A ticket has its own lifecycle, and understanding each stage is crucial to providing top-notch customer support. One of the most critical help desk metrics is the Escalation Rate. This Key Performance Indicator (KPI) reflects the percentage of tickets that require the intervention of a higher-level support team.
Understanding how this KPI works can help identify gaps in the support process, improve team efficiency, and increase customer satisfaction. Tracking it is essential to measure the effectiveness of your solution.
If you’re looking to enhance your support processes, read on to find out:
- What Escalation Rate is and its relevance.
- How to calculate it accurately and efficiently.
- The pros and cons of measuring it.
- Best practices for reducing Escalation Rates.
Having the right tool to manage your service desk is crucial for tracking and analyzing metrics. InvGate Service Management is a powerful solution that helps organizations monitor the Escalation Rate, among other metrics, to optimize their support operations and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Want to know how to do it? Let’s dive in!

What is Escalation Rate?
Escalation Rate represents the percentage of support tickets that are passed on to a higher level of support. The escalation process in ticket management follows a hierarchical support structure with various tiers of team members that handle different customer issues based on their complexity and other key factors.
The Escalation Rate can be vertical, when the transfer is to a senior or more experienced agent, or horizontal, when the ticket is passed on to the appropriate department or additional team members are called upon for assistance or consultation.
The goal of escalating a ticket is to ensure it receives the necessary attention and expertise. By resolving the issues more quickly and efficiently, organizations aim to improve customer satisfaction. It also helps prevent tickets from falling through the cracks and ensures the appropriate resources are allocated to address the issue.
Why is it relevant to track Escalation Rate?
Tracking Escalation Rate is crucial for any business that provides IT support services. Here are some reasons why it's essential to monitor this KPI:
- Identify areas for improvement - Organizations can determine which areas of their support operations might need some adjustments. If the Escalation Rate is high, it could indicate that tier 1 agents need additional training or resources to handle customer issues more effectively.
- Improve customer satisfaction - Customers want their issues solved quickly and efficiently. If a support team can solve problems at the first point of contact, it can lead to higher customer satisfaction rates. On the other hand, if they are being passed around to different agents or departments, it can cause frustration and damage the customer relationship.
- Reduce operational costs - Escalations can be costly for businesses. A ticket escalated multiple times can result in longer resolution times and higher operating costs. Companies can streamline support operations and save money by reducing the Escalation Rate.
How to calculate Escalation Rate on InvGate Service Management
Calculating the Escalation Rate on InvGate Service Management is simple. Here are the steps you should follow:
- Navigate to the "Reports" section.
- Create a new request.
- Below the “Requests” metric, add “Assignments (Escalations).”
- Optionally you can add columns like “Ticket Type” (e.g., incidents, service requests, questions) and the priority that you want to include in the report (e.g., high, medium, low).
- Add a filter with the period you want to calculate the Escalation Rate (Creation and Solution Date).
The report will display the total number of tickets escalated during the selected period and the total number of tickets solved during the same time.
The formula used for calculating Escalation Rate is as follows:
Escalation rate = (Number of escalated tickets / Total number of support tickets) x 100%
The total number of escalated tickets must be divided by the total number of solved tickets, and the result is multiplied by 100 to get a percentage.
For example, if there were 50 escalated and 500 resolved tickets in the last month, the escalation rate would be (50 / 500) x 100 = 10%.
But, what makes up this formula? This is the information you need for calculating Escalation Rate:
- Period - This is the range you want to consider to calculate the Escalation Rate. It could be a year, a quarter, a month, or even days.
- The total number of support tickets - You need the total quantity of tickets received during the defined period. It should include all incoming support requests, regardless of whether they were escalated or not.
- The number of escalated tickets - How many of the support tickets received during the defined period were escalated to a higher level of support? For example, it could include escalated tickets from Level 1 to Level 2.
- The Escalation Rate formula - To obtain the percentage, divide the number of escalated tickets by the total number of tickets received during the defined period. Then, multiply the result by 100.
What is a good Escalation Rate?
There is no single industry benchmark for Escalation Rate as it can vary based on factors such as the organization's size, the complexity of the product/service being supported, the support model used, and the customers' expectations.
However, keeping the Escalation Rate below 10% of cases is advisable as a reference point. In addition, the focus should be not only on meeting industry benchmarks but also on continuously improving the support process to deliver the best possible customer experience.
Pros and cons of measuring ticket Escalation Rate
While there are many benefits to tracking the Escalation Rate, there are also some potential drawbacks to keep in mind.
Pros of measuring ticket Escalation Rate
- Predicting future support needs - By analyzing trends in the Escalation Rate over time, companies can anticipate when support demand will likely increase and make staffing and resource decisions accordingly.
- Identifying product or service issues - Escalations can sometimes shine a light on underlying issues with a product or service. Organizations can identify patterns that may indicate a need for product or service improvements by analyzing the reasons for escalation.
- Boosting team morale - Providing support agents with the training and resources to handle customer issues more effectively can improve team morale and create a more positive work environment.
Cons of measuring ticket Escalation Rate
- Lack of context - Measuring Escalation Rate alone may not provide enough context to identify the root cause of escalations. Organizations should analyze the reasons for escalations to identify patterns or trends. In addition, they should combine Escalation Rate with other metrics, such as Time to Resolution and Customer Satisfaction rate.
- Overemphasis on metrics - An excessive focus on metrics can lead to a "tick the box" mentality, where support agents focus more on meeting metrics than providing quality support. It is essential to balance metrics with other qualitative measures, such as customer feedback or agent performance reviews.
- Inability to capture all escalations - The Escalation Rate metric may not capture all escalations. For example, a customer may escalate an issue through a different channel or to a different department. It's crucial to have a well-defined escalation process with clear channels for customers to do so. This can include providing multiple contact options, such as email, phone, and chat, and ensuring that all channels are monitored regularly.
5 Escalation Rate metric best practices
To get the most out of this metric, organizations must adopt best practices that ensure they're measuring the right things, analyzing the information effectively, and making data-driven decisions that improve customer experiences. Here are five best practices to help businesses maximize this essential KPI.
1. Define what counts as an escalation
Before measuring Escalation Rate, clearly defining what constitutes an escalation is essential. Is it a transfer to a higher-level support agent? A referral to a different team? Make sure everyone on the support team is on the same page so you're measuring the same thing consistently.
2. Set goals and benchmarks
Once you know what counts as an escalation, set goals and benchmarks for what you want your Escalation Rate to be. It can be to help you track progress over and identify areas for improvement.
3. Segment your data
Analyzing this metric for your entire support team can be informative, but segmenting the data by factors like the product or customer type can be more beneficial. This can help you identify specific areas where the Escalation Rate is higher and focus your improvement efforts accordingly.
4. Dig deeper into the reasons for escalation
Only measuring this KPI won't give you a complete understanding of why customers are escalating tickets. It's essential to dig deeper into the reasons for escalation to identify patterns or common issues that may be driving the trend.
For example, if most escalations are related to a recent software update that caused technical issues for customers, addressing the software update can ultimately reduce the escalation rate.
5. Combine escalation rate with other metrics
Escalation Rate is just one piece of the puzzle when evaluating your support team's performance. Combine it with other metrics like First Contact Resolution and Time to Resolution to get a complete picture of your team's performance and identify areas for improvement.
How to reduce the Escalation Rate KPI
Support teams must handle escalations effectively to solve customer issues as quickly and efficiently as possible. Some practices to reduce Escalation Rate KPI include the following items.
1. Invest in training and development
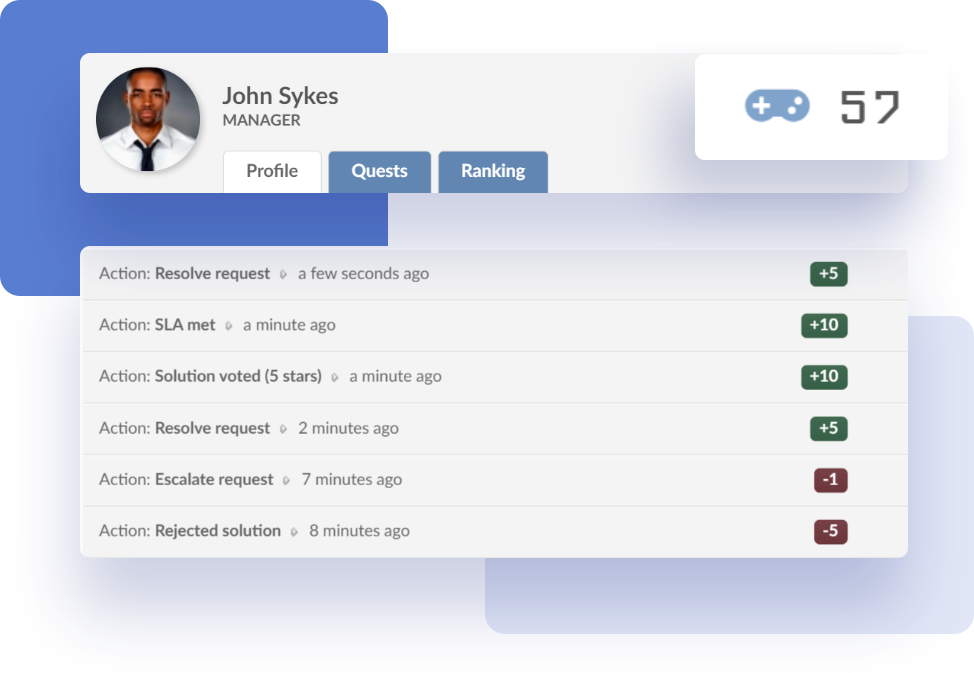
High Escalation Rates can often be attributed to a lack of expertise or experience from support agents. Investing in training and development programs can help agents build the skills and knowledge they need to handle a broader range of customer issues and reduce the need for escalations. Organizations can implement gamification as a way to make training more engaging and interactive. For example, offering badges and other game-like elements can incentivize agents to learn and apply new skills.
2. Improve communication and collaboration
Sometimes, escalations occur because support agents don't have access to the information or resources they need to solve an issue. Improving communication and collaboration across your support team can help agents access everything they need more quickly, reducing the need for escalations.
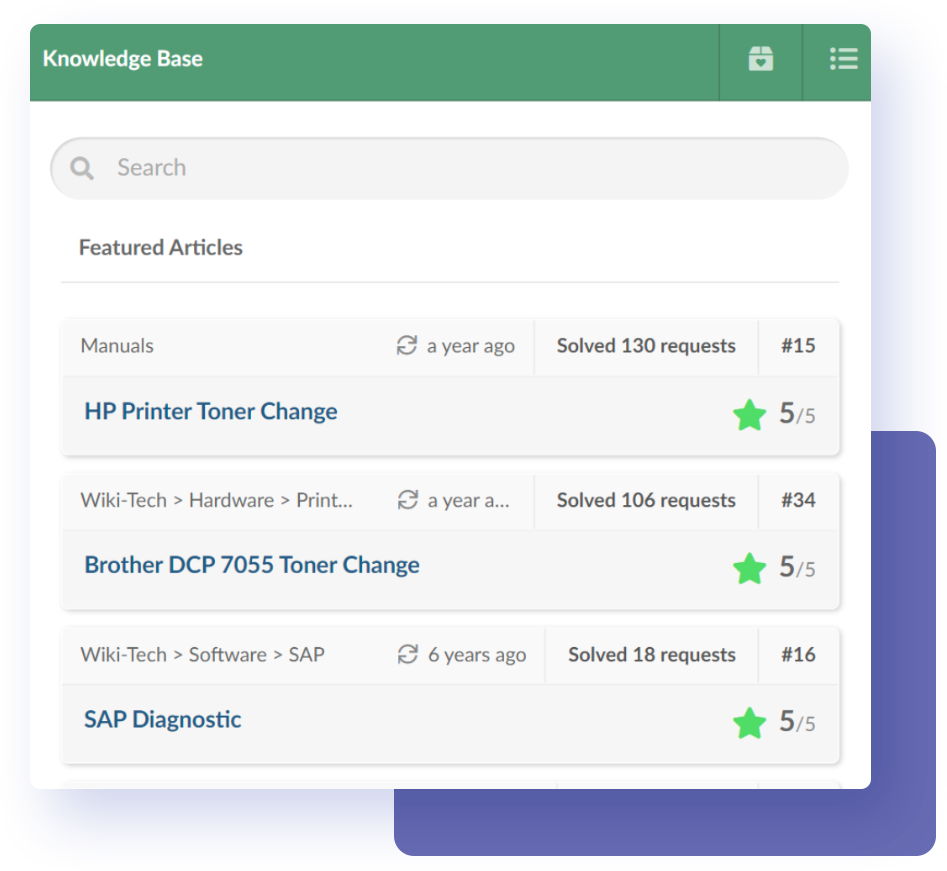
A good practice to achieve this is creating an internal knowledge base so that more experienced and high-level agents share their knowledge with low-tier agents and contribute to avoiding escalations.
3. Empower agents with the right tools and technology
Providing help desk agents with a user-friendly service desk that includes all the features mentioned above (a knowledge base, straightforward ticket escalation, gamification, etc.) will help them work more efficiently and effectively, reducing the need for escalations.
4. Identify and address underlying product or service issues
Escalations sometimes occur because of underlying product or service issues that companies must address. Analyzing the reasons for escalation can help you identify these issues and take steps to manage them, reducing the need for escalations in the future.
5. Listen to customer feedback and act on it
Listening to customer feedback can be an effective way to identify areas where support operations can be improved. Actively soliciting it from customers and taking action to address their concerns can help reduce the need for escalations and enhance customer satisfaction.
The bottom line
Escalation Rate is a crucial metric for organizations that provide customer support services. It helps identify areas that might need adjustments, improves customer satisfaction, and reduces operational costs.
While there are potential drawbacks to measuring Escalation Rate, adopting best practices can help organizations get the most out of this metric. These best practices include:
- Defining what counts as an escalation.
- Setting goals and benchmarks.
- Segmenting data.
- Digging deeper into the reasons for escalation.
- Combining Escalation Rate with other metrics.
Start calculating your IT service desk Escalation Rate today with InvGate Service Management. Ask for a 30-day free trial and take it out for a spin!















