An internal knowledge base puts the answers, processes, and expertise that your employees need right at their fingertips.Employees spend significant time searching for internal information, impacting productivity. According to a study by McKinsey, workers can spend nearly 20% of their time searching for information.
Think about it - how often have you been stuck waiting for a coworker to get back from vacation or a meeting just because they're the only one who knows how to solve a particular problem? An internal knowledge base prevents those bottlenecks.
In this article, we'll explore the key benefits of building internal Knowledge Management, and provide practical guidance on how to implement a strategy that empowers your team and strengthens your organization's operations as a whole.

What is an internal knowledge base?
As we just said, a knowledge base is basically a platform packed with information – usually in the form of knowledge base articles – oriented to answer questions, provide instructions, or offer tips and tricks. It can include images, videos, or any kind of file that will help the reader solve an issue on their own – and thus are an essential part of self-service portals.
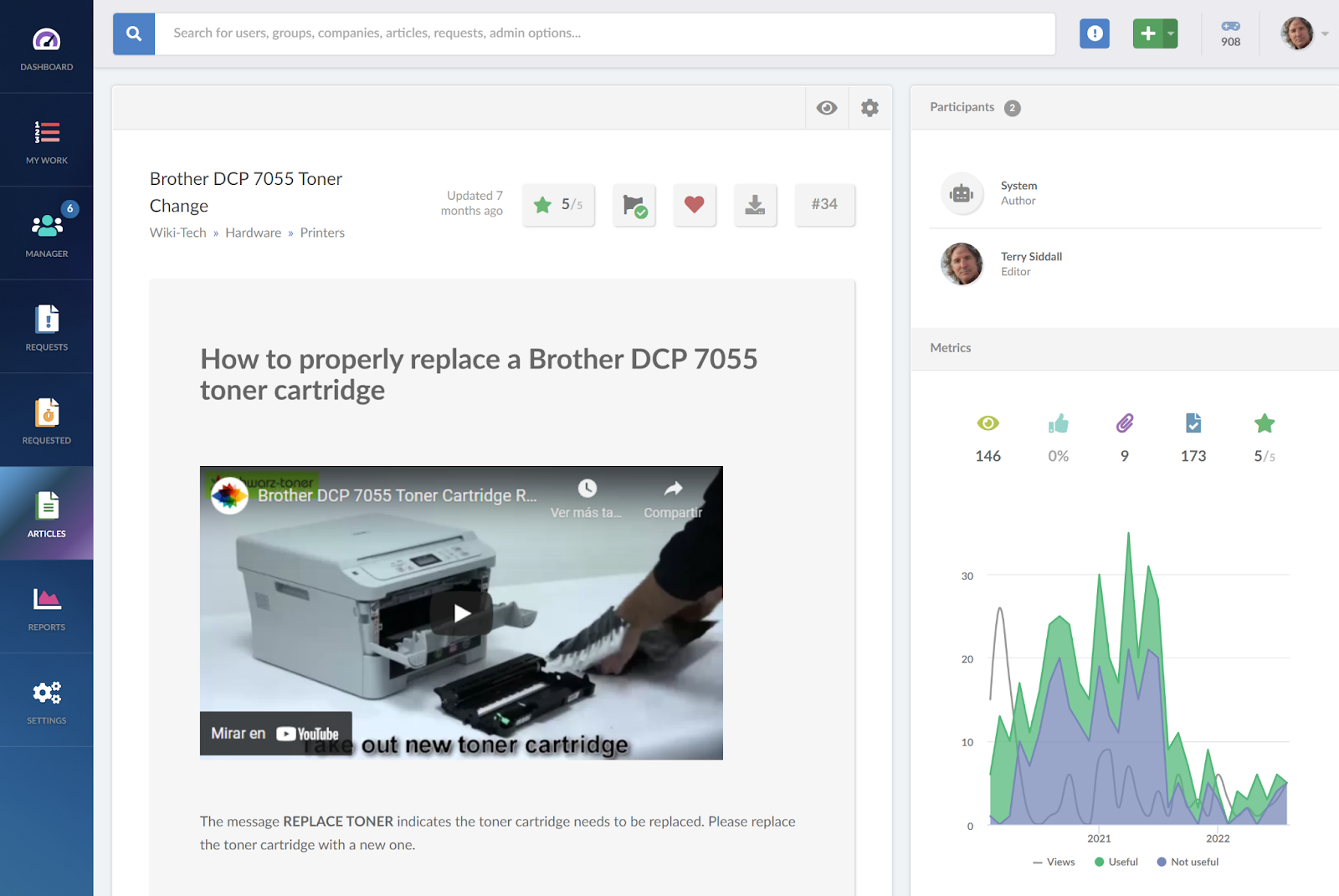
Until now, the description overlaps with that of an external knowledge base, which is available to end-users (customers or the general public). However, an internal knowledge base is accessible only to the employees, teams, and stakeholders within an organization.
The key distinguishing factors of an internal knowledge base are:
- Audience: The primary audience is the internal personnel of the organization rather than external users. This could include anyone from leadership to front-line staff.
- Scope: The content covers a wide range of topics and information that is relevant and specific to the internal workings, processes, and needs of the organization. This goes beyond just service or support-related material.
- Purpose: The main goals are to capture institutional knowledge, enable knowledge sharing, improve productivity, streamline processes, and ultimately enhance the organization's overall operations and efficiency.
In summary, an internal knowledge base (also called corporate, enterprise, or internal company knowledge base) is simply a way for teams to find what they need when they need it, without having to track down specific people or dig through old emails and documents.
When done right, it becomes a natural part of how your organization grows and is the central place for internal knowledge sharing.

4 benefits of having a corporate knowledge base
Though you might be wondering if it’s worth the effort, let us tell you that there are several advantages of using an internal knowledge base to gather all your company information:
- Consistency: It assures that tasks are resolved in the same way and according to the company’s best practices, regardless of the assigned agent.
- Time-saving: By centralizing the information, employees don’t need to waste time figuring out where to find the information they need or asking around.
- Availability: There are no problems with getting the information; it’s available to every agent, anywhere, at any time, and it doesn’t depend on the memory or goodwill of another team member.
- Training: An internal knowledge base can be handy while training juniors or new employees, as well as releasing training materials for everyone on new processes or best practices.
|
|
"Knowledge should be a quick question and answer. Somebody asked the question; here is the answer. And it should be easy to consume. I understand when you get into these more technical things, there are a lot of steps. But it should still be easy to consume. People don’t pick up technical manuals and read them. I mean, I’m sure a lot of people do that. But, when they are on a call with a customer, they can’t go back to their training, they don’t have time to read a full piece." Liz Bunger |
The knowledge base’s relevance for Enterprise Service Management
Integrating a knowledge base (KB) into Enterprise Service Management (ESM) is a great way of streamlining processes and driving digital transformation.
Here’s how it benefits organizations:
- Cross-departmental collaboration: When the KB is integrated into the ESM platform, all teams, from IT to HR to customer service, can access and share the same resources. This way, different departments collaborate easily, and you avoid the duplication of effort. For example, HR staff can resolve employee inquiries using the same knowledge base that IT teams use to troubleshoot issues.
- Self-service and efficiency: A KB within the ESM system allows employees and end users to solve issues independently. They can quickly find solutions across various departments, reducing the need to create support tickets and boosting employee productivity.
- Automation and consistency: With a unified KB in the ESM platform, the system can automatically suggest relevant knowledge articles when users create tickets. Agents working on tickets also have immediate access to these articles, ensuring consistency in responses and speeding up issue resolution. Workflow automation reduces errors and ensures that support staff are always working with the most up-to-date information.
In short, a knowledge base integrated with an ESM platform accelerates digital transformation by supporting automated processes, reducing manual work, and enabling quicker decision-making. It provides a solid foundation for remote work and agile practices and gives your organization an edge when it comes to adapting quickly to changes.

Building an internal knowledge base
Here’s a simple, practical approach to help you create an internal knowledge base:
- Step 1 - Identify content needs
Start by gathering common questions and challenges your team faces. Talk to support staff and check frequent service requests—these often highlight the best topics to cover in your KB. - Step 2 - Write your first articles
For top-requested topics, create articles that are clear and to the point. Use step-by-step instructions, and don’t hesitate to include visuals like screenshots or diagrams to help users understand. - Step 3 - Review and approve
Before publishing, set up a review step for accuracy and relevance. A dedicated team should manage the internal knowledge base for regular updates. You can also define someone with experience as a knowledge manager to check each article so it’s as helpful as possible. - Step 4 - Organize everything
Structure content into categories like “IT Support,” “HR Resources,” and “Onboarding” so users can find what they need easily. A clear layout makes the KB more user-friendly from the start.
If you’re using InvGate Service Management, you can automate this process with a Knowledge Management workflow. Employees can suggest topics, which then go through a review and approval process to ensure everything’s accurate and well-organized.
Once your KB is live, keep it relevant by adding these two steps:
- Get user feedback: Enable ratings or comments so users can suggest improvements, keeping the content tuned to their needs.
- Calendarize: Establish a project calendar to help plan content creation and implementation.
- Update regularly: Review content periodically to make sure it reflects the latest processes and systems, so your KB stays helpful as things change.
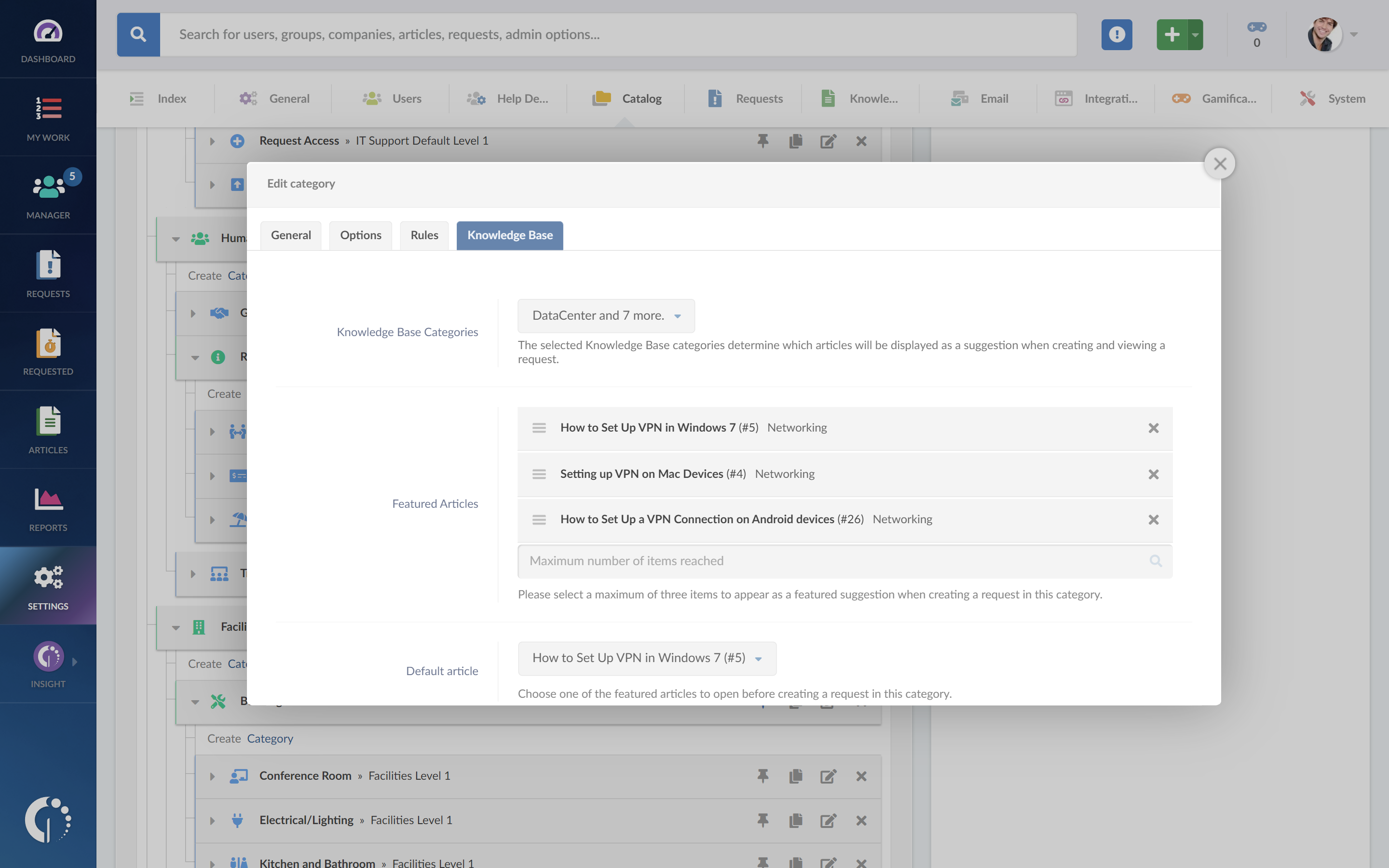
Content examples for an internal knowledge base
Your internal knowledge base can include a wide variety of resources that help your team work more efficiently. Here are some popular content types that add value to organizations:
- How-to guides and processes: Step-by-step instructions for common tasks, like setting up new employee accounts or handling customer escalations. This includes standard operating procedures (SOPs).
- Troubleshooting guides: Solutions to recurring technical issues, including workarounds and fixes that have worked in the past.
- System configurations: Details about critical settings, network architecture, and integration setups that teams often need to reference.
- Project templates: Standard formats for project plans, reports, and other frequently used documents.
- Best practices: Documented approaches that have proven successful, helping teams maintain consistency and quality.
- Department-specific procedures: Essential workflows and guidelines unique to each team.
- Change Management records: Documentation of system updates, policy changes, and their impacts.
The key is to focus on content that your team frequently needs, or that preserves critical institutional knowledge. This makes your internal knowledge base a valuable resource that teams actually want to use.
Don’t forget that, if you need some advice with the writing, you can check out these tips from marketers to write compelling articles (they write for a living, after all!).

Enterprise knowledge base software
Knowledge base software is a tool designed to help organizations create, organize, and share information efficiently. It’s more than a simple document storage system; it provides searchable access to guides, FAQs, and policies, all organized in a way that makes finding answers easy for teams across the company.
Specialized knowledge base software like Helpjuice comes with its own set of tools and flexibility, and there are many options available, from basic document storage to fully customizable knowledge management systems. However, using standalone software means managing it separately from other platforms, which can complicate the flow of information and require additional integrations. The result is often more time spent switching between tools or building custom links to keep everything connected.
For enterprise environments, having an internal knowledge base solution directly within your service desk can be a more practical option. When the knowledge base is integrated, agents can document solutions straight from tickets, and users can often find answers on their own — reducing the need for new support requests.
What to look for in enterprise knowledge base software:
- Easy-to-use interface: The platform should make it simple to create, organize, and find information, with clear navigation and mobile access.
- Advanced search: Users should be able to find answers quickly, even if they don’t know exact terms.
- Content management tools: Features like categorization and tagging make it easy to keep content organized and up-to-date.
So, while dedicated knowledge base software exists, having it built into your service desk tool can offer similar benefits without extra cost. For example, InvGate Service Management includes knowledge base features that:
- Show relevant articles to users as they type
- Help agents find solutions faster
- Create new articles from resolved tickets with AI
- Gather user feedback through ratings
- Automate common tasks with templates
All of this is done with an integrated approach that helps your teams manage knowledge effectively while avoiding switching between platforms.

Internal knowledge base best practices
A well-organized knowledge base can transform how your team works. Here's how to build and maintain one that your employees will actually use:
# Keep content clear and scannable
- Write in simple language without jargon
- Break down complex processes into steps
- Use headings, bullet points, and short paragraphs
- Include relevant screenshots or diagrams
# Make information easy to find
- Create a logical structure with clear categories
- Use consistent naming conventions
- Add relevant tags to improve searchability
- Link related articles to help users dig deeper
# Keep your knowledge base alive
- Assign owners to maintain different sections
- Schedule regular content reviews
- Remove or update outdated information
- Track which articles are most used
# Encourage team participation
- Make it easy for experts to share their knowledge
- Allow feedback and suggestions for improvements
- Recognize employees who contribute valuable content
- Create templates to maintain consistency
- Assign roles within the knowledge base to streamline content management
Remember: The most valuable knowledge base is one that grows with your organization and reflects how your team actually works. Focus on making it practical and easy to maintain rather than perfect from day one. And, with that in mind, let’s see how you can leverage AI.

How AI enhances your knowledge base
AI can be the perfect ally to make more out of your Knowledge Management best practices - it can help you capture and share knowledge naturally, right where the work happens.
Take resolved tickets, for instance. Instead of letting valuable solutions sit in closed tickets, AI can automatically turn them into knowledge base articles.
This means that every time your support team solves a complex issue, knowledge is preserved and ready to help others. InvGate Service Management's AI-powered Article Generation does exactly this - it learns from your team's real problem-solving work and creates clear, structured articles automatically.
AI also helps deliver knowledge where your team already works. InvGate’s Virtual Agent for Microsoft Teams allows employees to search and access knowledge base articles. No need to switch apps or remember another login - the answers are right there in a chat, making it more likely that people will actually use the knowledge base.
Leveraging AI in these ways, your knowledge base becomes more:
- Dynamic - Growing naturally from actual support work
- Accessible - Available where employees already spend their time
- Efficient - Reducing duplicate work by reusing solutions
- Practical - Based on real issues and proven solutions
The result? A knowledge base that truly captures your team's expertise and makes it easy to share valuable information across the organization.

Key takeaways
We've covered a lot about internal knowledge bases in this article - from what they are to how to build one that your team will actually use. I hope you've picked up some useful ideas to help your organization capture and share knowledge more effectively.
The truth is, managing organizational knowledge doesn't have to be complicated. Start small, focus on what your team actually needs, and let the system grow naturally. With the right tools and practices in place, you'll find that knowledge sharing becomes part of your daily workflow rather than another task on your to-do list.
Remember that perfect is the enemy of good when it comes to knowledge bases. What matters most is getting started and building momentum.
And with InvGate Service Management, all you need to focus on is the content. Once that’s settled, you can have it published in a matter of seconds! Request a 30-day free trial today, and get ready to make the difference on your (and your team's) day-to-day job.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to structure an internal knowledge base?
Sort your content into clear categories that match how your team thinks about and looks for information. Use consistent templates, add relevant tags, and make sure your search function works well.
What is an Enterprise Knowledge Management system?
It's a platform that helps large organizations store, organize, and share internal information. This includes documentation, processes, best practices, and institutional knowledge.
What is an organizational knowledge base?
An organizational knowledge base is a central repository where companies store and share important information. This can include how-to guides, policies, procedures, troubleshooting steps, and best practices.














.jpg?upsize=true&upscale=true&width=780&height=205&name=how-to-create-a-service-level-agreement%20(1).jpg)
