There are plenty of reasons why it’s a smart move to have a cloud CMDB (Configuration Management Database). As companies embrace the cloud for its flexibility, scalability, and operational benefits, it’s no surprise that many are either purchasing cloud-based services or accelerating cloud migration strategy.
According to the Cloud Computing Study 2024 by FOUNDRY, 63% of IT decision-makers report having accelerated their cloud migration over the past 12 months. Additionally, nearly three-quarters (70%) of organizations are now defaulting to cloud-based solutions when upgrading or purchasing new technology.
A cloud CMDB, then, isn’t just a trend—it’s a strategic necessity. But exactly why? In this blog post, we’ll explore the top reasons to embrace a cloud environment and uncover the many benefits of a cloud CMDB. Let’s get started!
What is a cloud CMDB?
A CMDB cloud, more commonly referred to as a cloud-based CMDB, is a system for managing and tracking all Configuration Items (CIs) in an organization, but hosted in the cloud rather than on-premises. As any other CMDB, it serves as a central repository that stores information about the IT environment's hardware, software, networks, and their relationships and dependencies.
So, what exactly is the difference? Well, there are many differences between a cloud CMDB and a traditional CMDB. We summarized them in the following subtitles.
#1: Accessibility and CMDB Cloud Management
Cloud-based CMDBs revolutionize accessibility and CMDB Cloud Management by enabling remote teams to collaborate effectively from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility is particularly beneficial for organizations with distributed or hybrid teams, as it ensures everyone can view and update configuration data in real time, regardless of location.
By centralizing oversight, cloud CMDBs enhance operational efficiency and allow IT teams to stay coordinated even across multiple time zones. Unlike on-premises solutions, which often require employees to be on-site or use VPNs for secure access, cloud CMDBs eliminate such limitations, streamlining workflows and reducing delays. This modern approach to CMDB Cloud Management ensures your team is always aligned, proactive, and ready to tackle potential issues.
#2: Maintenance and updates
One of the standout advantages of a cloud-based CMDB is automated maintenance. With cloud hosting, updates and security patches are handled by the provider (the company or a vendor), ensuring the system is always current with minimal manual effort. This hands-off approach frees up IT resources and allows the team to focus on higher-priority tasks.
An on-premises CMDB, however, requires regular manual maintenance, including updates, security patches, and potential hardware upgrades. These tasks can be resource-intensive, requiring dedicated personnel and infrastructure, which may increase the total cost of ownership.
#3: Cost and Resource Management
Cloud-based CMDBs typically operate on a subscription or usage-based pricing model, reducing upfront costs and enabling predictable budgeting. This pricing structure eliminates the need for costly physical infrastructure, as everything is managed by the cloud provider, freeing up resources for other strategic projects.
An on-premises CMDB requires significant initial investments in hardware, software, and infrastructure. Additionally, it demands ongoing costs for maintenance, updates, and potential hardware replacements. These costs can add up over time, especially if the organization has budget constraints or lacks dedicated IT personnel.
#3: Scalability and flexibility
A cloud-based CMDB offers seamless scalability. It can adjust resources dynamically to accommodate growing data or increased usage, making it ideal for organizations that experience fluctuations in demand. This flexibility allows businesses to pay only for what they use, keeping costs predictable and optimized.
On-premises CMDBs, on the other hand, face physical limitations when scaling. Adding more capacity often requires purchasing additional hardware, which can be costly and time-consuming. This lack of flexibility can be challenging for organizations needing rapid expansion or dealing with fluctuating workloads.
#5: Security and compliance
Cloud-based CMDB providers often incorporate advanced security features, including data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular audits, to protect sensitive data. Providers also stay compliant with industry standards, such as GDPR or HIPAA, which can ease the burden of regulatory compliance for organizations.
In contrast, security for an on-premises CMDB is entirely the responsibility of the organization. While this setup allows for custom security configurations, it can also be challenging to maintain, especially if the organization lacks a dedicated security team. Compliance with regulations may also require additional investment in specialized resources and tools.
#6: Disaster recovery and business continuity
With a cloud-based CMDB, disaster recovery and redundancy are generally built into the service. Data is backed up across multiple locations, ensuring quick recovery in case of outages or other disruptions, which minimizes downtime and supports business continuity.
An on-premises CMDB, however, relies on the organization’s own disaster recovery plan. This approach can be costly, requiring additional infrastructure and resources to implement effective backup and recovery protocols. If disaster recovery systems aren’t in place, data loss and extended downtime can pose significant risks to business operations.
Why use a CMDB for cloud assets?
We already know that a CMDB is traditionally used to CIs such as servers, network devices, and software applications. However, modern cloud-based CMDBs have evolved to also handle cloud-specific assets, bridging the gap between traditional IT environments and virtualized or cloud infrastructures.
Managing cloud assets in a CMDB ensures that your organization has full visibility and control over resources like virtual machines, containers, storage instances, and SaaS applications. This capability allows IT teams to treat these cloud assets as part of the broader IT ecosystem, maintaining consistent documentation of their relationships, dependencies, and configurations.
By integrating cloud assets into a CMDB, organizations can track them alongside traditional CIs, providing a unified view of the IT landscape. This ensures optimized resource allocation, enhanced compliance, and proactive decision-making. Far from being limited to on-premises IT components, today’s CMDBs are indispensable for managing cloud resources as part of a modern IT strategy.

5cloud-based CMDB software to kick off Configuration Management
Configuration Management can be daunting, but finding the right tools can make all the difference. Today, there are many dedicated CMDB tools specifically designed to help organizations manage their IT assets and maintain an up-to-date record of all CIs and their dependencies. On top of this, a growing number of IT Asset Management (ITAM) platforms now offer CMDB functionality as part of their feature set, combining IT Asset Management with configuration insights.
In between these options, a new generation of cloud-based CMDB tools is emerging, offering all the advantages of accessibility, scalability, and minimal maintenance that come with the cloud. These cloud CMDB solutions are great choices to kick off your Configuration Management journey without the hassle of traditional on-premises setup. Below, we explore five of the top cloud-based CMDB tools that offer powerful, user-friendly features to get you started.
#1: Device42
Device42 was known for its industry-leading IT infrastructure discovery and mapping capabilities. It was acquired by Freshworks and since then Device42's functionalities have been integrated into Freshworks' suite of IT Service Management and IT Asset Management solutions.
Device42 main features:
- Automated discovery: Continuously scans the network to identify and document all connected devices, applications, and services, ensuring the CMDB remains current without manual intervention.
- Dependency mapping: Visualizes relationships and dependencies between Configuration Items (CIs), aiding in impact analysis and informed decision-making.
- Visualization tools: Provides customizable visual representations of data centers, including room layouts, rack diagrams, and heat maps, facilitating efficient resource management.
- Integration capabilities: Offers RESTful APIs and pre-built integrations with various IT Service Management (ITSM) tools, such as Jira, ServiceNow, and Zendesk, enabling seamless data exchange and process automation.
- Data enrichment with EnrichAI: Utilizes artificial intelligence to standardize and enhance discovered CI data, addressing inconsistencies and providing actionable insights for improved IT operations.
- Pre-configured CMDB structure: Comes with a predefined set of CIs and relationships, allowing for quick deployment while offering flexibility for customization to meet specific organizational needs.
#2: ServiceNow - IT Service Management
 ServiceNow IT Service Management is (obviously) a ITSM tool. But with CMDB capabilities. Ideal for large organizations, ServiceNow’s CMDB provides a detailed view of CIs across the IT landscape, integrating seamlessly with the broader ServiceNow platform.
ServiceNow IT Service Management is (obviously) a ITSM tool. But with CMDB capabilities. Ideal for large organizations, ServiceNow’s CMDB provides a detailed view of CIs across the IT landscape, integrating seamlessly with the broader ServiceNow platform.
ServiceNow IT Service Management main features:
- Incident Management: Facilitates the efficient handling of IT incidents to restore normal service operations promptly.
- Problem Management: Identifies and addresses the root causes of incidents to prevent recurrence and minimize impact.
- Change Management: Manages IT changes with minimal risk and disruption, ensuring that modifications are systematically evaluated and implemented.
- Configuration Management: Maintains information about CIs and their relationships, supporting informed decision-making and impact analysis.
#3: BMC Helix CMDB
BMC Helix CMDB is a powerful cloud-based Configuration Management tool that leverages AI and machine learning to improve service delivery and IT Asset Management. Designed for enterprise environments, BMC Helix offers scalability and robust features that support complex IT infrastructures.
BMC Helix CMDB main features:
- AI-powered insights: Uses machine learning to analyze asset performance, predict issues, and automate fixes where possible.
- Service impact model: Maps relationships between CIs to help visualize potential impacts of incidents or changes on services.
- Comprehensive discovery: Integrates with BMC Discovery for real-time asset discovery and automated updates to the CMDB.
- Cloud flexibility: Offers cloud, hybrid, and on-premises deployment options to meet diverse organizational needs.
#4: InvGate Asset Management
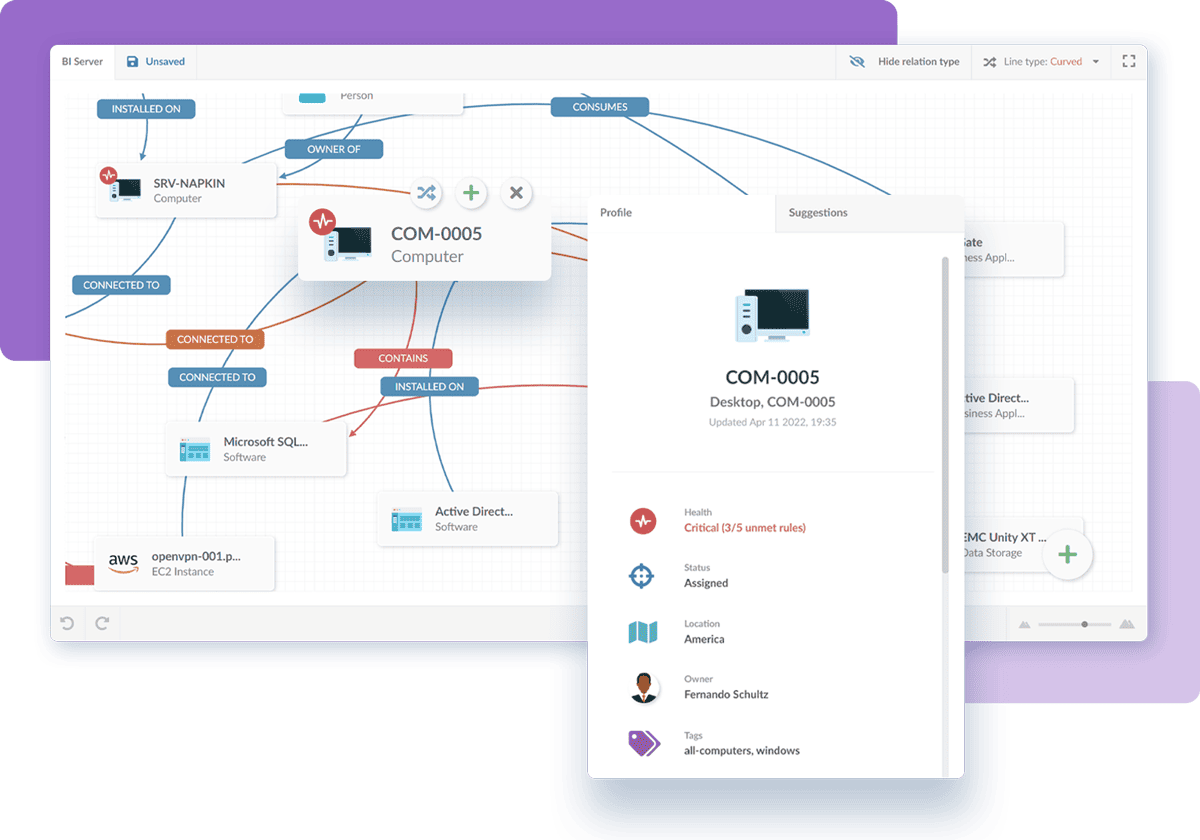 InvGate Asset Management is an IT Asset Management solution that includes powerful CMDB capabilities. Its CMDB functionality maps relationships between applications, systems, and other CIs, making it easy to centralize and track the inventory.
InvGate Asset Management is an IT Asset Management solution that includes powerful CMDB capabilities. Its CMDB functionality maps relationships between applications, systems, and other CIs, making it easy to centralize and track the inventory.
Additionally, InvGate integrates seamlessly with InvGate Service Management, allowing teams to link CIs to tickets and quickly manage incidents, changes, or service requests.
InvGate Asset Managementmain features:
- Unified ITAM and CMDB: Combines Asset and Configuration Management into a single platform, allowing IT teams to handle both seamlessly.
- Automated discovery: Automates the discovery of assets and CIs across the network, ensuring that the CMDB stays up-to-date.
- Customizable dashboards: Provides interactive dashboards to monitor and visualize CI relationships, asset statuses, and health metrics.
- Advanced reporting: Offers detailed reports on asset usage, lifecycle, and dependencies, helping IT teams make data-driven decisions.
- ITSM integration: InvGate Asset Management integrates with many ITSM tools, including InvGate Service Management.
- Visual modeling: Map all IT components and their relationships using a visual CMDB data model, enabling clear identification of trends, patterns, and outliers in an intuitive presentation.
#5: SolarWinds Service Desk CMDB
 SolarWinds Service Desk CMDB is part of SolarWinds’ ITSM suite, offering a straightforward, cloud-based Configuration Management tool suitable for mid-sized organizations. SolarWinds Service Desk focuses on delivering a cost-effective CMDB solution with core features that simplify IT asset and Configuration Management.
SolarWinds Service Desk CMDB is part of SolarWinds’ ITSM suite, offering a straightforward, cloud-based Configuration Management tool suitable for mid-sized organizations. SolarWinds Service Desk focuses on delivering a cost-effective CMDB solution with core features that simplify IT asset and Configuration Management.
SolarWinds Service Desk CMDB main features:
- Asset and Configuration Management: Provides tools for managing both assets and Configuration Items, with automated data entry and updates.
- Incident and change correlation: Tracks and correlates CIs with incidents and changes, helping to assess potential impacts on the IT environment.
- Customizable fields: Allows users to customize CI fields and classifications to align with specific organizational needs.
- Affordable pricing: Offers a competitively priced solution for IT teams looking for essential CMDB functionality without excessive cost.
Conclusion
A cloud-based CMDB is an essential tool for organizations looking to optimize their IT environments. Choosing a CMDB in cloud environments ensures scalability, automation, and a proactive approach to IT management.
By leveraging features like accessibility, scalability, and automated maintenance, organizations can reduce overhead while improving operational efficiency. Embracing a cloud CMDB isn’t just about keeping up with technology—it’s about staying ahead and future-proofing your IT operations.















