Organizations today must prioritize IT process automation to stay competitive. Automating repetitive and complex IT tasks, such as server management and network monitoring, lets organizations free up resources, reduce the risk of human error, and allocate more resources to strategic initiatives.
Don’t take our word for it: organizations and financial leaders increasingly embrace automating IT processes. Indeed, nearly two-thirds of CFOs consider automating tasks a strategic priority.
But putting automation into action isn’t always straightforward. Deciding which processes to automate, figuring out how to fit new tools into existing systems, and keeping things flexible as needs change can be tricky. This guide is here to help. It covers the basics of automation, outlines its benefits, shares real-life examples, explores tools you can use, and offers tips for getting it right.
What is IT process automation?
IT process automation (ITPA) refers to using software to automate IT tasks and workflows, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors. It streamlines operations by enabling systems to handle repetitive tasks, respond to incidents, and manage complex workflows without direct human intervention.
Automation in IT has grown significantly, driven by increasing demands for efficiency, reliability, and security. Organizations use ITPA to reduce downtime, accelerate incident resolution, and improve compliance.
For example, a service desk can automate ticket assignments based on priority and workload. When an issue is reported, the system automatically categorizes it, assigns it to the appropriate technician, and sends status updates to the user—eliminating delays and manual triaging.
Traditional automation often requires custom scripting or coding. However, nowadays, modern platforms provide user-friendly interfaces for building workflows without code. Many IT automation tools offer drag-and-drop configurations, prebuilt workflow templates, and integration options, making automation accessible even to teams without programming expertise.

What is an IT process?
Before understanding automation, it's important to define what an IT process is. IT processes are structured activities that support an organization's technology infrastructure, software applications, and IT services. These processes ensure smooth operations and consistent performance across an IT environment.
Examples of IT processes include:
- Incident Management: Handling IT service disruptions and resolving them efficiently.
- Change Management: Managing system updates and modifications while minimizing risks.
- User provisioning: Granting and revoking access to systems and applications.
- Data backup and recovery: Ensuring critical business data remains available and secure.
Each of these processes follows specific steps, often requiring approvals, documentation, and execution in a defined sequence. Automating them improves consistency, reduces manual errors, and accelerates execution times.
Why automate IT processes?
Automating IT processes benefits organizations in multiple ways. Reducing manual intervention not only increases efficiency but also enhances security, compliance, and scalability.
1- Reduced operational costs
Manual IT tasks require significant time and labor. Automation decreases reliance on manual efforts, reducing costs associated with repetitive work. As we already mentioned, automated workflows improve resource allocation and allow IT teams to focus on higher-value activities.
2- Faster response times
IT incidents, outages, and cybersecurity threats demand quick action. Automated processes allow systems to detect, analyze, and respond to events faster than human operators. This minimizes costly downtimes and mitigates potential damage.
3- Improved accuracy and compliance
Human errors in IT tasks can lead to misconfigurations, security vulnerabilities, and compliance issues. Automation enforces standardized procedures, reducing mistakes and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
4- Scalability
As organizations grow, IT demands increase. Manual processes can become bottlenecks, limiting scalability. Automation enables IT teams to handle higher workloads without proportionally increasing headcount or complexity.

IT process automation examples
ITPA can be applied to a wide range of tasks, from routine maintenance to complex orchestration of services. Here are some common use cases:
Automated incident response
IT teams use automation to have a better incident management process that lets them detect, classify, and respond better and quickly.
For example, an automated system can detect a server failure, create a ticket, assign it to the right technician, and attempt predefined remediation steps before escalating the issue.
Patch management
Keeping software up to date is crucial for security and performance. Automated patch management tools scan systems, identify outdated software, and apply patches according to predefined schedules without manual intervention.
User provisioning and deprovisioning
When employees join or leave an organization, IT teams need to grant or revoke access to systems. Automation streamlines this process, ensuring users have the right access levels while maintaining security policies.
Backup and disaster recovery
Automated backup solutions create, verify, and restore backups on a scheduled basis. In case of data loss or system failure, these solutions provide rapid recovery options, minimizing downtime.
Security compliance enforcement
ITPA tools help enforce security policies by automatically monitoring system configurations, detecting non-compliant settings, and making corrections in real-time.

How to implement IT process automation
Implementing automation requires careful planning, the right tools, and ongoing optimization. Below are key steps to successfully adopt IT process automation in an organization.
1. Identify repetitive and time-consuming tasks
The first step is to assess which IT processes consume significant time and resources. Look for high-volume tasks prone to human error, such as password resets, log monitoring, or software deployment.
2. Define automation goals
Clearly outline what automation should achieve. Whether the goal is reducing response times, improving security, or cutting costs, setting clear objectives helps measure success and refine strategies.
Choosing the right tool depends on the complexity of the tasks and the existing IT environment.
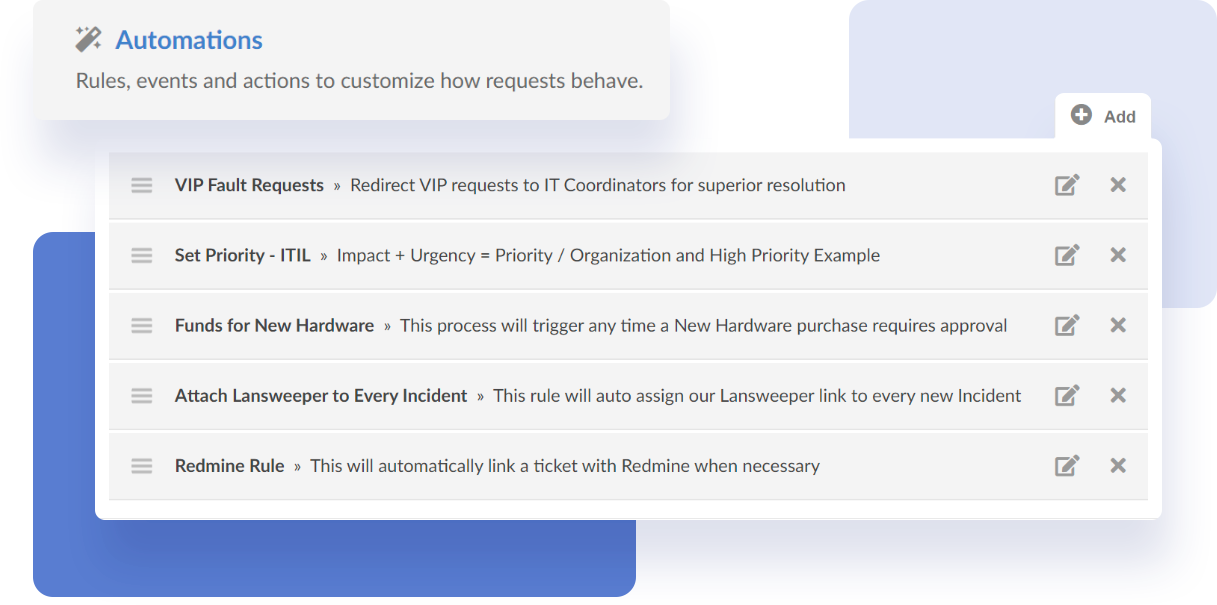 3- Choose the right IT automation tools
3- Choose the right IT automation tools
Selecting the right mix of tools requires evaluating the organization's existing IT environment, automation goals, and integration needs. Some options include:
- IT Service Management (ITSM) tools: Many ITSM platforms, Like InvGate Service Management, offer built-in automation features that help IT teams manage incidents, service requests, and all kinds of workflows more efficiently. These tools integrate with other IT systems, allowing automated ticket creation, approvals, and escalations.
- Workflow automation platforms: Some organizations use standalone workflow automation tools, which may or may not be part of ITSM solutions. These platforms enable the automation of multi-step IT processes, approvals, and data synchronization across different systems.
- Robotic process automation (RPA): RPA is useful for automating repetitive, rule-based tasks such as password resets, data entry, and account management. It mimics human interactions with software, reducing the need for manual work.
- Infrastructure as code (IaC): IaC tools automate IT infrastructure provisioning, configuration, and deployment. They help standardize infrastructure management, reducing errors and improving scalability.
- Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR): SOAR solutions are designed for security teams to automate threat detection, investigation, and response. These tools integrate with security information and event management (SIEM) systems to improve incident handling.
4. Map out workflows and test automation
Document the steps involved in the process and determine how automation will interact with existing systems. Running pilot tests ensures the automation functions as expected before deploying it across the organization.
5. Monitor and optimize
After implementation, regularly review automated processes to identify inefficiencies or failures. Adjust workflows and configurations as needed to keep automation effective and aligned with business needs.

Key takeaways
The reliance on manual processes often leads to inefficiencies and errors. Automation provides a practical solution to boost reliability, accelerate response times, and alleviate the strain on IT teams.
Organizations that adopt IT process automation gain a competitive advantage by improving IT operations and service delivery.
- IT process automation improves efficiency by reducing manual effort, minimizing errors, and enhancing compliance.
- Common applications include incident response, patch management, user provisioning, and security enforcement.
- Successful implementation requires identifying repetitive tasks, selecting the right tools, and continuously optimizing workflows.
- Automation supports IT teams in handling growing demands, reducing costs, and maintaining system reliability.















