You know you're taking IT security seriously when you start looking at ISO 27001. Done well, it can be a game changer for your organization, since it has the power to level up your security, protect your information, and reduce risk.
This article will look at how the ISO 27001 standard works and some of the main benefits it brings. Then we will explain how to implement the framework in your organization and the requirements for obtaining accreditation. Finally, we will describe some of its most popular alternatives.
Ready to get excited about information security? Let's get started.

What is ISO 27001?
The ISO IEC 27001 standard, jointly developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), is the globally recognized standard for Information Security Management. It uses a Risk Management approach to provide a framework for managing, controlling, and protecting privileged and sensitive information.
The standard sets out the requirements for establishing, maintaining, implementing, and continually improving an organization's Information Security Management System (ISMS).
It codifies a systematic and proactive approach to managing information security risks and continuously monitors and improves its effectiveness. The keywords you need to pay attention to here are proactively and continuously.
Applying a reactive approach to IT security is no longer good enough. Do that, and you're set up to fail because you will be constantly firefighting. And it's the same with continuously. Information security is not a one-and-done situation – it will always be in motion. As the threat landscape adapts and changes, so must your response.

What is ISMS, and why do you need it?
In a nutshell, you need an Information Security Management System to periodically secure corporate information on assets' confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA). In this sense, an ISO 27001 ISMS comprises policies, procedures, and other controls involving people, processes, and technology.
ISO 27001 vs. NIST
Though they might be thought of as similar instruments, ISO IEC 27001 and NIST are not exactly equal.
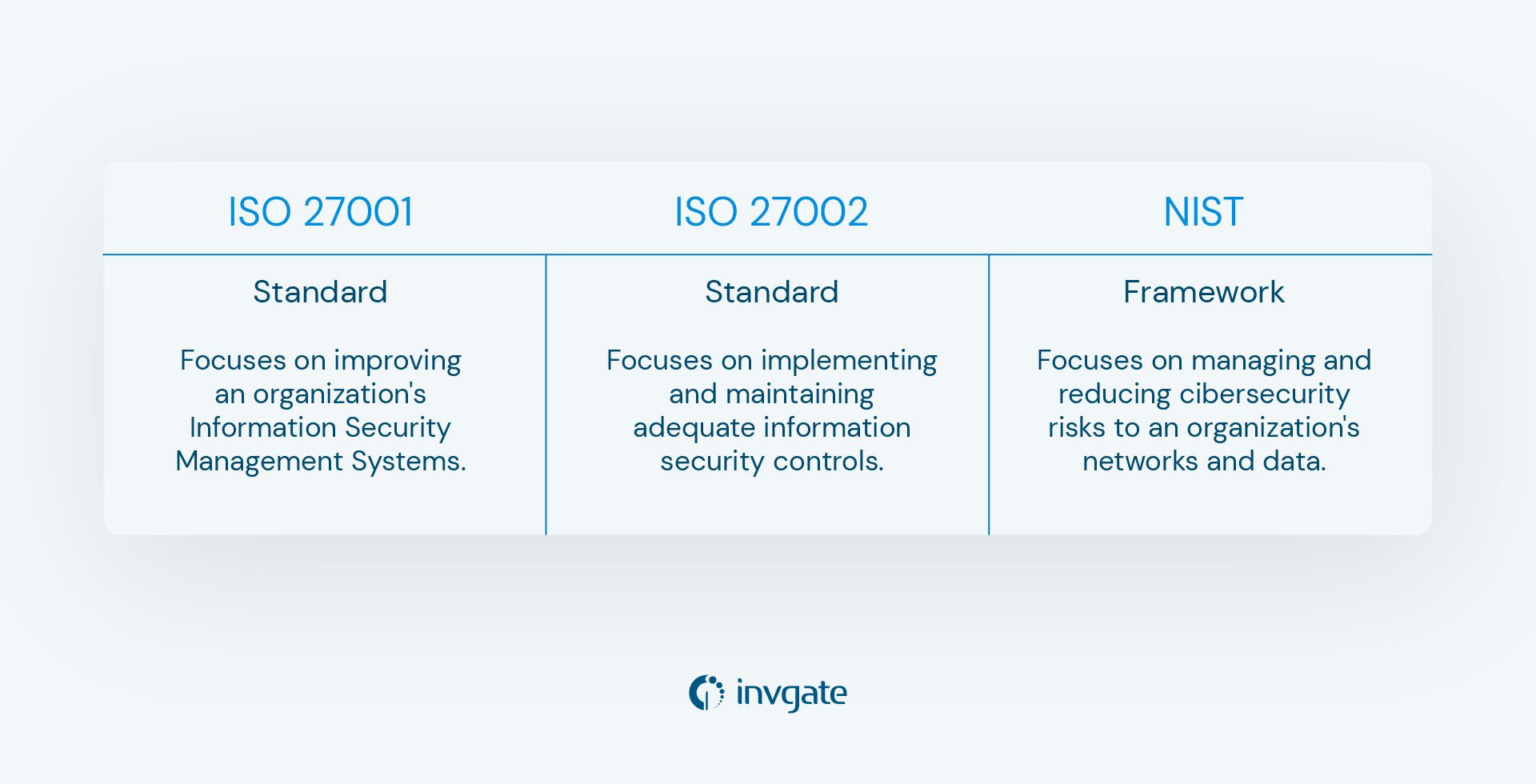
ISO 27001 is an international standard for improving an organization's ISMS. Meanwhile, NIST controls help manage and reduce cybersecurity risks to their networks and data.
While both effectively contribute to a more robust security posture, ISO 27001 is the standard, and NIST is a framework.
ISO 27001 vs. ISO 27002
Another common question is the difference between ISO 27001 and ISO 27002. Well, they both pertain to information security, but with very different functions:
- ISO IEC 27001 is an international standard to improve an organization's Information Security Management Systems.
- ISO 27002 provides guidelines for implementing and maintaining adequate information security controls. It covers a wide range of topics related to information security, including Risk Management, access control, cryptography, and Incident Management.

How ISO 27001 works
This is a standard for ISMS to provide a structured approach to managing company data so it remains secure.
Part of the ISO 27001 process work includes:
- Establishing policies and procedures.
- Conducting risk assessments.
- Implementing controls to mitigate and manage risks.
To fulfill the items above, the security standard specifies the requirements for an ISMS – which includes documentation management, the internal audit process, and the management review process.
And for organizations that demonstrate their Information Security Management capabilities and commitment to best practices, they can receive a certification to prove it.
ISO 27001 clauses

The standard is made up of several clauses:
- Scope - The requirements for establishing, maintaining, implementing, and continually improving the ISMS. This is an essential clause. Many people struggle with information security because they don't take the time to determine an appropriate reach for their organizations. Every company is different, so setting out your areas with biggest risks will be more beneficial than trying to do too much at once.
- Normative references - Other relevant and associated standards and documents.
- Terms and definitions - The definitions of the terms used throughout the standard.
- Context of the organization - Internal and external context, stakeholders, and requirements. This is important because, as we've said before, no two organizations work the same, so it's crucial to set out your context so everyone knows what they're dealing with.
- Leadership - All requirements for leadership commitment, policy, roles, responsibilities, and authorities. We all know that ISO 27001 won't work without support from the leadership, but what does support look like? This clause makes clear and codifies the responsibilities of those in leadership positions.
- Planning - List of possible risks, in order to establish objectives and the plans to achieve them. It's important to have a strategy for risks so that you can arrange the appropriate actions to mitigate and manage them.
- Support - The requirements for resources, competence, awareness, communication, and documented information. This is much more than the traditional people, process, and technology we're all used to hearing about when dealing with IT best practices: it should include best practice documentation, processes, tools, knowledge, and people. It should also incorporate relationship building, training, and risk management. The standard will require support to work effectively, so this clause will ensure that you have the right things in place to succeed.
- Operation - Register of the relevant processes for managing information security risks and responding to incidents.
- Performance evaluation - Monitor, measurement, analysis, evaluation, audit, and review of the performance of the ISMS. Trust but verify, making sure we're doing what we say we're doing and having those actions independently verified.
- Improvement - Improvement opportunities and implementation of corrective and preventive actions. Think about it - the one thing about IT is that things don't stay the same for very long. As best practices continue to evolve, we need to build continual improvement to our day-to-day information security activities to align with business needs.

ISO 27001 controls

So ISO 27001 is a big undertaking, and any big undertaking requires a lot of controls to keep the show on the road. ISO 27001 specifies a comprehensive set of 114 controls that can be used to manage security risks. These controls are organized into 14 categories, as follows:
- Information security policies - Establishes and maintains information security policies, procedures, and guidelines.
- Organization of information security - Defines the roles and responsibilities of information security personnel and ensures that they are competent and have appropriate resources.
- Human Resource security - Screens, trains, and manages personnel to ensure they're aware of and comply with information security policies and procedures.
- Asset Management - Identifies and classifies information assets and ensures that they are appropriately protected. If you want to further explore this control category, the annex A.8.1 has all the information regarding ISO 27001 and the details to create an asset inventory in compliance with the ISO standard.
- Access control - Manages user access to information systems and data and prevents unauthorized access.
- Cryptography - Uses cryptography to protect information, such as encryption and digital signatures.
- Physical and environmental security - Protects information systems and data from physical threats, such as theft, fire, and natural disasters.
- Operations security - Guarantees the secure operation of information systems and networks, such as backup and recovery procedures, Change Management, and monitoring.
- Communications security - Ensures the secure transfer of information, such as through secure protocols and network segmentation.
- System acquisition, development, and maintenance - Makes sure that information systems and applications are developed and maintained securely.
- Supplier relationships - Manages the security of information provided to or received from external suppliers.
- Information Security Incident Management - Identifies, reports, and responds to information security incidents.
- Security aspects of Business Continuity Management - Ensures that information security is integrated into Business Continuity Management processes.
- Compliance Management - Controls that the organization complies with regulatory and legal requirements related to information security.
Seven benefits of the ISO 27001 standard
The ISO IEC 27001 standard can help companies to demonstrate their commitment to protecting information assets, and provide confidence to stakeholders, customers, and end users that they're taking appropriate steps to manage and respond to information security threats and risks.
But that’s not all, it also has several other benefits, including:
- A more resilient IT security ecosystem and less vulnerability to threats and cyber attacks.
- Data CIA (data confidentiality, integrity, and availability).
- A consistent level of IT security across the organization.
- Cost savings in terms of protection from cyber attacks, ransomware, and lost productivity.
- Being prepared for new challenges as the threat landscape changes and always having a plan.
- Knowledge and understanding of the importance of information security.
- Commitment to quality.
We wish we could say that there are no downsides to ISO 27001 and that if you do all the hard work, you and your organization will always be safe. But as we know, that's not how it works in the real world.
The standard isn't a fast or cheap undertaking; you must invest time, money, and effort to meet it. It also doesn't guarantee that your system will remain secure forever; it is only a snapshot of a company's security position at a particular time.
ISO 27001 requirements
So what do you need to do to get certified against ISO 27001? Luckily, the standard specifies requirements for implementing and continually improving your ISMS.
The ISO 27001 requirements are as follows:
- Define the scope of the ISMS - Set the boundaries and applicability of the ISMS.
- Conduct a risk assessment - Identify the risks that could impact its information assets' confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
- Implement a risk management process - Implement a process to assess and manage the identified risks to take appropriate action.
- Establish a management framework - Establish a management framework to ensure the effective implementation and maintenance of the ISMS.
- Assign information security roles and responsibilities - Assign roles and responsibilities for managing the ISMS so everyone is aware of what they are accountable for and there is no confusion. Ideally, you should codify them in a RACI chart.
- Train employees and raise awareness - Make sure that employees know their responsibilities for information security and are trained on how to fulfill them, and that they have periodic training sessions to refresh it.
- Manage documentation - Establish, implement, and maintain documents that define the policies, procedures, and controls used in the ISMS.
- Manage records - Establish, implement, and maintain a set of records that provide evidence of the implementation and effectiveness of the ISMS.
- Implement and operate controls - The organization must implement controls designed to mitigate the identified risks.
- Monitor and review the ISMS - Monitor, measure, analyze, and evaluate the ISMS and review it at regular intervals to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness.
- Continual improvement - Improve the effectiveness of the ISMS by taking corrective and preventive actions and implementing lessons learned so that information security practices continue to mature and improve over time.

Extra tips for an ISO 27001 implementation
Apart from the specific requirements listed above, here are some additional tips and practical advice to help you successfully implement the ISMS:
- Obtain management commitment - Management should understand the benefits of an ISMS and be committed to providing the necessary resources.
- Get buy-in from support teams - You will also need support from your service delivery teams, who will carry out the day-to-day activities.
- Create an information security policy - Develop an information security policy that reflects its commitment to information security.
- Develop a statement of applicability - Develop a statement that documents the controls that will be implemented to manage the identified risks.
- Design procedures and work instructions - Create procedures and work instructions to support the implementation of the controls.
- Conduct internal audits - Internal audits are a very useful way to monitor your work and make sure that the ISMS is effective and compliant with ISO 27001 requirements.
ISO 27001 best practices
When implementing the security standard, don’t forget to follow some best practices to ensure the process goes smoothly:
- Communicate - Before you even consider going for the certification, communicate with your stakeholders. The implementation takes serious time, energy, and money commitment, so talk to your people. Why are you considering it? Is it a regulatory requirement? Are your customers requesting it? What problems do you think it will solve?
-
Be clear on your scope - Don't try to do too much at the start. Use your risk assessment to drive your focus to deal with your biggest pain points and exposure areas. Remember, ISO 27001 is a marathon, not a sprint. Follow a systematic approach, and make sure you listen to your people. Take your time, you can review the key implementation points on an ongoing basis until you get there.
-
Ask for help -There are lots of organizations and forms out there. Please don't do it alone. There are many ISO 27001 special interest groups and some very active communities on LinkedIn. It's much less daunting when you have other industry colleagues to bounce ideas and war stories off!
ISO 27001 certification
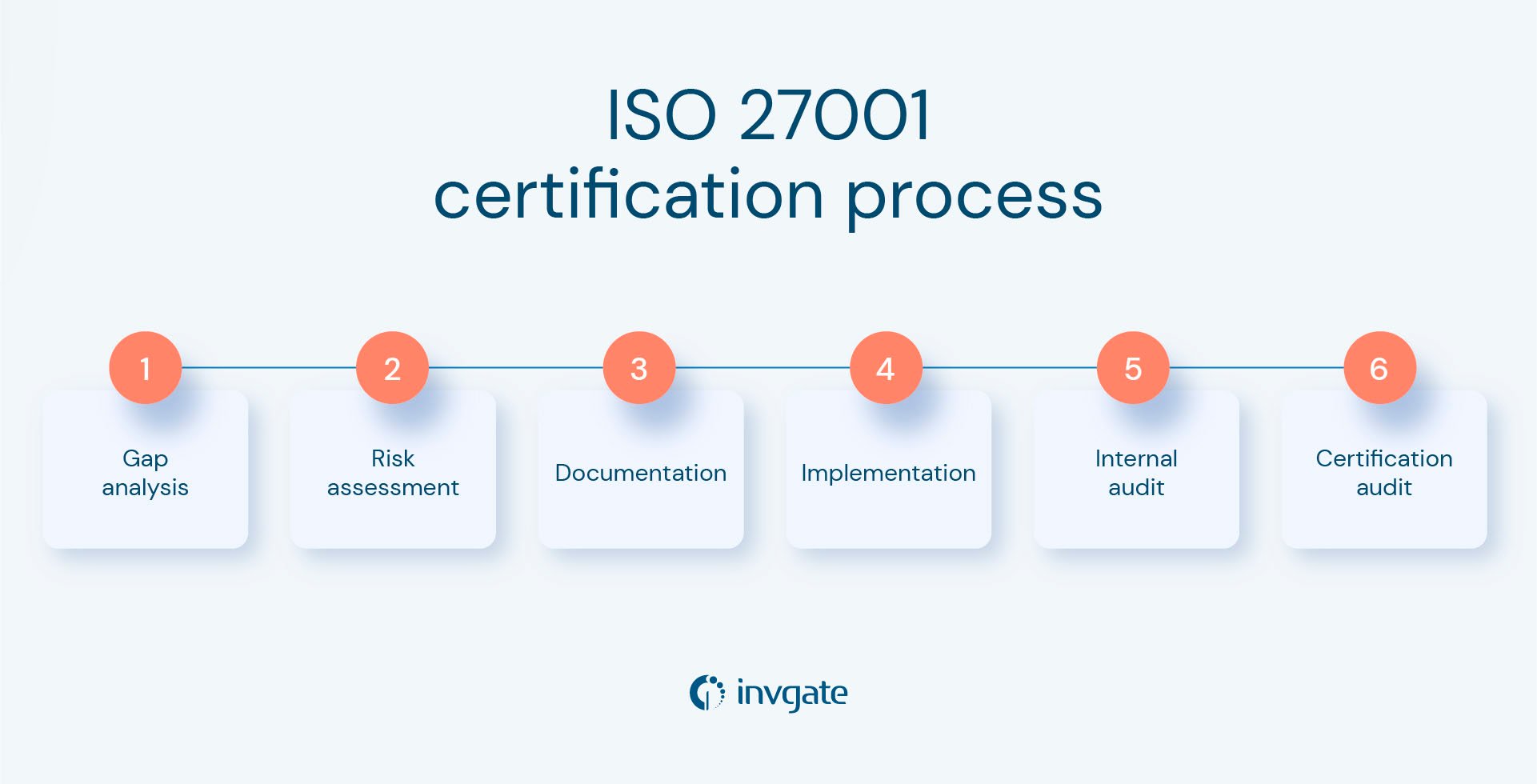
One of the many benefits of the standard is that as well as giving your organization the necessary knowledge to protect its most valuable information, you can also get a certification to prove to partners and customers how you use the highest standards to safeguard their data. This requires several steps:
- Gap analysis - This is an exercise in "Where am I now?" This stage involves assessing the organization's existing information security management practices against the requirements of the ISO standard to identify any gaps and areas for improvement.
- Risk assessment - It involves identifying and evaluating the risks to the organization's information assets and determining appropriate controls to mitigate those risks.
- Documentation - This stage involves developing policies, procedures, work instructions, and other documentation to support implementing the information security management system.
- Implementation - It involves implementing the ISMS, including the controls identified in the risk assessment stage and the documentation developed in the previous step.
- Internal audit - The internal audit involves analyzing the current security controls with our colleagues to ensure that they are operating effectively and in compliance with the standard.
- Certification audit - The final stage ins an external audit by a certification body to verify that the organization's ISMS meets the requirements. The organization will be awarded ISO 27001 certification if it passes the audit.
Individuals can also get ISO 27001 certified by attending a course, passing the exam, and, in this way, proving their skills at implementing or auditing an ISMS to potential employers. Keep in mind: the certification body will be measuring not just academic knowledge but various aspects of the international standards and their real-world practitioner expertise.
Alternatives to the ISO 27001 security standard
While ISO 27001 is a widely recognized and respected international standard, organizations can consider several alternatives based on their specific needs and requirements. Here are some different options:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework - NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) Cybersecurity Framework provides a risk-based approach to managing cybersecurity risk. It’s widely adopted in the United States and applies to organizations of all sizes.
- CIS Controls - CIS, or The Center for Internet Security Controls is a set of cybersecurity best practices designed to provide organizations with prioritized actions to improve their cybersecurity posture.
- PCI DSS - PCI DSS, or The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. This is a set of requirements to ensure that all businesses that store, accept, process, or transmit credit card information keep a secure environment.
- HIPAA Security Rule - HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) Security Rule is a set of standards designed to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of electronically protected health information (ePHI).
- SOC 2 - SOC 2 (Service Organization Control) is a set of criteria which measures a service organization's controls related to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
- GDPR - GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is a European Union (EU) regulation that governs the protection of the personal data of all EU residents.
- IASME - The IASME Cyber Assurance standard, formerly known as IASME Governance, is a comprehensive, flexible, and affordable cyber security standard. It assures that an organization has put a range of important cyber security, privacy and data protection measures into place.
Key takeaways
ISO 27001 is an international standard to improve an organization's Information Security Management systems. It is particularly beneficial for organizations that manage sensitive or confidential information, such as financial data, personal information, intellectual property, or trade secrets.
Implementing the standard has many benefits, but essentially it will provide you with useful knowledge and practices to help manage and protect your information and reduce risks of data breaches. Both organizations and individuals can receive certifications in the standard to demonstrate their knowledge and compliance with the framework.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who needs ISO 27001?
Anyone that needs an information security function in their organization that has been certified against an ISO standard.
Why is ISO 27001 certification important?
Because it holds you accountable and proves you hit the required measures.
What does having ISO 27001 mean?
It means that you have satisfied the requirements set out in the standard.
What are the three principles of ISO 27001?
Think CIA - confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Who needs to be ISO 27001 certified?
Ideally, anyone handles sensitive or confidential information, such as financial data, personal information, intellectual property, or trade secrets.
Why is ISO 27001 certification required?
ISO 27001 certification is required if the company or the professional handles sensitive or confidential information.
What is the difference between ISO 9001 and ISO 27001?
ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 are both different standards that serve different purposes. ISO 9001 is a Quality Management System standard, while ISO 27001 is an Information Security Management System standard.
What are the six stages of the ISO 27001 certification process?
They six stages are gap analysis, risk assessment, documentation, implementation, and internal and certification audits.