There is no way around it: Incidents are bound to happen. Whether it’s a minor hiccup or a major outage, how your team handles these situations can make or break your business’s reputation.
This is where a well-defined Incident Management process comes into play. It’s not just about fixing issues; it's about doing so efficiently, minimizing impact, and ensuring that similar problems don’t occur in the future.
Understanding and implementing an effective Incident Management process is crucial for maintaining smooth operations. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from the basic concepts to the step-by-step actions you can take to ensure your process is robust and effective.
Let's get into it!

What is an Incident Management process?
An Incident Management Process is a structured framework that IT teams use to handle unplanned disruptions in IT services. This process is a critical component of IT Service Management (ITSM) and ensures that IT teams can handle incidents effectively, maintaining service quality and availability.
Its main goal is to restore normal operations as quickly as possible while minimizing impact on users and business processes. The process involves several steps: logging incidents, categorizing and prioritizing them based on severity, assigning responsibility to the appropriate support personnel, resolving the issue, and documenting the resolution.
Why do you need an Incident Management procedure?
A formal Incident Management procedure ensures consistency and efficiency in handling IT service disruptions. Without it, responses can vary depending on who is available or how the problem is discovered, leading to delays, duplicated effort, or incomplete resolutions.
Having a documented procedure guarantees that incidents are properly logged, tracked, and communicated, making it easier for teams to follow best practices. It also enables organizations to analyze past incidents, identify recurring patterns, and implement preventive measures. For example, if a network outage affects multiple departments repeatedly, recorded incident reports can help pinpoint the root cause and prevent similar issues in the future.
Central to this approach is having an Incident Management process document. This formal guide outlines how IT teams handle incidents from detection to resolution, defining roles, responsibilities, workflows, escalation paths, and reporting requirements. It also links to related ITIL processes, such as Problem Management, Change Management, and Knowledge Management, helping teams coordinate their efforts effectively. Maintaining this document supports standardization, facilitates training for new staff, and provides a foundation for continuous improvement by allowing teams to review and refine procedures based on historical incidents.
Benefits of an IT Incident Management process
Implementing a structured Incident Management process brings multiple advantages to organizations:
-
Faster resolution of issues – Clear guidelines and defined responsibilities help IT teams respond quickly and reduce service interruptions.
-
Minimized downtime – Prioritization and escalation procedures ensure that critical incidents are addressed promptly, reducing the impact on business operations.
-
Efficient use of resources – Teams can allocate their efforts effectively, focusing on high-priority incidents rather than addressing all issues equally.
-
Improved user satisfaction – Consistent communication and faster resolution build trust with users, who experience reliable support when problems occur.
-
Better reporting and analysis – Detailed records of incidents allow IT managers to track trends, identify recurring issues, and make informed decisions to improve infrastructure and processes.
-
Compliance and accountability – Proper documentation ensures that organizations meet regulatory requirements and can demonstrate accountability for incident handling.
Types of Incident Management processes
Contrary to what some might think, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all Incident Management process. Different organizations, based on their size, industry, and specific needs, adopt varying processes tailored to their unique environments. Some companies might follow a strict framework, while others might have a more flexible, ad-hoc approach.
One of the most popular frameworks used to guide Incident Management processes is ITIL (formerly known as Information Technology Infrastructure Library). ITIL provides a set of best practices for IT Service Management, including Incident Management. However, some organizations choose to blend ITIL guidelines with their internal processes, creating a hybrid approach. Others might rely on agile methodologies, DevOps practices, or other ITSM frameworks to build their Incident Management strategies.
-
ITIL-based Incident Management follows a structured framework with standardized best practices for IT Service Management. It provides clear guidance for logging, categorizing, prioritizing, and resolving incidents, making it ideal for larger organizations that need consistency across teams and departments.
-
Hybrid Incident Management blends ITIL principles with internal processes or custom workflows. This approach gives organizations the flexibility to adapt standard practices to their specific needs while maintaining some level of structure and consistency.
-
Agile Incident Management emphasizes speed, collaboration, and iterative improvement. Teams focus on rapid response and continuous feedback between IT and business users, making it well-suited for environments with frequent changes or fast-moving IT projects.
-
DevOps-oriented Incident Management integrates development and operations practices to improve incident handling. It encourages automated monitoring, fast detection, and continuous learning from incidents, which is especially valuable when IT teams manage both infrastructure and applications.
-
Ad-hoc or informal Incident Management relies on individual experience and team judgment rather than a formal framework. While easy to implement, it can lead to inconsistent handling and limited tracking, and is generally used by smaller organizations or teams with lower incident volumes.
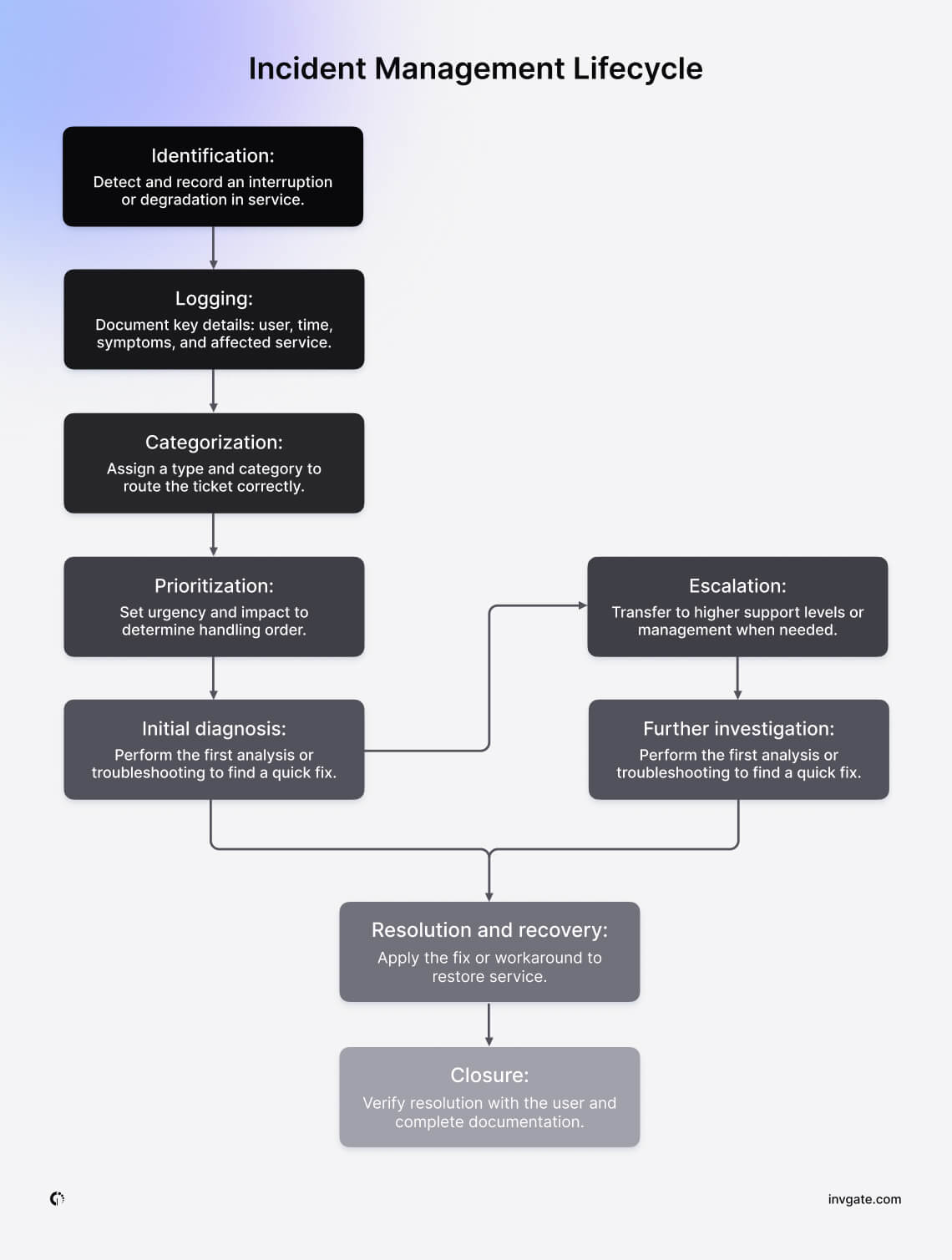
IT Incident Management process steps
Whether you’re following ITIL or creating a custom approach, certain steps are essential to ensure your Incident Management process is effective. The key is to have a clear, well-documented process that everyone on your team understands and follows. Below, we break down these steps and explain their importance.
1. Incident detection and recording
The first step in any Incident Management process is detecting and recording the incident. Detection can come from various sources—end-users, monitoring tools, or even automated alerts. It’s crucial to have a system in place that captures all relevant information about the incident, including the time of occurrence, symptoms, and affected services.
Recording incidents accurately is vital because this information forms the basis for all subsequent actions. It helps in analyzing the root cause, determining the impact, and deciding on the next steps. Without proper recording, incidents can fall through the cracks, leading to bigger issues down the line.
2. Classification and prioritization
Once an incident is recorded, the next step is to classify and prioritize it. Classification involves categorizing the incident based on its type, such as a network issue, software bug, or hardware failure. This helps in routing the incident to the appropriate team or individual for resolution.
Prioritization, on the other hand, determines the urgency of the incident. Not all incidents are created equal—some require immediate attention, while others can wait. Prioritization ensures that critical incidents are addressed first, minimizing their impact on business operations.
3. Incident assignment
After classification and prioritization, the incident needs to be assigned to the right team or individual for resolution. The assignment should be based on the expertise required to resolve the incident efficiently. For example, a network-related issue should be assigned to the networking team, while a software bug might go to the development team.
Clear assignment of incidents prevents confusion and ensures that the right resources are focused on resolving the issue. It also helps in tracking the progress of the incident and ensuring accountability. Automatic ticket assignment is a good option to streamline your process.
4. Incident resolution and recovery
Incident resolution and recovery is the stage where the actual problem-solving happens. The assigned team works to identify the root cause of the incident and implements a solution. The goal is to restore normal service operation as quickly as possible while ensuring that the solution is sustainable and doesn’t cause further issues.
Recovery might involve rolling back to a previous state, applying patches, or implementing workarounds. It’s essential to test the solution to ensure that the incident has been fully resolved and that normal operations can resume.
5. Incident closure and documentation
Once an incident is resolved, it’s crucial to close it formally and document the entire process. This includes recording what caused the incident, how it was resolved, and any lessons learned. Proper documentation is essential for future reference and to prevent similar incidents from recurring.
Incident closure also involves communicating the resolution to the affected stakeholders and ensuring that they are satisfied with the outcome. It’s a good practice to conduct a post-incident review to identify any areas for improvement in the process.
Automating the Incident Management process
Most Incident Management tools and ITSM platforms let you automate core aspects of the Incident Management process to improve efficiency and consistency. Typical automations include:
-
Ticket creation and logging: Automatically capture incidents from email, chat, monitoring tools, or self-service portals.
-
Categorization and prioritization: Apply predefined rules to assign categories and set priorities based on impact and urgency.
-
Routing and assignment: Direct tickets automatically to the correct team or agent based on expertise or workload.
-
Notifications and updates: Keep users informed with automatic alerts about ticket creation, status changes, and resolution times.
-
SLA monitoring: Automatically track service level agreements and trigger escalations when deadlines are at risk.
Beyond these basics, more advanced automations can further enhance the Incident Management process:
-
Automated resolution suggestions– Use historical data or AI recommendations to suggest potential solutions to agents.
-
Recurring incident detection: Identify patterns in incidents to flag recurring issues and trigger preventive actions.
-
Dynamic priority adjustment: Automatically escalate incidents if related events indicate a higher impact than initially assessed.
-
Workflow integration: Connect Incident Management with other ITSM processes, like Problem Management, Change Management, or Asset Management, to automate handoffs and approvals.
-
Analytics and reporting automation: Generate dashboards and trend reports automatically to track performance and identify improvement opportunities.
Using InvGate Service Management as your Incident Management software
InvGate Service Management provides a structured environment to manage the full ITIL Incident Management lifecycle, from logging to resolution. Designed around ITIL best practices, it helps teams handle incidents efficiently while maintaining visibility and control over service performance.
Automation handles repetitive tasks like categorization, prioritization, and escalation, while dashboards offer insights into ticket volume, SLA compliance, and resolution trends. Integration with assets and configuration items ensures that incidents are assessed and addressed with accurate context.
AI features further enhance incident handling by recommending suitable collaborators, spotting recurring issues, detecting potential major incidents early, and predicting tickets at risk of SLA breaches.
With customizable workflows and reporting, InvGate allows organizations to align the Incident Management lifecycle with their operational needs. Start your 30-day free trial today!
4 ITIL Incident Management process best practices
-
Encourage collaboration across ITIL processes.
Effective Incident Management depends on close coordination with other ITIL processes, such as Problem Management, Change Management, and Asset Management. Working together across teams ensures incidents are resolved efficiently, root causes are addressed, and any required changes are implemented smoothly, reducing the chance of recurring issues. -
Maintain clear communication with users.
Keeping affected users informed throughout the incident lifecycle helps manage expectations and improve satisfaction. This includes providing status updates, estimated resolution times, and any workarounds, ensuring transparency and trust while the incident is being resolved. -
Leverage knowledge management.
Documenting incident resolutions in a knowledge base allows teams to reuse solutions, speed up the resolution of similar incidents, and support self-service portals for users. A strong knowledge management practice turns incident handling into a proactive tool for reducing future disruptions. -
Focus on continuous improvement.
Regularly reviewing incident trends and performance metrics helps identify opportunities to improve processes, workflows, and tools. Continuous improvement ensures that the Incident Management process evolves alongside the organization’s IT environment, preventing recurring incidents and increasing overall service quality.














.jpg?upsize=true&upscale=true&width=780&height=205&name=how-to-create-a-service-level-agreement%20(1).jpg)
