The ITIL service lifecycle is a comprehensive framework for introducing ITIL principles into your organization. It provides a solid structure and valuable knowledge to help ensure the quality and effectiveness of IT Service Management practices are met throughout the whole lifecycle of a service.
It was originally contained within ITIL v3 and was replaced by the Service Value System (SVS) in ITIL 4. Nevertheless, it is still used by thousands of organizations; so, we're about to take a look at its main benefits, stages, and application.
Ready to get started with the service lifecycle? Let's go.

What is the ITIL service lifecycle?
The ITIL service lifecycle is a framework made up of all the processes needed to effectively manage the whole service lifecycle of any product or service offered by an organization. Its scope encompasses the entire lifecycle of IT services, from their initial concept to day-to-day management and operations, and their final retirement. It comprises five core stages or phases, each focusing on specific activities and processes.
The service lifecycle is one of the key differentiators of the ITIL framework. Essentially, it's a way of managing the functions, processes, and ways of working for effectively managing your products and services.
Benefits of applying the ITIL service lifecycle framework
The benefits of the service lifecycle framework include:
- Practical approach - The service lifecycle promotes adopting best practices by using a transparent and organized framework for managing IT services. There's a clear structure with defined start and end points.
- Clear responsibilities - RACI models underpin it so everyone knows what is expected of them regarding being accountable, responsible, consulted, and informed.
- Constant improvement - The Continual Service Improvement (CSI) stage keeps everyone honest; the business doesn't stand still, nor should its services. The ITIL lifecycle approach helps us to collectively up our game.
- Holistic approach to ITSM - The framework ensures that services are aligned with business needs, delivered effectively, and continuously improved over time.
The 5 stages of the ITIL service lifecycle
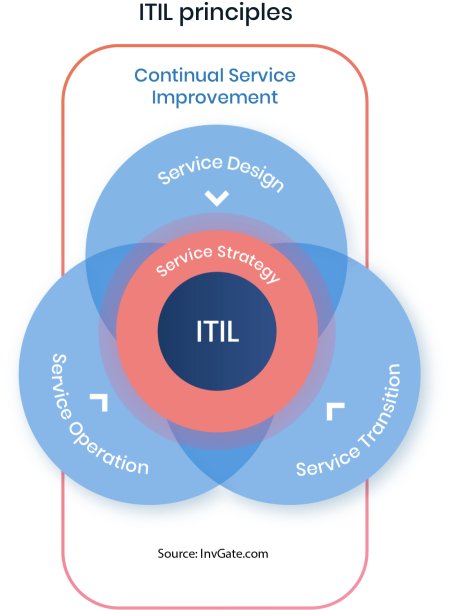
The ITIL lifecycle is the end-to-end life of a service, and each stage can be considered a quality gate in the progression of the service. On the other hand, service capabilities specifically refer to the assets, skills, and resources needed to deliver each stage. Both are required and must work together to effectively provide the service.
The ITIL 3 framework divides the service lifecycle into five stages to provide a logical and systematic approach to managing IT services from initial conception to ongoing operation and improvement. Each one has its specific goals, processes, and activities, and together they form a cohesive lifecycle that helps organizations deliver value to their customers and achieve their business objectives.
The five stages of the service cycle are:
- Service Strategy - Defines the perspective, position, patterns, and plans that a service provider needs to be able to execute to meet an organization's business outcomes and needs.
- Service Design - Designs IT services, together with the governing IT practices, processes, and policies to realize the service provider's strategy. The design stage is all about making sure that the proposed service is fit for purpose and use and is designed with the end user and supporting business value in mind.
- Service Transition - Provides the overall planning for service introduction, transformation, and retirement, as well as coordinating the required resources.
- Service Operation - Coordinates and carries out the activities and processes needed to deliver and manage services to business users and customers.
- Continual Service Improvement - Aligns IT services with changing business requirements by identifying and adopting improvements to IT services that support business processes.
Let's have a look at each stage in greater detail, to better understand their specific goals and processes involved.
ITIL service lifecycle stage 1: Service Strategy
Service Strategy is about getting it right from the planning stage so that the services we design, move, run, and improve align with the business objectives and customer and stakeholder needs.
The following processes are positioned in the strategy part of the service lifecycle:
- Strategy Management for IT services is responsible for pulling together all service strategy activities.
- Service Portfolio Management looks at the future state through the service pipeline, the current state through the catalog, and legacy or previous states through the retired services system.
- Financial Management ensures the appropriate accounting, budgeting, and costing activities are in place to ensure IT services deliver value.
- Demand Management identifies critical business periods through activity patterns and ensures the appropriate plans are in place to ensure service supply can support demand.
- Business Relationship Management ensures good relationships between IT and the rest of the business are developed and maintained.
ITIL service lifecycle stage 2: Service Design
Service Design creates the blueprint for the overall service. It designs the service with business objectives and user experience in mind, and comprises the following processes:
- Design coordination provides a single point of coordination for all service design activities.
- Service Catalog Management enables colleagues to access services more effectively by signposting them to the relevant service information.
- Service Level Management ensures services are underpinned with the appropriate Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to manage performance.
- Supplier Management ensures suppliers and partners are an effective part of the service ecosystems.
- Information Security Management ensures IT security best practices, policies, and procedures are in place.
- Availability Management ensures that service is available when needed and any unplanned downtime is minimized.
- Capacity Management captures the performance and throughput aspects of the service.
- IT Service Continuity Management ensures a plan is in place to maintain services if a business continuity or disaster recovery event occurs.
ITIL service lifecycle stage 3: Service Transition
The Service Transition phase deals with transitioning new or modified services into the live environment or returning them safely from production services. Service transition is made up of the following processes:
- Transition planning and support acts as a single point of coordination for all transition activities.
- Change Management ensures that the appropriate change governance is in place; that changes are reviewed in a way that is appropriate to the business, and reviewed and scheduled transparently and safely.
- Release and Deployment Management is in place to plan, schedule, and organize the build, test, and deployment of all software and hardware releases.
- Service Asset and Configuration Management captures and ensures that the information about the building blocks that make up our services and the relationships between them are accurate and maintained.
- Service Validation & Testing ensures the appropriate testing is in place to support safe change and release activity.
- Change Evaluation Process is in place to support major changes.
- Knowledge Management ensures the correct data, information, knowledge, and wisdom is in place at the right time to enable informed decisions.
ITIL service lifecycle stage 4: Service Operation
This phase involves the ongoing management and delivery of IT services to customers. The primary goal of service operations is to ensure that services are delivered efficiently and effectively to meet agreed-upon service levels. Service operation is made up of the following processes:
- Event Management detects events and alerts and takes appropriate action to prevent incidents.
- Incident Management resolves anything that breaks or disrupts IT services as quickly as possible and with as little adverse business impact as possible.
- Problem Management investigates the underlying root cause of incidents to prevent future occurrences.
- Access Management applies the principles of the information security policy agreed upon in the design phase of the lifecycle and ensures they are working in real life.
- Request Fulfillment coordinates and manages all service requests.
Service operations also contain the following functions:
- Service desk - The single POC for all business users to access IT help and support.
- Technical Management - Resources to support the service lifecycle – to design, build, transition, operate, and improve the technology needed to deliver and support IT services from a hardware and infrastructure perspective.
- Application Management - Resources to support the service lifecycle from a software and application perspective.
- IT Operations Management - Ongoing activities and procedures required to maintain and manage the IT infrastructure. This includes the management of data centers and IT facilities management activities such as power management and temperature control (especially important for server farms, comms rooms, and network equipment).
ITIL service lifecycle stage 5: Continual Service Improvement
The CSI phase is a continuous feedback loop that runs throughout the service lifecycle (the clue is in the name - it's continual!). It focuses on identifying areas for improvement in IT services, processes, and overall performance. Activities include service measurement and baselining, service metrics, service review meetings, customer feedback and implementing improvement initiatives.
The CSI phase of the lifecycle is supported by the Deming cycle to ensure improvement activities are planned, carried out, checked, and any further improvements acted upon.
| Scope | Goal | Value | |
| Service Strategy | Perspective, position, plans, and patterns that must be executed to meet an organization's business outcomes. |
|
A clear vision for the service to ensure it delivers business outcomes. |
| Service Design | Appropriate and innovative IT services designed to meet current and future agreed upon business requirements. | Design IT services effectively, so that only minimal lifecycle improvements will be required. | Services with the appropriate quality to meet business requirements. |
| Service Transition | New, retired, or modified services that must meet the expectations of the business. | Plan and manage service changes effectively, efficiently, and safely. |
|
| Service operation | Processes, functions, organization, and tools used to underpin the ongoing activities required to deliver and support services. |
|
The day-to-day support and delivery of IT services. |
| CSI | IT services that are aligned with changing business needs by identifying and implementing improvements to IT services, which support business processes. | Recommend improvements in each lifecycle stage. | Service improvements that are captured, prioritized and acted on. |
Applying the ITIL service lifecycle to a new service
So, now we've talked about the theory, the next step is applying it in real life. When doing so, following certain useful tips can come in handy to not get lost and get your focus right during each stage.
First, when planning new services, it's important to have a strong plan. Start with building a strategy so that you can aim for value. Design your services so that the appropriate availability, performance, security, and continuity practices are in place and your service is visible to end users and supported by the correct SLAs and contractual agreements.
Then, when making your service live, use Change and Release Management to deploy it safely, Service Asset and Configuration (SACM) to document the components and their relationships and Knowledge Management to support your people. When maintaining the service, use Incident Management to fix faults quickly and effectively, Problem Management to reduce recurring incidents, and request fulfillment to deal with service requests. Finally, build an improvement cycle so that your services improve and improve over time.
Service Lifecycle Management in ITIL 4
The ITIL service lifecycle was replaced by the Service Value System in ITIL 4. The SVS is a key part of it and facilitates value co-creation. It shows how all an organization's components and activities work together to create value.
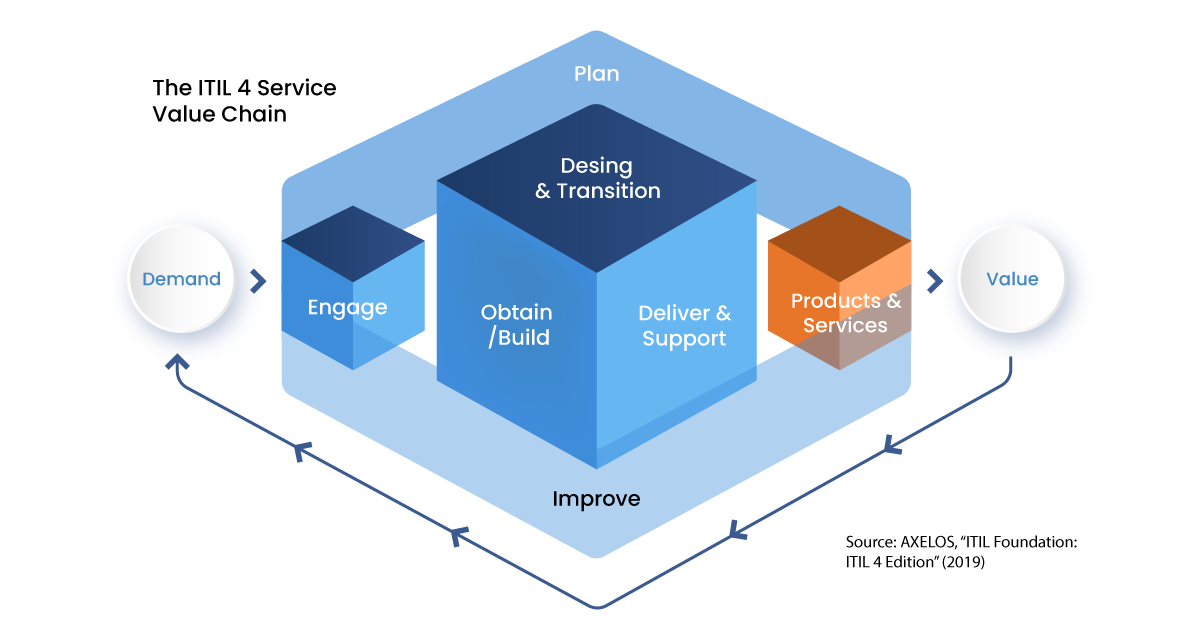
The SVS has interfaces with other organizations and forms an ecosystem through which it can create value for those organizations, their stakeholders, and customers. The SVS takes the ITIL v3 concept of the service lifecycle and focuses more on value co-creation by emphasizing all the multiple facets of service delivery, including the guiding principles and updated practices.
In conclusion
The ITIL Service Lifecycle is a structured and organized system defined in ITIL v3 and designed to manage a product or service throughout its lifecycle. It is divided into five phases, each one with their own specific processes: strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement.
Implementing in your organization will not only provide you with practical tools to ensure the whole service delivery process is working as it should, but it also promotes periodic revision and improvement to make sure that you're always striving for success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where does the service catalog fit in the ITIL Service Lifecycle?
The service catalog is positioned in the design phase of the service lifecycle.
What is the structure of the ITIL Service Lifecycle?
The service lifecycle is structured into five distinct partial strategies, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement.
Which of the stages of service lifecycle manage the technology?
Service Operations. One of the 4 ITIL service operation function is IT Technical Management, which is the function responsible for supporting IT hardware and maintaining a stable technical infrastructure