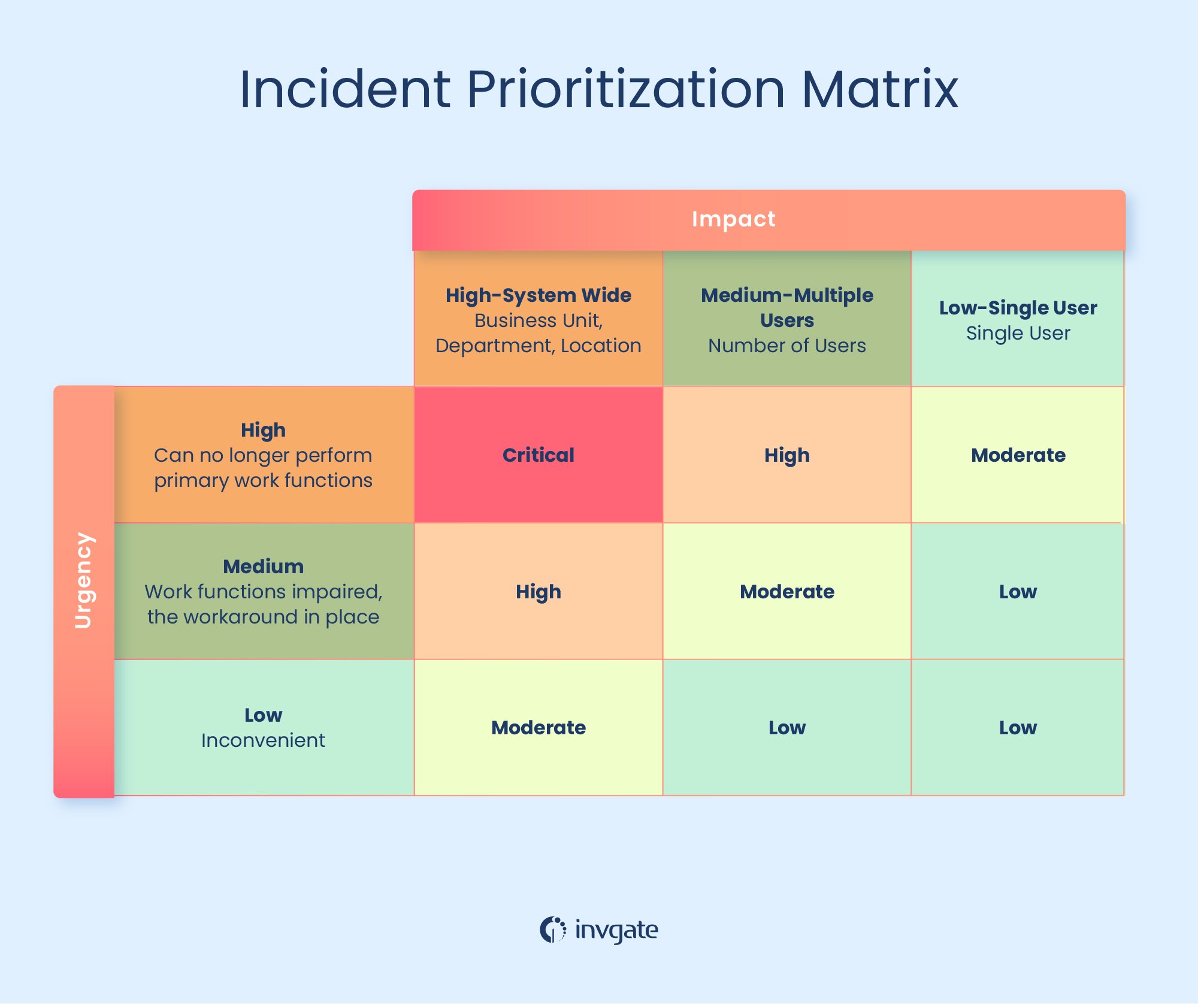
Having the objective impact information clearly available in the Service Portfolio or CMDB is very helpful in quantifying the impact.
2. Set clear Service Level Agreements
Once you have determined a ticket's priority, SLAs are set to stipulate the agreed amount of time available to solve it. There are countless ways to calculate this, but some frequent aspects considered include urgency, impact, service affected, and customer in question.
SLAs are subject to change during the lifecycle of a ticket, so make sure you continue to review and improve as you work through tickets and perform continual service improvement.
The SLAs determine triage tactics, escalation rate, and in some cases when to escalate to vendors or top-tier support. At a very basic level, they can also be used to measure end-to-end service delivery.
3. Give agents easy access
In order to help agents stay proactive, it is necessary to empower them with the right tools and information, and to give them the right amount of autonomy. Providing them access to all the data and systems they need to triage a ticket is fundamental for the process to run smoothly. This includes asset Records, change status, and past incident data.
Certain teams can include communication preferences, working styles, and other useful information for the agent's to incorporate. In order to encourage proactive management, giving agents power and autonomy to improve shared knowledge, automate resolution, and improve procedures is more than welcome.
Always remember to move at the right pace for your organization and its security needs and to incorporate only what works best for the specific employees and the role they serve.
4. Encourage clear communication
Motivating regular, easy-to-read, and respectful interactions with the people you serve is just the beginning of creating a successful communication environment. Using emojis, videos, images, and other dynamic content to communicate during triage can avoid additional back-and-forth and quickly summarize additional details. However, it's important to state clear protocols and accepted tools for this to work properly.
Ticket triage examples
A great example to illustrate ticket triage is when a laptop gets stolen. This would be an issue that falls under the responsibility of Enterprise Service Management (ESM), as it involves multiple departments of an organization and is one of those cases where it's particularly useful to have a predefined process that involves:
- IT
- Cybersecurity
- Legal
- Finance
- HR
- External entities
- Documentation.
Another frequent case falls under the category “Evergreen Incident,” which refers to generic issues that have not been reported before and consequently don't fit into any existing category.
In this case, it's even more important to document every detail: What was that person doing? What's their system? Don't forget to track the serial number and the OS version and validate their specs. If the issue keeps happening, it may be related to a major incident, problem, or change.
The last example includes incidents related to change, which sometimes are hard to turn into processes. It is very important to understand which changes cause service degradation and outages and which don't. Often, it's not as simple as seeing a problem in a system and triangulating the change calendar.
You have to make sure to document the whole process so agents can track where it comes from when this type of incident comes up. Registering changes on the CMDB while also tracking CIs on Incidents helps identify causation and potential impact.

Ticket triage and AI
In the last few months, at InvGate, we've been working on two AI-powered features to speed up and improve ticket triage automation processes.
Let's first recap the AI features we mentioned earlier that help streamline ticket management:
- Expert collaborator suggestion: This feature analyzes similar requests to identify the most experienced agent to add to the request to help with the resolution. It helps you connect tickets with the most qualified agents to achieve faster resolution times and fewer errors.
- Smart request escalation: This feature analyzes historical case data to identify potential SLA risks and suggest timely escalations. It will reduce the need for constant monitoring while improving overall service quality.
- Knowledge base article generation: The system can automatically create knowledge base articles from successfully resolved tickets, helping to build a comprehensive knowledge repository for future reference.
We should also explain the AI-powered response suggestions here. This powerful feature recommends agents take certain actions when working on a ticket and gives advice regarding the need to update priority, update category, or escalate the ticket to a major incident.
The AI looks through and analyzes all previous requests made on that instance and the actions that were taken on similar tickets in order to make the suggestion. This way, InvGate Service Management can take on a big fraction of the agents' workload, saving teams a lot of time.
After agents draft the response, they have to click on the magic wand icon, and select whether to improve, shorten, or expand the draft. The feature then comes up with a new text – which they can adjust freely before sending, saving time and energy.
Key takeaways
Ticket triage is an essential step of the Incident Management process. Investing time and effort into optimizing and automating this operation is crucial to building an efficient service desk. It shouldn't be utopic to plan ahead; it should be a basic requirement.
Setting up a clear categorization protocol is crucial to:
- Organize the workflow.
- Empower your agents with the information and tools they need, like a Ticketing System.
- Give them the right amount of autonomy to efficiently solve tickets and easily communicate with customers.
And you can easily establish your ticket triage process on InvGate Service Management. Request the 30-day free trial to see it for yourself today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Who should triage tickets?
The lowest level in the service desk should triage tickets. The lower the level, the simpler the issue, and the quicker and cheaper it should be to solve.
How do I triage a customer support ticket?
The basic steps for general ticket triage are:
- Search the knowledge base.
- Search past tickets with similar requests.
- Search the web, stack overflow, Reddit, google, bing, and other vendor sources.
- Ask a peer.
- Ask a team leader.
Can you triage a ticket over the phone?
Yes. The key is to create a standard procedure to ensure the team has all the information they need to operate. Agents should be able to ask questions and understand what's happening with the customer while also documenting work and information in real-time.
What does ticketing triage include?
Ticket triage includes incident logging, categorization, prioritization, assignment, task creation and management, SLA management and escalation, incident resolution, and closure.















