So, here's the thing. We all know that we need structure to work effectively, but where do we start with so many options available? One tool worth considering is the Business Model Canvas (BMC). Used effectively, it can give solid structure to your planning.
In this article we will examine how the model works and a few ways to use it effectively. Then, we will describe its best practices and some recommendations on getting started. Finally, we will explore possible alternatives.
Ready to get to know all about the BMC? Let's begin.

The Business Model Canvas, explained
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that helps businesses visualize and analyze their business models. It consists of 9 fundamental building blocks that describe the core aspects of a company's value proposition, infrastructure, customers, and finances (more on that later, we promise).
By using it, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of their overall business model, identify areas for improvement, and develop new strategies for growth. One of the key benefits of the BMC format is that it's very visual. Used adequately, it allows organizations to create a display of their business model in alignment with strategic business objectives and the overall value proposition.
The nine BMC building blocks were initially presented in 2005 by Alexander Osterwalder. They were based on his Ph.D. work on business model ontology, supervised by Yves Pigneur. Since its release, the authors have developed other related tools, such as the Culture Map and the Value Proposition Canvas, which have helped the BMC tool to evolve and added value to it.
Business Model Canvas examples
Some examples of the BMC include:
- Strategy planning
- Business planning
- Business modeling
If you're looking for inspiration or guidance on structuring your business plan, explore various business plan examples to see how others have applied the BMC to their strategies.
Lean Canvas vs. Business Model Canvas
Both the Lean and Business Model Canvas enable you to capture your entire model on a single page. The primary difference between them is that the Lean Canvas focuses mainly on solving a particular problem. The Business Canvas Model, on the other hand, is more sales orientated and usually focuses on selling products or services.

Advantages and disadvantages of the Business Model Canvas
Even though the BMC offers a series of features in order to effectively visualize and analyze your organization's business model, there are also some possible drawbacks to be aware of – and avoid.
To start on the right note, the benefits of the Business Model Canvas include:
- A clear and comprehensive business model overview in a single visual format. This makes it easier to understand, articulate, and communicate.
- Strong collaboration and breaking down silos. Using the BMC approach incentives people to work as one team, as it involves all stakeholders, and enables them to actively participate in developing, improving, and refining the business model.
- Colleagues constantly progressing with feedback (to borrow from an ITIL principle). The BMC approach allows for a fast and efficient testing of different business model configurations, speeding up the innovation process and reducing the time to market.
- A structured and systematic approach to analyzing and designing business models, which helps identify areas for improvement and innovation.
- A flexible approach that enables innovation instead of limiting it. The framework can be adapted to different types of businesses, industries, and customer groups.
However, if you choose to work with this management tool, you need to consider its potential disadvantages:
- Using the BMC approach effectively can be challenging without prior knowledge of business modeling concepts and terminology. You will need to put the work in and do some pre-reading to get the most out of it.
- Because it's so visual, it may oversimplify the complexity of a business model, making it more challenging to articulate some of the aspects of the organization's operations and performance. This makes it unsuitable for highly-specialized or complex businesses.
- Because it's a framework rather than a prescriptive standard that must be strictly adhered to, it doesn't provide detailed guidance on implementing or executing the business model, which can lead to difficulties in translating the canvas into action.
- It can rely on assumptions and hypotheses, which may not always be accurate or relevant for real-world situations.
The 9 building blocks of a Business Canvas Model
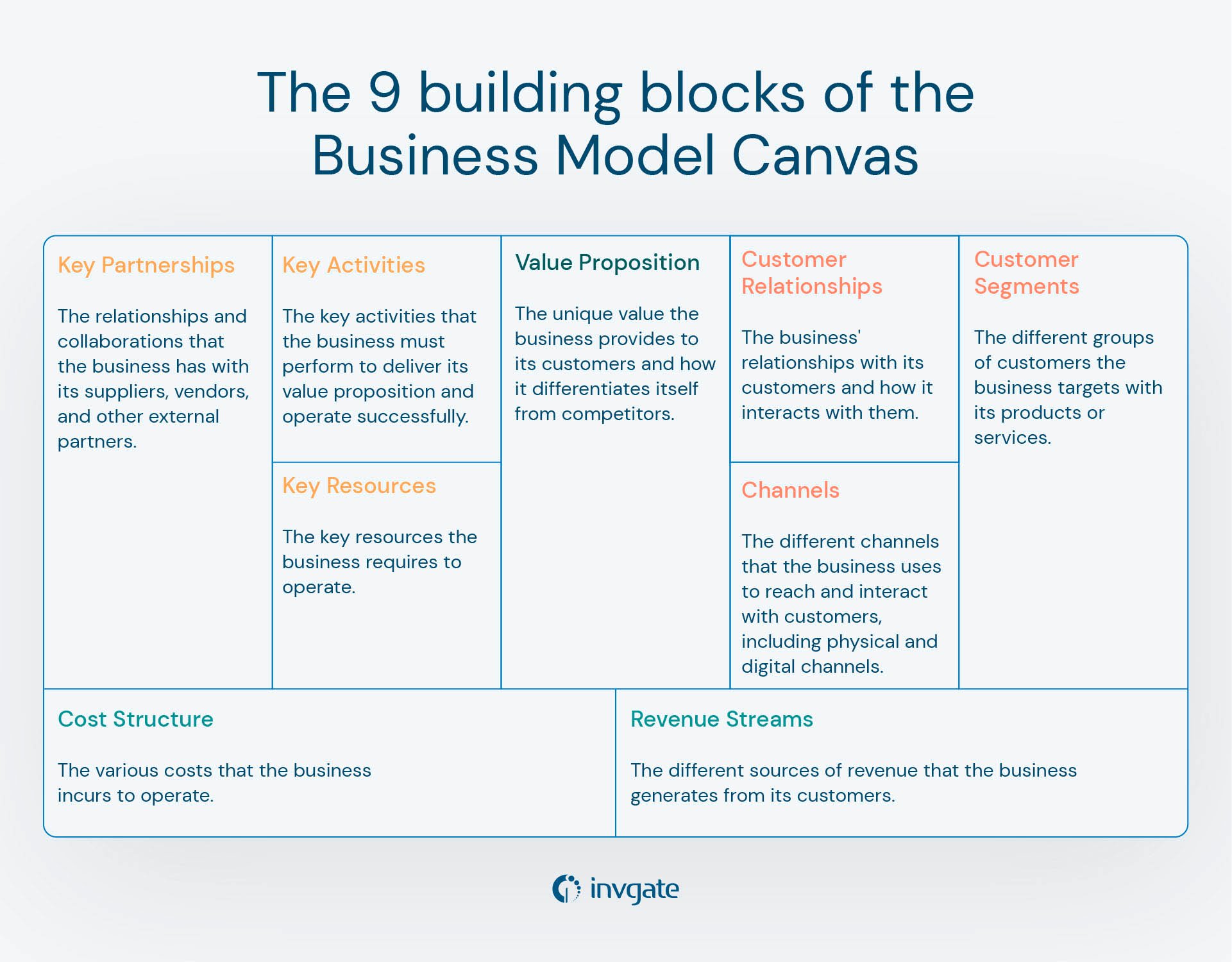
The Business Model Canvas is organized in nine building blocks that represent a business model's key elements. These building blocks are:
- Value Proposition - The unique value the business provides to its customers and how it differentiates itself from competitors. In other words, it’s what sets your business apart, what makes it special, and what value it brings.
- Customer Segments - The different groups of customers the business targets with its products or services. This building block looks at your most important customers.
- Customer Relationships - The business' relationships with its customers and how it interacts with them. This is a fundamental building block as not only does it help you build and maintain a relationship, it also enables you to map out the cost and deliverables needed to continue to improve that relationship.
- Channels - The different channels that the business uses to reach and interact with customers, including physical and digital channels.
- Key Partnerships - The relationships and collaborations that the business has with its suppliers, vendors, and other external partners.
- Key Activities - The key activities that the business must perform to deliver its value proposition and operate successfully. This building block helps you to define your most mission-critical actions and prioritize them accordingly.
- Key Resources - The key resources the business requires to operate, including human resources, physical assets, and intellectual property. This can also include relationships, distribution channels, and virtual assets.
- Revenue Streams - The different sources of revenue that the business generates from its customers, including one-time sales, recurring revenue, and other revenue streams. This building block also helps determine how each stream contributes to the business profit.
- Cost Structure - The various costs that the business incurs to operate, including fixed costs, variable costs, and other expenses. It also helps you identify your most expensive assets and activities to make effective financial plans for the future.
How to build a Business Model Canvas in 14 steps
The Business Model Canvas is flexible – no one size fits all. But for our money, there are 14 steps to effectively build it.
Step 1: Define the purpose
The first step is to define the purpose of the Business Model Canvas. Where are you now, and where do you want to be? What do you hope to achieve? Who is the target audience? Have you double-checked to ensure what you want to achieve is in line with the strategic objectives of the rest of the business?
Step 2: Identify the nine building blocks
Identify the nine building blocks of the BMC, review each in relation to your business, and understand their purpose.
Step 3: Define the Value Proposition
What will add value? Start by defining the unique value that your business offers to customers. This will be the foundation of your canvas.
Step 4: Identify your Customer Segments
Define the different groups of customers your business targets and their specific needs and preferences so you can focus and direct your efforts accordingly.
Step 5: Define Customer Relationships
Identify your business' relationships with its customers and how it interacts with them. You can also use this step to identify your most important relationships so you can focus more effort on maintaining and improving them.
Step 6: Determine the Channels
Identify your business's channels to reach and interact with its customers, including physical and digital channels. From a service desk perspective, this could be offering a tier 0 channel with self-service or AI-enabled support capabilities before providing tier 1 and level 2 channels which offer a more people-centric user experience.
Step 7: Define Key Partnerships
Identify your business's relationships and collaborations with its suppliers, vendors, and other external partners. Remember, it's not just relationships with customers and stakeholders that matter, your suppliers are part of your team, so manage those relationships appropriately.
Step 8: Identify Key Activities
Define the key activities that your business must perform to deliver its value proposition and operate successfully.
Step 9: Determine Key Resources
Identify the key resources that your business requires to operate, including people, knowledge and wisdom, financial assets, and IT assets.
Step 10: Determine Revenue Streams
Identify the different sources of revenue that your business generates from its customers. If you have a finance team, work with them to identify current revenue streams and plan for future ones.
Step 11: Determine Cost Structure
Work with your finance team to identify the various costs that your business incurs to operate, CAPEX, and OPEX costs.
Step 12: Build the Canvas
Once you have defined all of the building blocks, you can start creating the canvas to visualize what you are planning to accomplish.
Step 13: Review and refine
The BMC isn't a one-and-done approach. Review your model and seek feedback from your stakeholders to correct the course when needed.
Step 14: Keep going!
In the words of Walt Disney, "Keep moving forward." Build and refine your model over time to reflect current and future activities more accurately.
How to complete a Business Model Canvas
No one likes a blank page, do they? The difficult part is always getting started, but I promise, if you follow these steps, you'll be off to a great start:
- Start with the Value Proposition - Before you do anything else, fill in the Value Proposition block in the center of the canvas. This should describe the unique value that your business provides to customers and how it differentiates itself from competitors. Focus on getting this point right because value is everything in terms of the BMC.
- Add in your enablers - This will include your key activities, customer segments, relationships (both customer and supplier relationships) assets, key activities, and channels.
- Add in your financials - Put in your revenue dreams and your cost models to make your BCM more transparent and ensure there are no hidden costs.
- Progress iteratively with feedback - Once you have filled in all the building blocks, review your canvas, iterate, and redefine as needed. Seek input from stakeholders and make adjustments.
- Give the gift of clarity - Remember, this is a visual model, so don't get too stuck on the details or use too much jargon. The effect you're looking for is clear, concise, and visual.
- Relationships matter - We are talking about the relationship between each building block, so ensure they are correctly represented in your diagram.
Six alternatives to the Business Model Canvas
While the Business Model Canvas is a popular tool for developing and communicating a business model, other options are available too. Some alternatives include:
- Lean Canvas - This tool is similar to the BMC but focuses on startups and small businesses. It includes fewer blocks and focuses on validating hypotheses and testing assumptions quickly.
- SWOT Analysis - This tool helps to identify a business's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This can be a valuable tool for assessing the current state of a company and identifying areas for improvement.
- Business Model Innovation - This involves developing a new business model that is different from the traditional one used in the industry. It can be done through creative thinking, exploring new technologies, or adopting a new approach to customer relationships.
- Blue Ocean Strategy - This framework helps businesses to create new markets and uncontested market space. It involves identifying and focusing on areas of innovation that competitors have not explored.
- Value Proposition Canvas - This tool helps businesses to define and communicate their value proposition to customers. It focuses on the customer's needs, desired outcomes, challenges, and how the company can better meet those needs than its competitors.

Key takeaways
The Business Model Canvas or BMC is a strategic management tool that helps businesses visualize, design, and analyze their business models. Some of its common applications include business planning, value propositions, and modeling.
If you want to give it a shot to plan your organization’s strategy, make sure that you have your BCM template ready with the nine key elements that need to be completed. And don’t forget to follow through our six tips on how to get started!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you make a good Business Model Canvas?
To make a good Business Model Canvas, clearly define the unique value proposition of your business and ensure that the key building blocks of the canvas (such as channels, revenue streams, and cost structure) are aligned with the overall strategic objectives of the business. Review and improve the canvas as needed to continue improving and aligning with business needs.
What are the four types of business models?
The four types of business models are product, service, platform, and sub-subscription-based.
What are the three sections of the Business Model Canvas?
Value Propositions, enablers, and financial planning.















