Every incident goes through a series of stages before it’s resolved. It starts when an issue is reported, moves through diagnosis and resolution, and ends once the service is fully restored. That sequence is known as the Incident Management lifecycle.
Understanding how this lifecycle works is key to managing IT incidents efficiently. It gives structure to what could otherwise feel like a constant rush of unrelated requests, helping teams organize, prioritize, and act in a consistent way.
In this article, we’ll walk through each part of the Incident Management lifecycle, explain why it’s worth formalizing, and outline the main benefits it brings to IT teams and organizations.
In this article, we’ll break down what the Incident Management lifecycle is, why it’s crucial for your IT operations, and how you can implement it effectively using best practices like. So, grab a cup of coffee, sit back, and let’s dive into the world of Incident Management—minus the jargon and confusion!

What is the Incident Management lifecycle in ITIL?
The ITIL Incident Management lifecycle refers to the sequence of activities an organization follows to handle incidents from detection to closure. It gives structure to how incidents are identified, categorized, prioritized, resolved, and reviewed.
It’s important to clarify that in ITSM, “incident” doesn’t mean a security breach. Instead, it refers to any unplanned interruption or drop in the quality of an IT service — for example, a user unable to access email or a printer going offline.
The lifecycle defines how the service desk records these situations, assigns them for resolution, and restores normal service levels.
Why do you need an incident management lifecycle process?
A structured lifecycle provides clarity and repeatability. When you define explicit stages, roles, and standards for incidents, the service desk and support teams can respond faster, track tickets more consistently, and reduce service disruptions. Managers can monitor progress, escalate when necessary, and gather data for improvement.
Without such a process teams may operate in an ad-hoc way, leading to inconsistent incident resolution, missed service-level agreements (SLAs), and weak visibility into trends.
Furthermore, documenting how incidents flow gives you reference data for improvement (for example, identifying recurring causes and shifting into Problem Management). The lifecycle ties into business continuity and user satisfaction by enforcing a standardized way to handle incidents.
Benefits of the ITIL Incident Management lifecycle
Following a defined lifecycle for incidents provides several advantages:
-
Consistent responses: Every incident follows the same process, reducing confusion and delays.
-
Faster recovery: Teams waste less time deciding what to do and move directly into diagnosis and resolution.
-
Better visibility: Data collected during each step helps analyze patterns, workloads, and performance.
-
Improved user experience: Users receive timely updates and reliable resolutions.
-
Actionable insights: Metrics from incident trends can feed into preventive strategies and service improvement plans.
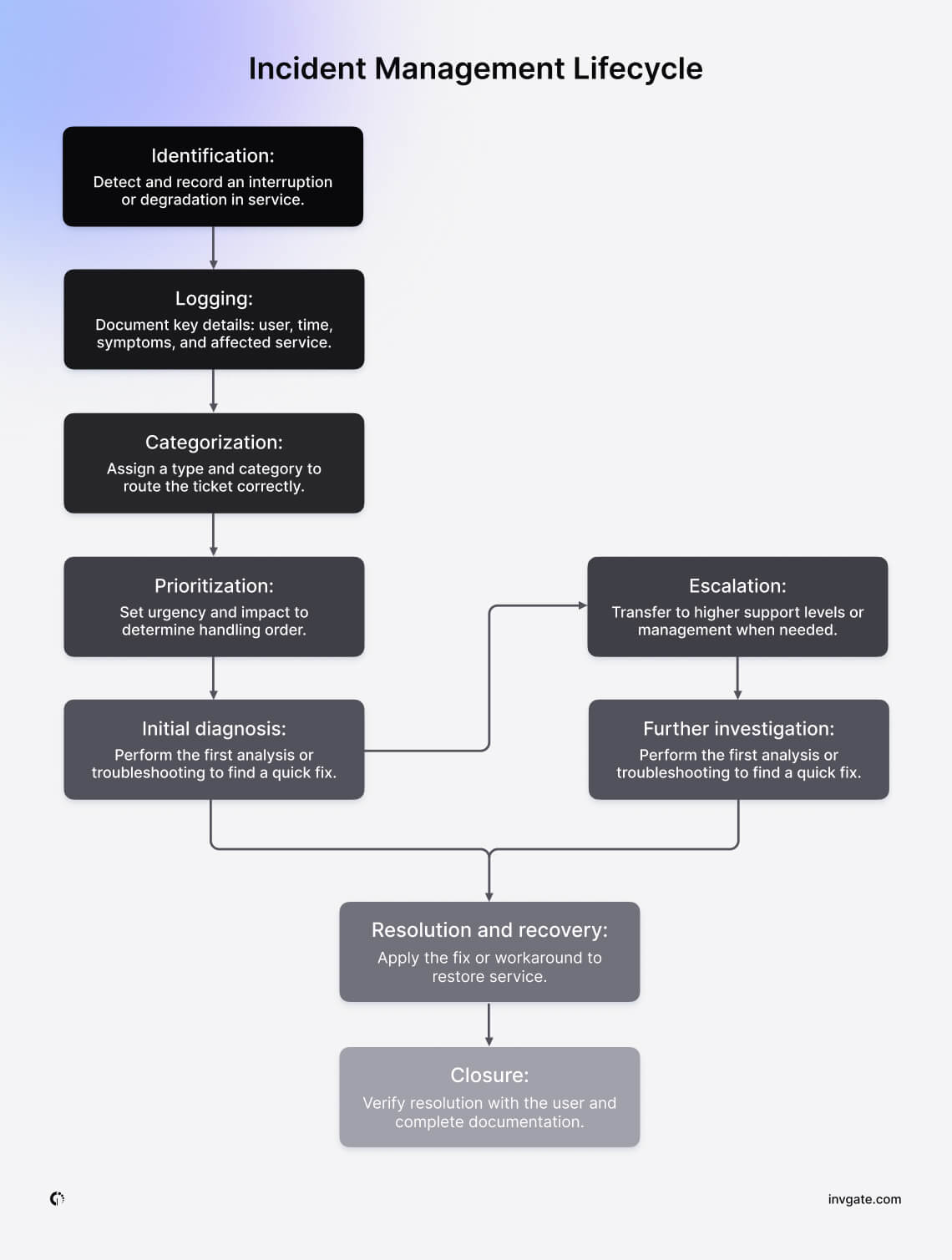
9 steps in ITIL incident lifecycle
Let’s go through each stage of the ITIL Incident Management lifecycle, one by one. The process is often visualized as a flow that begins when an incident is reported and ends when it’s closed after confirmation from the user.
1. Identification
The first step in the ITIL Incident lifecycle is Identification. This is where the incident is detected and reported. It could be through automated monitoring tools, a user submitting a ticket, or even an IT staff member noticing something off.
The key here is to recognize the incident as soon as possible so that the resolution process can begin. Early detection is crucial because the quicker you identify an issue, the quicker you can resolve it.
Many organizations rely on automated detection to spot service anomalies before users even notice them. For example, a network monitoring tool might report a drop in availability that triggers an incident automatically.
2. Logging
Once confirmed, the incident must be logged with complete and accurate details. Record who reported it, the affected service or asset, and a short description. Good logging practices save time later, especially when incidents are reassigned or analyzed.
A simple way to improve this step is to create predefined templates in your ITSM tool. They guide agents in collecting consistent data without needing to remember every required field.
3. Categorization
Categorization gives structure to your backlog. By classifying incidents (for instance, “hardware > printer,” “software > email,” “network > VPN”), you can route them automatically to the right team and generate meaningful reports.
When categories are too broad, teams struggle to find recurring problems. When they’re too granular, data becomes inconsistent. A balanced, reviewed list of categories makes the process easier to maintain and connects directly with Problem Management, since accurate data supports root cause analysis.
4. Prioritization
Here, the team determines how much attention the incident requires. ITIL provides a framework for this, where priority depends on impact and urgency: how many users or services are affected, and how fast the issue must be fixed.
A good practice is to make your prioritization matrix visible to everyone handling incidents. It avoids debates and speeds up decision-making. For example, if a payroll system is unavailable before a payment deadline, the priority is automatically high, regardless of how simple the fix might be.
Consistency at this stage helps maintain SLA commitments and manage workload fairly across teams.
5. Initial diagnosis
Next comes the initial diagnosis, where first-line support investigates the problem using troubleshooting guides or known solutions. The goal is to restore service quickly without unnecessary escalation.
Many common issues — like password resets or minor configuration errors — can be solved right here. At this stage, teams benefit greatly from a well-maintained knowledge base. When technicians can find previous cases or step-by-step instructions, they resolve incidents faster and reduce backlog.
6. Escalation
If the incident cannot be resolved during the initial diagnosis, it may need to be escalated. This means passing the incident to a higher level of support or involving more specialized teams.
Escalation is a critical step in ensuring that incidents are resolved efficiently, especially when the initial team lacks the expertise or resources to handle the issue. ITIL defines two types of escalation: functional (escalating to someone with the right skills) and hierarchical (escalating to higher management).
Clear escalation rules keep incidents from getting stuck in limbo. A quick win is to use automation for predefined conditions — for example, automatically escalating incidents that stay open longer than a set time. This prevents delays and maintains service continuity.

7. Further investigation
After escalation, if needed, the next step is a deeper Investigation and Diagnosis. This involves a more thorough analysis of the incident to pinpoint the exact cause.
The assigned team reviews system logs, configuration data, and related configuration items (CIs) to understand what triggered the issue. A structured diagnostic checklist can help teams stay consistent and avoid missing key details. In many cases, insights gathered here also inform Problem Management, especially when similar incidents appear repeatedly or point to a deeper system flaw.
8. Resolution and recovery
After identifying the cause, teams apply the fix or implement a temporary workaround to restore service availability. The goal is to return operations to normal as quickly as possible while maintaining accuracy and documentation.
If the solution involves a system change, it’s good practice to connect the record with Change Management to track approvals and avoid unplanned disruptions. Before moving on, validate that the incident is fully resolved and that users can resume work without issues.
9. Closure
Closure finalizes the lifecycle. Before closing the ticket, confirm with the user that the issue is resolved and update all related fields — time to resolution, category, and any associated configuration item. A clean closure supports accurate reporting and long-term process improvement.
Some organizations also perform short post-incident reviews for major outages. These sessions don’t assign blame; they identify what can be improved, from escalation paths to monitoring configurations. It’s one of the most effective ways to strengthen your ITIL practice over time.
The role of the incident lifecycle coordinator in ITIL
Within the incident management process, the role of the incident lifecycle coordinator (sometimes called incident manager or incident process owner) is to oversee the end-to-end lifecycle of incidents. They manage the incident management process itself, ensuring roles are defined, stages are followed, SLAs are met, and continuous improvement occurs.
The coordinator also reviews performance metrics, drives adherence to the defined lifecycle, and often chairs major incident review meetings. They might also liaise with Problem Management, Change Management, and Configuration Management to ensure incidents are not merely resolved but future recurrence is reduced.
Streamlining Incident Management with InvGate Service Management
InvGate Service Management supports the full ITIL Incident Management lifecycle by providing an organized environment to log, track, and resolve incidents.
You can automate categorization, assign priorities, and escalate tickets based on predefined workflows. Dashboards display incident volume, SLA compliance, and resolution time, helping teams monitor performance. The platform also integrates with asset data and configuration items, which makes identifying service impact faster and more accurate.
With built-in automation capabilities, routine tasks like incident categorization and escalation can be handled automatically, freeing up your team to focus on more complex issues. InvGate also helps you apply AI for Incident Management, bringing predictive insights and contextual recommendations. The system can suggest the right specialists for collaboration, detect recurring issues, and identify potential major incidents early to safeguard business operations.
Moreover, InvGate Service Management is highly customizable, allowing you to tailor the Incident Management lifecycle to fit your organization’s specific needs.
InvGate is certified by PeopleCert in ITIL best practices, including Incident Management. With its user-friendly design and powerful features, it’s an invaluable asset for any IT team looking to enhance their Incident Management capabilities. Start your 30-day free trial right now!
Best practices to handle the full lifecycle of Incident Management
Adopting ITIL processes is one thing; applying them effectively is another. Here are a few practical suggestions to help your team handle the lifecycle efficiently:
-
Keep communication open. Update users regularly and make it easy for them to follow progress through self-service portals or notifications.
-
Automate repetitive tasks. Use your ITSM tool’s automation to route incidents and trigger escalations instead of handling them manually.
-
Document and learn. Treat every incident as an opportunity to collect data. Record resolutions and workarounds in your knowledge base to prevent repetitive work.
Small, consistent improvements in how incidents are managed can have a strong impact on service quality and IT team productivity.














.jpg?upsize=true&upscale=true&width=780&height=205&name=how-to-create-a-service-level-agreement%20(1).jpg)
