ISO 27001 is the top internal standard for information security. When carried through correctly, it protects your environment, and makes people feel safer when using IT equipment.
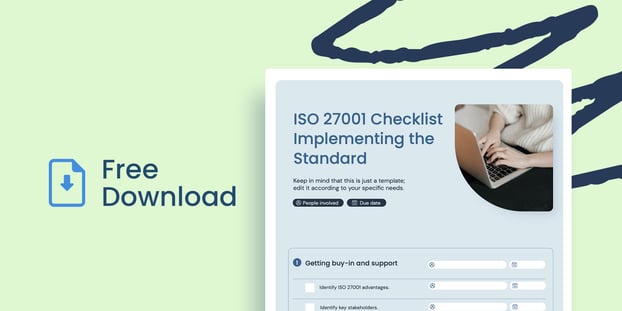
That being said, implementing the standard is no small task; many organizations feel overwhelmed, as they don't know where to start, or struggle and feel lost during the process. That's why we created the definitive ISO 27001 requirements checklist to implement the standard.In this article we will look at some of the benefits of the ISO 27001 standard and see how it can help your organization. Then, we will break down the process into manageable steps through an implementation checklist you can follow and adapt to your specific scenario and needs.
We have made available a downloadable template below to help you get started with the process right away. Finally, we will provide some best practices and useful tips for the whole implementation to turn out successful.
Are you ready to implement ISO 27001? Let's go!

Table of contents
- Who can benefit from an ISO 27001 implementation?
- ISO 27001 checklist download
- Three tips to ensure ISO 27001 compliance
Understanding the core principles of ISO 27001
ISO 27001 revolves around three key pillars: confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. These core principles ensure that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized individuals, remains accurate and complete, and is available when needed.
-
Confidentiality: Protecting information from unauthorized access is critical to prevent data breaches and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
-
Integrity: This focuses on safeguarding the accuracy and consistency of data throughout its lifecycle, preventing unauthorized modifications or destruction.
-
Availability: Information must be accessible when needed to ensure business operations can continue without disruption.
By embedding these principles in your Information Security Management System (ISMS), your organization can better manage risks and maintain data security in line with ISO 27001 requirements.
Who can benefit from an ISO 27001 implementation?
There is no doubt that implementing ISO 27001 provides numerous crucial benefits. Let's explore some of the key ways in which this standard can significantly enhance how organizations operate.
1. Strengthen data security
ISO 27001 helps organizations create a robust framework for managing and protecting sensitive information. By implementing stringent security controls, businesses can mitigate risks and prevent costly data breaches.
2. Increase employee engagement
Employees are more likely to follow well-structured processes when they understand the importance of safeguarding information. ISO 27001 ensures that security policies are communicated effectively, fostering a culture of responsibility and accountability.
3. Continuously refine processes
One of the core tenets of ISO 27001 is continuous improvement. This standard promotes regular risk assessments and process reviews, helping organizations adapt to evolving security threats and fine-tune their operations.
4. Secure information assets
ISO 27001 focuses on the protection of all types of information assets, whether they are physical, digital, or in the form of intellectual property. This ensures that critical business data is protected from unauthorized access, loss, or damage.
5. Prepare for the future
By adhering to ISO 27001, organizations position themselves to meet future regulatory requirements and anticipate security challenges. This forward-thinking approach enables businesses to stay ahead in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
6. Stand out in a crowded market
ISO 27001 serves as a differentiator in competitive industries. Certification demonstrates a commitment to security excellence, giving your organization a competitive edge and building trust with customers and stakeholders.
While all organizations can benefit from ISO 27001, those managing sensitive information will find it particularly vital. This applies to:
- Healthcare providers, hospitals, and authorities.
- Financial institutions and banks.
- Government agencies.
- Educational institutions, including colleges and universities.
- Insurance companies.
- E-commerce businesses and online retailers.
- Technology and software companies.
- Non-profit organizations and charities.
- Manufacturing and industrial companies.
- Service providers.
By implementing ISO 27001, organizations can safeguard their sensitive information, reduce the risk of security breaches, and showcase a commitment to security best practices. This not only protects employees and customers but also enhances the organization’s reputation in a data-driven world.
ISO 27001 implementation sends a clear message: your organization is serious about securing its data and protecting its people and customers.

Key challenges of ISO 27001 implementation and how to overcome them
Implementing ISO 27001 can be daunting for organizations, especially those new to formal security standards. Some of the most common challenges include:
-
Resource constraints: Many organizations underestimate the time, money, and personnel needed for implementation. It’s crucial to conduct a thorough resource assessment early on.
-
Understanding scope: Defining the right scope for your ISMS can be tricky. Ensure that your scope includes all critical systems and information that require protection.
-
Cultural resistance: Changing security practices can face resistance from employees. Building a culture of security awareness through training and engagement will ease the transition.
-
Managing documentation: ISO 27001 demands extensive documentation of security processes. Automating documentation tracking with tools and templates can help streamline this effort.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, stakeholder involvement, and the right technology to support implementation.

How ISO 27001 works: Official steps vs. implementation flexibility
ISO 27001 provides a flexible, risk-based framework for organizations to establish and maintain an Information Security Management System (ISMS). While the standard outlines key requirements—such as risk assessment, leadership commitment, and continual improvement—it doesn't prescribe a single, mandatory way to implement these steps. Instead, organizations can adapt the process based on their size, industry, and specific information security needs.
Broadly, the standard involves phases like defining the scope of the ISMS, identifying information security risks, implementing controls, and conducting an external or an internal audit. However, there are variations in how businesses choose to execute these steps. Some may opt to use compliance automation platforms to streamline certification, while others bring in consultants to ensure that security practices align with their business objectives.
This means there is no one "official" or unique pathway to ISO 27001 certification. Organizations have the flexibility to customize their approach, as long as they meet the standard's core requirements. The steps that follow are a commonly used framework to guide you through ISO 27001 implementation.

What is an Information Security Management System (ISMS)?
An Information Security Management System (ISMS) is a structured framework of policies, processes, and controls designed to manage and protect an organization’s sensitive information. The primary goal of an ISMS is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, minimizing the risk of security breaches and ensuring compliance with relevant legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements.
ISO 27001, an international standard, provides the specifications for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an ISMS. The ISMS encompasses risk management practices, including identifying information security risks, implementing appropriate controls, and continually monitoring and improving security processes. It involves not only technology but also people and processes, making it an essential part of an organization’s overall risk management strategy.
ISO 27001 checklist: Implementing the standard in 20 steps
Implementing ISO 27001 is a significant investment in time, effort, and resources: if you try to do too much at once, you'll get overwhelmed. This is why the best way to tackle this task is to break the exercise into smaller, more achievable work packages so you can implement the standard effectively without losing focus.
Here are the main steps to follow:
- Getting buy-in and support.
- Establishing a governing body.
- Creating a roadmap.
- Defining a scope.
- Creating an Information Security policy.
- Defining the risk assessment methodology.
- Creating a risk register.
- Performing the risk assessment.
- Writing the statement of applicability.
- Writing the risk treatment plan.
- Defining how to measure the effectiveness of your controls.
- Implementing your security controls.
- Creating a training and awareness schedule.
- Operating the ISMS.
- Monitoring and measuring the ISMS.
- Building and inventory.
- Conducting internal audits.
- Setting up regular reviews.
- Taking corrective actions where appropriate.
- Building in continual improvement.
Now let's have a look at each one of them in more detail.
1. Getting buy-in and support
Before you do anything at all, get buy-in, from the business, your support teams, and your colleagues. ISO 27001 is not a one-and-done activity; you will need support, so set the scene accordingly, or you will fail at the first hurdle.
When planning for buy-in:
- Collect information about the advantages of ISO 27001 to clearly explain the benefits and why it is needed.
- Identify stakeholders in your organization who will act as cheerleaders for the initiative.
- Don't forget about your service desk and technical support teams, who will need to be aware of their requirements relating to information security.
2. Establishing a governing body
ISO 27001 will need governance in place to support it. When assembling who will be responsible of this:
- Appoint a project manager to oversee the implementation of the ISMS.
- Select a team to carry out the implementation activities.
- Treat the implementation as a project so that it has the appropriate support and governance.
3. Creating a roadmap
Successful implementation needs a well constructed guideline to guide the team:
- Use the Deming or Plan, Do, Check, Act cycle to recognize gaps or challenges and capture any ideas for improvement and remediation.
- Work with your governing body and project team to set key milestones.
- Create quality criteria so that you and your team can be confident that everything at each stage has been completed effectively before moving on to the next phase.
4. Defining a scope
So many organizations struggle with ISO 27001 implementations because little attention is paid to the scope. When defining it remember to:
- Check the standard scope requirements and compare them with the specific needs of your organization.
- Work with your team to determine what needs to be protected or secured within your organization so it matches any other strategic objectives.
- Identify any dependencies and touchpoints
- Understand the total impact on your organization; identify any other teams that could be impacted by your decisions regarding information security.
5. Creating an Information Security policy
Creating an Information Security policy is crucial in your implementation journey as it sets out what colleagues can and cannot do clearly and effectively.
- When creating a policy, ask for help! If you have a governance, risk, or compliance team, ask if there are any templates you can use so that it has a consistent look and feel with other policy documentation, and it is easy for colleagues to navigate.
- Remember it should define your organization's basic information security requirements and that the detail comes with the processes and procedures that will underpin it.
- Ensure you include an objectives section to set out what information security is needed.
- Assign roles and responsibilities to ensure everyone knows who owns the implementation, maintenance, and reporting of ISMS performance.
6. Defining the risk assessment methodology
Managing risk is a key component of the standard. As such, it's crucial to create a robust assessment methodology to define the rules for identifying the risks, impacts, and their likelihood, and to define the acceptable level of risk for the organization. When designing an assessment methodology for risk:
- Create a risk assessment methodology to codify how your organization will handle information security risks.
- Create a matrix to identify risk probability and its impact.
- Identify scenarios in which information, systems, or services could be compromised.
7. Creating a risk register
Creating a risk register to identify, prioritize, and act on risks when they appear is also essential. When creating the register:
- Make sure it's easy to record and manage risks.
- Create clear, easy-to-understand summaries of each risk.
- Make sure the probability and impact of each risk is visible.
8. Performing the risk assessment
Once you have your register, it's time to conduct the ISO 27001 risk assessments. When conducting risk assessments:
- Ensure everyone is familiar with the risk methodology defined in the previous steps.
- Identify threats and vulnerabilities.
- Assess the likelihood and impact of risks.
- Select and prioritize risk treatment options.
- Implement chosen risk treatments.
- Monitor and review all risks on an ongoing basis.
9. Writing the statement of applicability
After concluding the risk assessment and treatment process, you will clearly understand the ISO 27001 Annex A controls required. The Statement of Applicability (SoA) document must list all applicable controls, provide reasons for their selection or omission, and describe how they are implemented in the organization.
When writing your SoA:
- Identify which controls apply to your organization.
- Provide a brief description of each applicable control.
- Explain the reasons for including or excluding controls from the SoA.
- Describe how each control is implemented and managed.
- Provide evidence that the control is performing as intended and is effective in reducing risks to an acceptable level.
- Ensure that the SoA is reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changes in the organization's information security management system and to ensure that each control is still fit for purpose.
10. Writing the risk treatment plan
The risk treatment plan is needed to react to risks that could affect information assets' confidentiality, integrity, and availability or CIA.
When creating your risk treatment plan:
- Design a response for each risk (Risk Treatment).
- Assign an owner to each identified risk.
- Assign risk mitigation and activity owners.
- Establish target dates for completing risk treatment activities so they can be tracked and managed over time.
11. Defining how to measure the effectiveness of your controls
You need a solid guideline to measure your controls' effectiveness; otherwise, you have Schrödinger's ISMS.
When measuring the effectiveness of your controls:
- Have a plan in place for measuring control objectives.
- Create key performance indicators or KPIs to measure the effectiveness of your controls, such as the number of security incidents prevented, the reduction in risk exposure, the percentage of colleagues who have completed the appropriate training, or the rate of compliance with relevant regulations or standards.
- Carry out regular testing of controls to identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities and determine how well the controls work in practice.
12. Implementing your security controls
This stage in the implementation supports IT departments to control risks that could affect the integrity of information assets.
When implementing controls:
- Ensure the appropriate policies and procedures support your new controls.
- Have protocols in place for enforcing any new behaviors and managing exceptions.
13. Creating a training and awareness schedule
An ISO 27001 will need training and an awareness plan to ensure the changes to behaviors and ways of working are embedded.
- Create training content and make it available to all colleagues.
- Work with HR to ensure that ISO training is part of any onboarding activity and that regular refresher sessions are required.
- Define expectations for colleagues regarding their role in ISMS maintenance.
- Train colleagues on common threats facing your organization and how to respond.
14. Operating the ISMS checklist
The ISMS checklist effectively helps you manage risks, controls, and security incidents. The checklist consists of four main sections:
- Planning for an Information Security Program.
- Developing Policies, Procedures, Standards, Guidelines, and Documentation.
- Implementing Controls.
- Measuring Performance Metrics.
15. Monitoring and measuring the ISMS
Build regular monitoring activities so you can measure your ISMS effectively. The monitoring and measurement practices should help you understand how the ISMS is performing, if any security incidents have been reported, and if all info security processes are working correctly.
Monitoring activities should include the following:
- Define what needs to be monitored within the scope of your organization's ISMS by considering risks, vulnerabilities, threats, and impacts resulting from not meeting standards or managing risk appropriately.
- Assign responsibility for monitoring each item to one individual or group in order to avoid duplication or confusion.
- Create a plan for how your activities will be monitored using resources such as policies, guidelines, or standards that are already in place.
16. Building and inventory
In order for your ISMS to be successful, you must build a complete and detailed inventory in compliance with the ISO 27001 standard of your information assets. It's important that your inventory includes both tangible and intangible assets, and that every asset has an asset owner assigned, who will be responsible for its security.
Having specific ITAM software supports you through this whole process and with staying compliant to ISO 27001. The tool helps you with:
- Monitoring IT asset security compliance.
- Detecting devices running unauthorized software.
- Reporting devices running outdated software versions.
- Checking assets with upcoming warranty expiration.
17. Conducting internal audits
Conducting internal audits is a great way to prepare for external audits and to keep everyone in the organization honest and transparent.
When conducting them, remember to:
- Allocate internal resources with the necessary skills and competencies independent of ISMS development and maintenance.
- Verify conformance with the standard requirements, with your scope, and with SoA.
- Share internal audit results with the ISMS governing body and senior management, including findings, risks, and nonconformities.
- Fix all identified issues before proceeding with the external audit.
18. Having a plan in place for external audits
This is one of the final steps. The hard work is done and you’ve conducted an internal audit to prepare. Here's what to do next:
- Engage an independent ISO 27001 auditor.
- Conduct Stage 1 Audit consisting of an extensive documentation review; obtain feedback regarding readiness to move to Stage 2 Audit.
- Conduct Stage 2 Audit consisting of tests performed on the ISMS to ensure proper design, implementation, and ongoing functionality, and to evaluate fairness, suitability, and effective implementation and operation of controls.
19. Taking corrective actions where appropriate
Have a plan in place for managing corrective actions. This should include the following:
- Ensure that all requirements of the ISO 27001 standard are addressed.
- Examine if the organization and its people follow processes specified and documented.
- Make sure the organization is upholding contractual requirements with third parties and partners.
- Address any non-conformities identified by the ISO 27001 auditor.
- Review the auditor's formal validation following the resolution of findings and non-conformities.
20. Building in continual improvement
Have a plan for improvement over time. Things to consider include the following:
- Plan reviews at least once per year; to ensure your controls remain aligned with the needs of the business and continue to be fit for purpose and use.
- Ensure the ISMS and its objectives continue to remain appropriate and effective.
- Ensure that senior management remains informed and updated on all critical information activities.
Three tips to achieve ISO 27001 compliance
Here are three crucial tips that will help you along the whole process of achieving compliance:
- Create a solid policy - Address any non-conformities identified by the auditor. The information security policy is a crucial component of ISO 27001 implementation. It outlines an organization's commitment to protecting sensitive information, and provides a framework for implementing effective, efficient, safe security controls.
- Ensure that third-party suppliers comply with ISO 27001 - Don't forget about third-party suppliers and partners. Ensuring they adhere to the standard is critical if you are truly serious about ISO 27001 accreditation. Be open about what is needed so that both parties can collaborate and work together effectively. Guarantee that everyone is comfortable by including contractual obligations to comply with the standard and regular audits of the suppliers' ISMS.
- Continually improve the ISMS - Achieving ISO 27001 compliance is not a one-time thing. It’s an ongoing process. Continually improving the ISMS through regular reviews and updates help ensure that it remains effective in protecting the organization's information security.
Final thoughts
ISO 27001 is the go-to standard for information security that will help you make sure employees, customers, assets, and your whole organization are fully protected. Staying compliant with the standard is also a way of showcasing your commitment to security to the world.
Following a thorough ISO 27001 checklist is the best way to keep your implementation efforts focused on one step at a time, and aligned with business objectives. It will help you guarantee that you are not missing anything important and stay confident through the whole process.
Download yours from the link above and start implementing the standard!
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is the leading international standard for managing information security. It outlines the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). By following ISO 27001, organizations can protect sensitive data, mitigate risks, and demonstrate a commitment to security, which builds trust with stakeholders.
2. Who can benefit from implementing ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is beneficial for organizations of all sizes and industries, especially those handling sensitive information such as personal, financial, or healthcare data. Industries such as banking, healthcare, education, technology, and e-commerce often prioritize ISO 27001 compliance to ensure data protection and business continuity.
3. Is there a unique way to implement ISO 27001?
No, ISO 27001 provides flexibility in how organizations can implement its requirements. While the standard outlines key steps like risk assessments and audits, each organization can tailor the process based on its size, industry, and security needs. The flexibility allows businesses to focus on what matters most to their operations.
4. What is an Information Security Management System (ISMS)?
An ISMS is a structured framework of policies and processes designed to protect an organization’s information. It ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data by managing security risks and implementing effective controls. ISO 27001 provides the guidelines for creating and maintaining an ISMS.
5. What role does the international organization ISO play in ISO 27001?
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) is responsible for developing ISO 27001. This global body sets international standards to ensure organizations worldwide follow consistent guidelines for information security. ISO 27001 helps organizations align with internationally recognized best practices for data protection.
6. How can ISO 27001 certification benefit my organization?
Achieving ISO 27001 certification enhances your organization's credibility and demonstrates a commitment to safeguarding information. It reduces the risk of security breaches, helps meet regulatory requirements, and serves as a competitive advantage in industries that prioritize data security.