Endpoint Management is so inherent to IT that it is canon in this industry, especially now that remote work is the new normal. Implementing a robust endpoint management system is non-negotiable for organizations relying on digital devices.
These devices are connected to the corporate network and can access its resources, so the goal is to ensure that they are secure, compliant with company policies, and operating efficiently.
Here, we've put together a comprehensive Endpoint Management guide to help you implement the practice. Keep on reading to learn more about its key components and processes, including security measures, policy enforcement and what are the best software solutions available for its implementation.
Let’s start!
Table of contents
- What is Endpoint Management?
- Why do you need Endpoint Management?
- Endpoint Management vs. UEM vs. EMM vs. MDM
- Benefits of using Endpoint Management tools
- How does Endpoint Management work?
- 6 Endpoint Management software options
What is Endpoint Management?
In short, an endpoint is whatever device that is connected to a network. So, Endpoint Management incorporates the strategies and tools deployed by IT teams to oversee, track, and safeguard these devices.
This includes computers, laptops, smartphones, and any smart device considered to be in the category of the Internet of Things (IoT) like a smartphone or sensor.
The term "endpoint" illustrates that there is a point where communication behind and/or ends within such a network. They are the devices through which users access and interact with the network.
Some of the tasks that are necessary for Endpoint Management in order to streamline and secure the IT environment can be:
- Deploying, updating, and troubleshooting software and hardware.
- Making sure that all endpoints are updated with the latest software updates.
- Ensuring that every device complies with their organization's standards.
- Managing the access rights of devices to network resources and data.
- Configuring devices according to the company’s needs.
Endpoint Management and Endpoint Security Management
A crucial branch of Endpoint Management that stands out is Endpoint Security Management. One thing is to make sure that the overall administration and control of devices within a network is running smoothly, and another thing is to implement security measures to protect the devices and the network from cyberattacks.
This includes deploying antivirus software, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security protocols to ensure that endpoints are not only managed efficiently but are also secure from potential threats.
Of course, Endpoint Management and Endpoint Security Management are deeply intertwined, as the first one lays the foundation for the second one to be robust.
Why do you need Endpoint Management?
Ensuring effective Endpoint Management is particularly important today, everyone relies on digital devices to make things happen in any business venture. And now that most new products are part of the Internet of Things, your company’s network and IT infrastructure can only keep expanding.
Also, you need a team to take care of company-owned hardware and also of devices brought in by employees, known as Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies.
Companies should care about Endpoint Management because it’s indispensable for their IT security, Compliance Management, budgeting efforts, and reputation in a digital-first world.
Well implemented, all devices adhere to security policies, receive timely updates, and are monitored for threats, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches.
And, on the other hand, unmanaged endpoints lead to increased support costs, wasted resources, and unanticipated downtime.
In return, you’ll get to meet the expectations of both customers and employees for seamless, secure access to services and information, while freeing up your IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Endpoint Management vs. UEM vs. EMM vs. MDM
In general terms, Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) is the most comprehensive, covering a wide range of devices and platforms with a single management interface.
Then, Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) narrows the focus to mobile devices and includes management of applications and content, while Mobile Device Management (MDM) is primarily concerned with the management and security of mobile devices themselves.
But let’s take a closer look at each practice and its scope.
Unified Endpoint Management (UEM)
Let’s start with our favorite one. UEM is an all-encompassing approach to securing and controlling desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, and tablets in a connected, cohesive manner from a single console.
UEM solutions go beyond traditional Device Management to include the management and configuration of operating systems, applications, and data across multiple device types.
This practice stands out by offering a broader and more integrated solution compared to other management frameworks. If you implement this approach your IT team will provide a single management interface for all endpoints.
Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM)
EMM is a set of services and technologies designed to secure corporate data on employees' mobile devices. It encompasses a range of processes and technologies such as Mobile Device Management, Mobile Application Management, Mobile Content Management, and Identity and Access Management.
EMM solutions focus on managing and securing mobile devices, applications, and content. The practice specifically targets the challenges and needs of mobile computing and, for this reason, EMM is often seen as a subset of UEM.

Mobile Device Management (MDM)
MDM is the process of monitoring, managing, and securing mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops that are deployed across multiple mobile service providers and across multiple mobile operating systems being used in the organization. MDM is a foundational component of both EMM and UEM solutions.
As you can tell, it’s the most specific and narrowly focused among these technologies. Also, it’s typically concerned with device-level management tasks such as device enrollment, provisioning, and remote wipe capabilities.

8 benefits of using Endpoint Management tools
At this point, it’s clear that Endpoint Management tools and integrations lead to improved productivity and user experience, as well as cost savings.
These are the main benefits for your organization's infrastructure.
- Stronger security: Endpoint management tools provide comprehensive security features such as antivirus, anti-malware, firewall management, and Patch Management, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
- Centralized Management: They enable the centralized management of all endpoints, making it easier for IT administrators to deploy, update, and manage software and policies across the entire organization, regardless of the location or type of devices.
- Automated updates: These tools can automate the process of updating software and applying security patches so all devices are running the latest versions of software and operating systems.
- Improved compliance: They enforce security policies, manage encryption settings, and keep detailed logs for IT audit purposes to comply with industry regulations and standards.
- Streamlined Asset Management: The tool can provide visibility into all devices connected to the network, allowing organizations to track and manage their hardware and software assets effectively.
- Habilitated remote troubleshooting and support: These tools enable your IT staff to remotely diagnose and resolve issues on any endpoint, reducing downtime and improving productivity.
- Stronger data protection: Endpoint Management tools can include DLP features to prevent sensitive data from being lost, leaked, or stolen.
- Network Access Control (NAC): They can enforce network access policies, restricting access to the network based on device compliance with security policies, to prevent non-compliant devices from harming the network.
How does Endpoint Management work?
The Endpoint Management process typically involves the following steps so all devices and networks operate efficiently.
1. The first step is to identify and catalog all endpoints connected to the network, and incorporate them into the IT asset inventory. This involves collecting information about the hardware, installed software, and operating systems of each device.
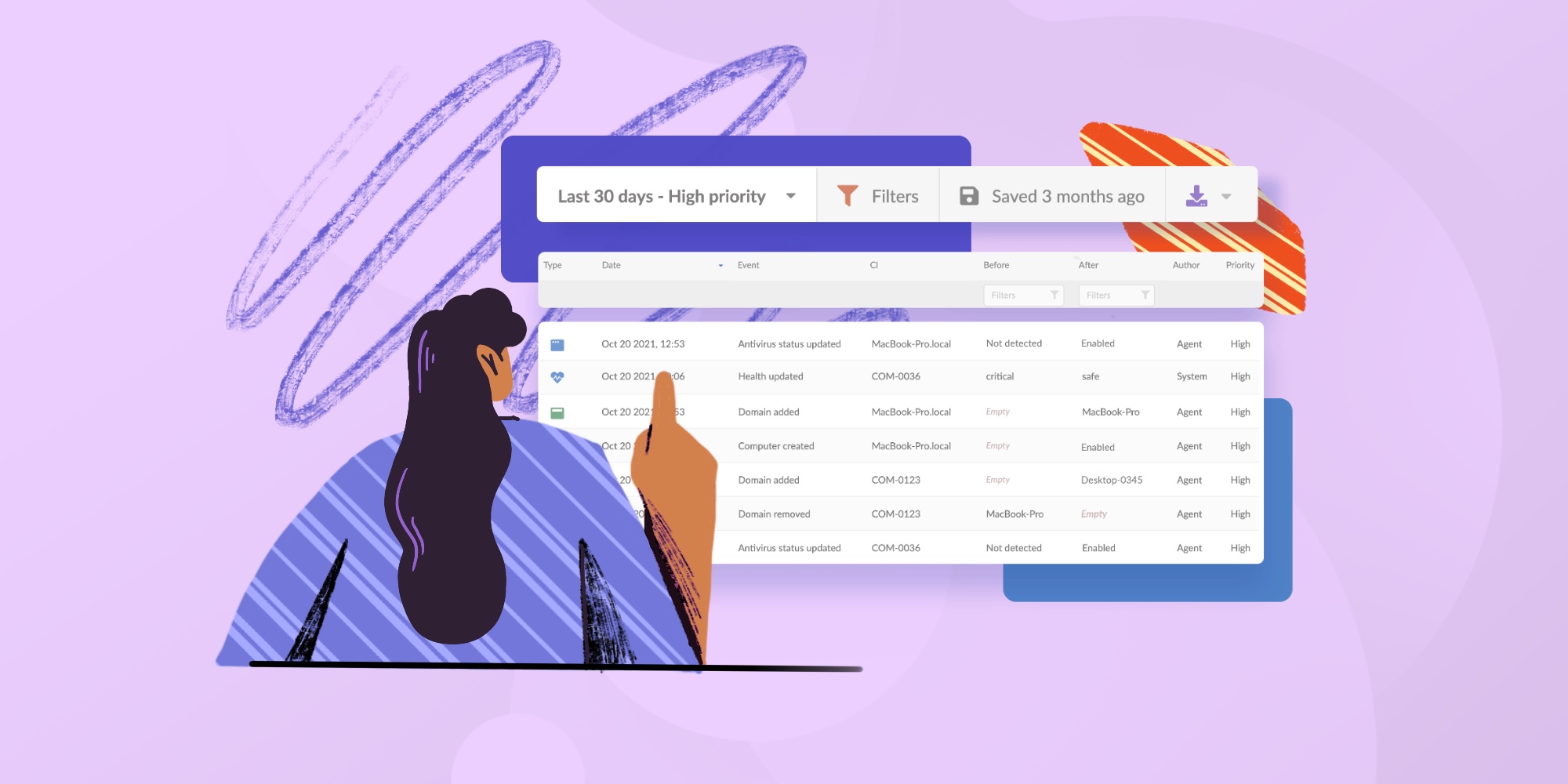
2. Then, you’ll want to install software and configure devices according to company standards remotely. We are talking about security software, setting up email accounts, and configuring network settings.
3. Administrators set and enforce policies to manage and secure devices, such as password policies, data encryption, and firewall settings.
In the meantime, the system will automatically apply software updates and security patches.
4. All device users will benefit from security features, such as antivirus and anti-malware protection, to respond to threats.
5. On a daily basis, your IT team is going to monitor endpoints for security threats, performance issues, and compliance with policies.
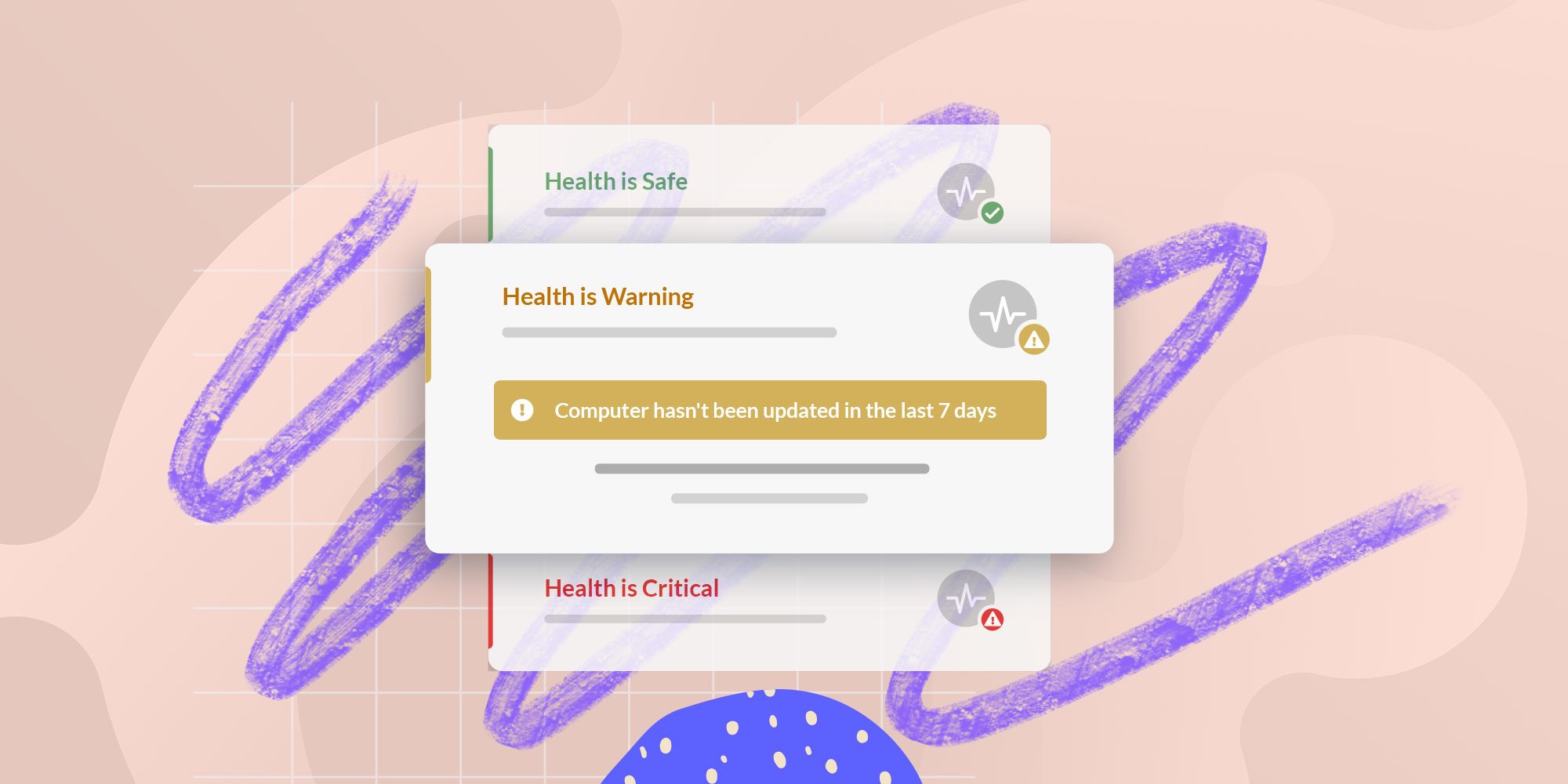
If necessary your IT staff can remotely access devices to diagnose and resolve issues that showed up in their reports.
Endpoint Management policies
Endpoint Management policies are the rules and configurations applied to endpoints to ensure they are used securely and efficiently.
Key policies include:
- Privilege use policy outlines the guidelines and requirements for assigning and using elevated access rights. Those users make significant changes to system configurations, access sensitive data, or perform administrative tasks that are beyond the capabilities of a standard user account.
- Password policy enforces password complexity, expiration, and history requirements to ensure strong authentication practices.
- Encryption policy requires that data stored on devices is encrypted, protecting sensitive information in case of theft or loss.
- Software installation policy controls which applications can be installed on devices to prevent the installation of unauthorized or malicious software.
- Firewall and security settings protect devices from unauthorized access and set up antivirus and anti-malware protections.
- Patch management policy ensures that devices are regularly updated with the latest security patches and software updates.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policy controls how sensitive data is accessed, used, and transferred to prevent data breaches.
- Remote wipe and lock policy that allows your IT team to remotely lock a device or wipe its data in case it is lost or stolen.
6 Endpoint Management options
Endpoint Management software is a centralized platform designed to monitor, manage, and secure devices such as computers, smartphones, and tablets within a network infrastructure.
These are some of the top solutions in the market:
- Microsoft Intune: A part of Microsoft's Enterprise Mobility + Security (EMS) suite, Intune is a cloud-based service focused on mobile device management (MDM) and Mobile Application Management (MAM). It allows IT administrators to manage devices and applications across various platforms, ensuring security and compliance.
- VMware Workspace ONE: Powered by AirWatch technology, Workspace ONE is a comprehensive enterprise platform that provides unified endpoint management (UEM). Workspace ONE's integration with VMware's virtualization technologies makes it a robust solution for managing both physical and virtual endpoints.
- InvGate Asset Management: With robust IT Asset Management capabilities, InvGate Asset Management offers a powerful solution for organizations looking to gain visibility into their IT infrastructure. Its integration with Intune and VMWare enhances its Endpoint Management capabilities, allowing for a more comprehensive view of both hardware and software assets across the organization.
- ManageEngine Endpoint Central: An Endpoint Management solution that helps manage servers, laptops, desktops, smartphones, and tablets from a central location. It automates regular endpoint management routines like installing patches, deploying software, and managing assets and software licenses.
- IBM MaaS360 with Watson: An UEM solution that utilizes artificial intelligence to manage devices and applications. It offers visibility and control over iOS, macOS, Android, and Windows devices, making it a versatile choice for organizations with a diverse device ecosystem.
- Cisco Meraki Systems Manager: Cisco's cloud-based Endpoint Management solution provides centralized control over all of an organization's devices. Its features include software and device inventory, remote troubleshooting, and application management, all accessible through a user-friendly dashboard.
If you are ready to decide between Endpoint Management solutions, our curated list can help:

Key takeaways
A company without an Endpoint Management system in place is going to quickly fall short; it is a critical aspect of your IT and cybersecurity strategy.
Its implementation requires a combination of robust technology, well-defined policies, and user education to address the complex landscape of today’s cybersecurity challenges. But in the end, it will make your organization stronger, protected, and more efficient.
Each of the endpoint management software options we mentioned offers a unique set of features designed to meet the specific needs of any company. The integration of InvGate Asset Management with Intune and VMware particularly highlights the trend towards solutions that offer greater interoperability and flexibility, enabling IT departments to manage a diverse and complex array of devices more effectively.
Want to see for yourself? You can book a 30 day free trial and explore in your own terms!















