Incident severity levels are a key concept in Incident Management, helping IT teams classify and respond to issues based on their impact and urgency. In simple terms, they define how serious an incident is and how quickly it should be resolved.
Incident Management, as part of IT Service Management (ITSM), is the practice of restoring normal service operations as soon as possible after a disruption. Within this process, severity levels act as a guide for prioritization — they determine which incidents demand immediate attention and which can be addressed later.
Understanding and defining clear severity levels helps support teams allocate resources efficiently, communicate status updates more effectively, and maintain service quality even during high-pressure situations.

What are incident severity levels in ITIL?
Incident severity levels in ITIL define how serious an incident is based on its impact on business operations. They help classify issues so that teams can respond in a consistent and structured way. For example, a system outage that prevents users from accessing critical applications would fall under a higher severity level than a single user experiencing a minor glitch.
In ITIL, Incident Management aims to restore normal service as quickly as possible. Severity levels help determine the appropriate response time and the resources that should be allocated. They act as a shared language for IT teams and stakeholders, making it clear how urgent each situation is and what kind of attention it requires. They are typically ranked on a scale of 1 to 5, with 1 being the most severe and 5 the least.
ITIL priority vs. severity
Severity and priority often get confused, but they serve different purposes in incident management.
Severity refers to how much an incident affects systems, users, or business operations. It’s a measure of impact. How does it disrupt business operations? Does it affect systems or services? Does it cause financial or reputational harm? The severity level helps classify incidents based on their potential consequences.
Priority, on the other hand, combines severity with urgency — meaning how quickly the issue must be resolved.
Let’s look at an example. A reporting tool outage affecting the finance team two days before payroll processing would have high severity and high priority, because it directly affects business continuity and time-sensitive tasks. However, if the same issue happens right after payroll has been completed, it might still have high severity but lower priority, as the business impact at that moment is limited.
Why are severity levels important?
Defining clear incident severity levels brings structure to the response process and reduces ambiguity when problems occur. Without predefined levels, teams often waste time debating how serious an issue is or who should handle it.
Severity levels help organizations:
- Maintain consistent response standards.
- Communicate expectations clearly to both users and support teams.
- Allocate resources to the incidents that truly affect service delivery.
If every incident is treated as urgent, support agents can easily become overwhelmed, and important issues might receive the same attention as minor ones. Severity levels help prevent that by introducing a logical order of response.
Benefits of having an incident severity matrix
An incident severity matrix translates these levels into a clear and practical tool for teams to follow. It provides criteria and examples that help classify incidents quickly and consistently. Here are some of the main benefits of using one:
-
Standardized decision-making – The matrix gives agents clear guidance to classify incidents objectively instead of relying on subjective judgment.
-
Faster response times – With predefined categories, incidents can be routed and addressed without unnecessary delays.
-
Better communication – Stakeholders know what to expect at each severity level, improving transparency and trust.
-
More efficient resource allocation – IT teams can assign the right people and tools to high-impact incidents first.
-
Improved reporting and continuous improvement – Data collected by severity level helps identify trends and improve service reliability over time.
The incident severity matrix
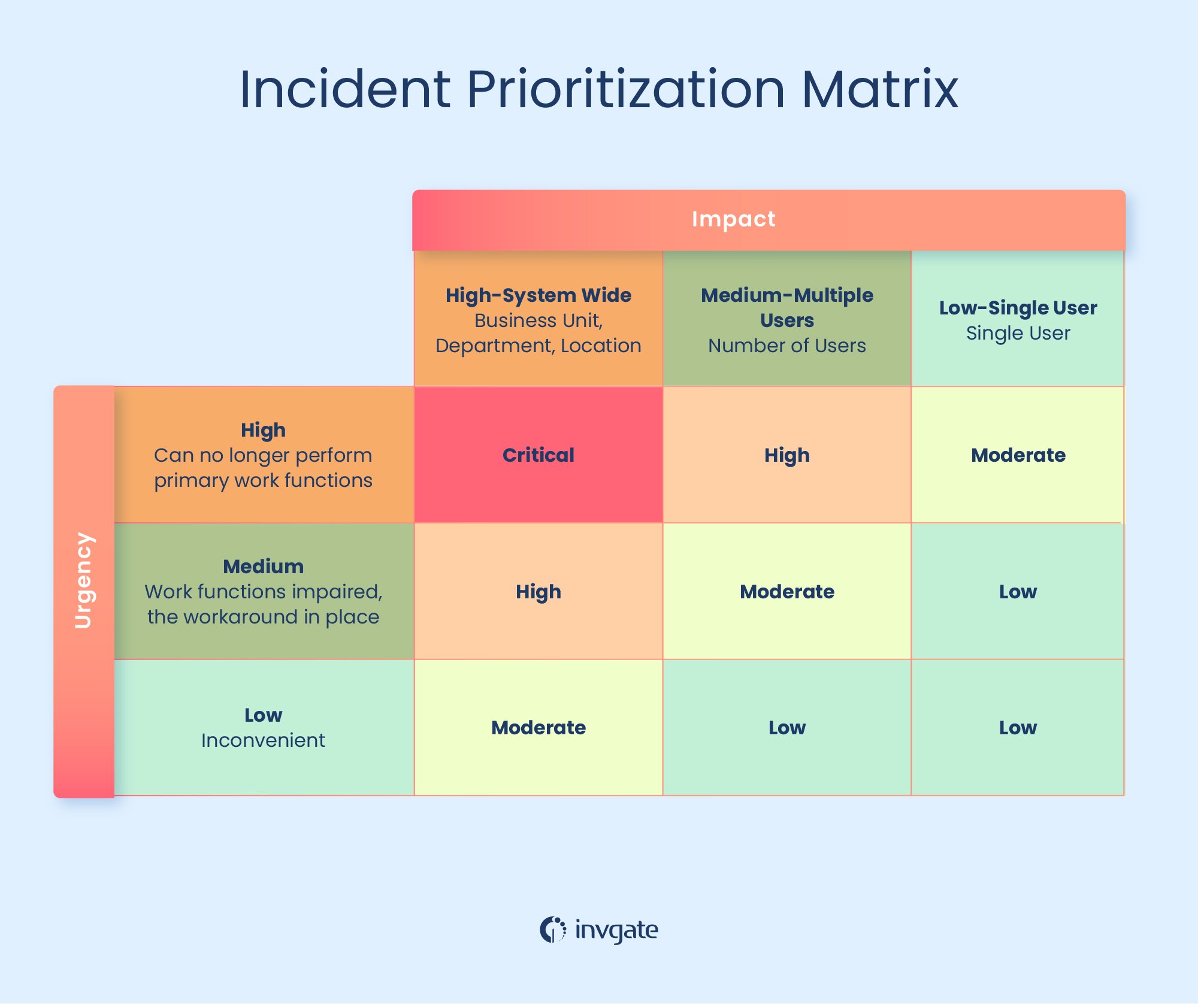
An incident severity matrix is a visual tool that helps IT teams classify and prioritize incidents, requests, and changes based on their impact and urgency on business operations. It brings structure to incident management by showing at a glance which issues should be addressed first.
The matrix typically includes two axes, as mentioned earlier when we explained severity vs. priority:
-
Impact – measures how much the incident affects the organization (for example, user productivity, service availability, or financial consequences).
-
Urgency – measures how quickly the issue needs to be resolved to prevent further disruption.
Together, these two dimensions help determine the severity level and, consequently, the priority of each incident.
To apply this model effectively, it’s helpful to follow a structured assessment process:
-
Evaluate the impact – Identify how the incident affects users and business operations. Consider factors such as:
-
Number of affected users or services
-
Financial loss or operational disruption
-
Reputational damage or compliance risk
-
-
Assess the urgency – Determine how quickly the issue needs to be resolved by analyzing:
-
Time sensitivity (e.g., payroll deadlines, service downtime)
-
Risk of escalation or further damage
-
Contractual or legal obligations
-
-
Combine impact and urgency levels – By matching these two dimensions, the matrix produces a corresponding severity level.
-
For example, high impact + high urgency often translates to Severity 1, requiring immediate response.
-
Low impact + low urgency, on the other hand, might fall under Severity 4, to be handled within regular business hours.
-
-
Define response and resolution targets – Each severity level should be linked to specific response times and escalation paths. This connection ensures consistent and fair handling of all incidents.
For practical implementation, many organizations use three levels of impact and three levels of urgency, producing a 3x3 matrix. This approach keeps the system manageable while still being detailed enough for accurate triage. However, the matrix can be customized according to your organization’s complexity, industry, or service structure. Large enterprises or service providers, for instance, might choose to add extra layers or categories for more precision.
Finally, it’s important to align the severity matrix with your Service Level Agreements (SLAs). SLAs define the response and resolution commitments between IT teams and customers or business units. When the severity levels defined in the matrix correspond with the timelines and escalation paths established in the SLA, teams can respond to incidents with consistency and transparency. It ultimately helps organizations maintain service quality, meet contractual obligations, and build trust with users and stakeholders.

The 5 incident severity levels explained
As seen earlier, incident severity levels provide a clear and standardized framework for assessing the impact and criticality of issues, enabling teams to prioritize their actions based on the urgency and potential impact.
Let's have a look at the five incident severity levels in greater detail and some examples:
| Severity | Description | Examples |
| SEV 1 | Critical incident that demands immediate attention. It significantly impacts business operations, causes extensive downtime, or results in substantial financial losses. | - Client-facing service is down for all customers. - Security breach. - Critical infrastructure failure. - Customer data loss. |
| SEV 2 | Major incident with a significant impact. It allows the organization to continue its operations, albeit with some limitations. | - Client-facing service is down for a subset of customers. - Critical functionality affected. |
| SEV 3 | Moderate incident that has a noticeable but manageable impact on business operations. | - Temporary disruption to a client-facing service. - Non-critical functionality affected. |
| SEV 4 | Minor incident that has minimal impact on business operations. | - Minor errors or inconveniences for users. - Temporary disruption to a non-critical system. |
| SEV 5 | Low-level deficiency that involves feature requests, usability improvements, or general feedback that can enhance the product or service in the long run. | - Minor performance issue. - Cosmetic error. |
Within ITSM, severity levels play a crucial role in the Incident Management practice, helping organizations effectively and efficiently plan how to respond to different incidents. These plans should include steps for:
- Identifying and classifying incidents.
- Escalating incidents to the appropriate level of management.
- Communicating with affected parties.
- Restoring service.
- Investigating the incident and taking corrective action.
In addition to incident response, proactive Incident Management practices are instrumental in mitigating potential issues before they become significant problems. Organizations can proactively identify and address potential issues by implementing Incident Management tools, having a preventive maintenance strategy, and performing security audits.
Using InvGate Service Management as your Incident Management software
Having the proper help desk software to streamline Incident Management processes is crucial. InvGate Service Management offers a range of features to automate the assessment and assignment of incident severity levels.
- Automatic incident classification: InvGate Service Management can classify and assign incident severity levels by analyzing attributes such as impact, urgency, and predefined criteria. This automation reduces manual effort and ensures consistent and accurate classification.
- Customizable severity rules: Administrators can create and adjust severity rules to reflect their organization’s specific priorities, systems, and SLAs.
- Incident response automated workflows: Once a severity level is assigned, the tool can automatically trigger escalation paths, assign responsibilities, and send notifications to the right people. For major or high-severity incidents, immediate alerts can reach key stakeholders, reducing delays and improving coordination.
- Analytics and reporting: Detailed dashboards and reports help track incident distribution, monitor response performance, and detect recurring problems.
-
AI capabilities for proactive operations
InvGate’s AI features for Incident Management strengthen both Incident and Problem Management by analyzing patterns and suggesting actions in real-time.-
Major Incident Detection identifies related high-impact incidents and suggests creating a major incident, helping preserve business continuity.
-
Common Problem Detection spots recurring issues, analyzes root causes, and recommends creating problem tickets to address them proactively.
-
Expert Collaboration Suggestion recommends agents with the right expertise based on past performance and ticket complexity, helping resolve specialized or cross-departmental issues faster.
-
Together, these capabilities make InvGate Service Management a complete solution for structured, automated, and data-driven Incident Management. Want to see its features by yourself? Request a free 30-day trial today and experience how the tool can streamline your Incident Management process.
3 best practices for a better incident severity classification
While the exact approach to Incident Management will always vary depending on your organization's industry, size, and operational characteristics, here are a few best practices to help you define severity levels effectively and align with the framework.
- Align severity levels with business impact: Consider the potential financial, reputational, regulatory, and customer satisfaction consequences of different incident types. Involving business stakeholders in defining these levels ensures that technical priorities match organizational goals.
- Define clear and measurable criteria: Establish specific and objective criteria for each severity level. Consider system availability, service disruptions, number of affected users, response time requirements, and business process dependencies. Clearly define the thresholds that differentiate one severity level from another to avoid ambiguity.
- Leverage historical incident data: Keep a detailed record of incidents, including their causes, impact, response times, and outcomes. This information is invaluable for identifying trends, recurring issues, and gaps in your current classification. By analyzing this data, you can adjust severity levels to reflect real operational conditions rather than assumptions. Sharing these insights across teams promotes learning and continuous improvement in your incident management process.














.jpg?upsize=true&upscale=true&width=780&height=205&name=how-to-create-a-service-level-agreement%20(1).jpg)
