Digital workplace solutions have played a huge role in streamlining the shift to remote work. It has improved the employee experience and organizational productivity and made work-from-home almost as smooth as in-office work. While it has certainly made work life easier for both employees and managers alike, from a cybersecurity standpoint, having a single integrated interface with all the data from the organization in one place leaves the company vulnerable.
As the place where all of the work in an organization gets done, an attack on the digital workplace solution can make the entire organization come to a standstill. And therefore digital workplace security is an important aspect of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy.
Why is digital workplace security important?
Implementing a digital workplace solution renders plenty of benefits to organizations, but without a proper cybersecurity strategy, it can create a lot of undefended fronts for an organization. Hackers or other malicious agents can exploit these vulnerabilities and create a cybersecurity nightmare for the company.
Particularly in the remote work context, the digital workplace creates a lot of access points for attackers to target. Device management is tricky when employees are logging in their home environment. Employees may use their personal devices for work and vice versa, and they are more susceptible to social engineering attacks and phishing outside the office environment.
Lack of digital workplace security creates the risk of data breaches
Companies face a huge risk of data breaches constantly. Hackers and attackers stand to gain a lot by targeting a company’s data. A data breach can also cause widespread damage depending on the nature of the company. For example, a pharmaceutical company working on developing a cutting-edge drug or an IT company developing a new technology may lose its competitive edge if its intellectual property is stolen. Even something as simple as a leaked internal memo can spoil the marketing plan or a product launch of a company.
Besides such indirect losses, threats like ransomware where hackers deny access to a company’s data for ransom can cause direct financial losses to the company. The average cost of a ransomware incident rose to $283,000 during a two-year period between 2018 and 2020.
Without a proper digital workplace security strategy, the risk of data breaches is amplified.

Safety and privacy of employees and clients
Besides protecting the company, digital workplace security is also important for ensuring the safety and privacy of its employees and clients. If an attacker gains access to the digital workplace, they can cause serious damage to them. In fact, the US Federal Trade Commission reported 1.4 million cases of identity theft in 2020.
An attacker can corrupt or leak data of your employees or your clients, or even gain access to their devices and cause further harm. For example, if you’re a SaaS provider, you may be storing client data in your servers. An attack on your servers will make your applications unavailable to your customer and disrupt their business processes. And it will create a data breach for their organization. If your company is developing IoT products, these devices will be using your cloud servers to function. Since these servers will be connected to your digital workplace, a hacker who gains access to your digital workplace may also gain access to these devices and cause a chain reaction leading to widespread damage to your clients and customers.
Legal risks of insufficient digital workplace security
A data breach or an attack on your digital workplace can lead to legal trouble too. End users and clients, and even your own employees may sue you for any damages they faced due to lack of security on your end. While it may be impossible to completely eliminate the threat of a cyber-attack, having an effective strategy can mitigate this to a large extent. And a robust cybersecurity mechanism can also limit your liabilities to an extent in case of an attack.
Besides lawsuits from your clients or customers, insufficient cyber security measures may invite legal trouble from regulatory commissions. For example, a HIPAA violation can result in fines anywhere between $50 to $50,000 and upto $1.5 million dollars a year. Similar data privacy legislations like GDPR, CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), and the Data Security Law from China can put your company at legal risk if your digital workplace security doesn’t meet these standards.
Digital workplace cybersecurity is directly reflected on client trust and brand reputation
A robust and secure digital workplace is important to build trust with your clients. If you’re in the IT service industry, you’d know that most clients want to know how you carry out your projects, communicate, and collaborate. Clients are also interested in your cybersecurity protocols, and digital workplace security can be an important factor for them.
Apart from the direct business possibilities of a secure digital workplace, your cybersecurity measures can also affect the value of your business. Every time there’s news of a security breach from an organization, there's associated news about the value of the company’s stock going down. Studies suggest that a year after a data breach, organizations have to spend a significant amount on advertising to build back their reputation.
How to reconcile digital workplace and cybersecurity
Security and convenience are often conflicting and most of the time one is compromised for the other. And since the main reason for investing in a digital workplace is the convenience, it is likely that security may take a step back. For example, to encourage employees to adopt a new digital workplace solution, organizations may opt for a simpler or familiar authentication method instead of a secure one.
But as we discussed earlier, the consequences of a security breach are so high that organizations must find a way to bring together cybersecurity along with the convenience of a digital workplace. A recent report from Interpol showed a 569% increase in malicious domain registrations between February and March 2020. Particularly during the initial implementation of a digital workplace solution or a shift to remote work, bad actors may take advantage of the confusion to carry out a cyberattack against the organization.
Begin from the very top
To reconcile cybersecurity and the digital workplace, the movement should start from the top. Since C-suite is also the primary target for hackers, it makes sense that they lead the way. The CTOs and CIOs have to emphasize the importance of security within the organization.
Cybersecurity: not an after-thought, but a design parameter
While training and raising awareness among your workforce about cybersecurity is important, baking in security features into your digital workplace solution will give your team a better perspective about the role of securing the workplace. For example, features like encrypted communication, two-factor authentication, and redundant storage in your workplace solution will drive the point home about the importance of security in the digital workplace. And building a secure solution from the scratch, or implementing security right from the start will keep your digital workplace safer.

IT asset management for digital workplace cybersecurity
Most digital workplace solutions have security-oriented modules, and IT departments can use these tools to improve digital workplace security, along with adding new security features. For example, IT asset management tools are used by organizations all over the world to keep track of their hardware and their software updated with the latest security patches. But with an asset management solution linked with your digital workplace, you can better monitor these assets. For example, if a laptop assigned to an employee is connected to an unsecured WiFi, or tries to plug in a virus-infected USB drive, an automated IT asset management system can quickly take measures to isolate the device and keep the rest of the workplace safe.
Integrate, but also microsegment
One of the main drivers of productivity and automation in a digital workplace is the level of integration. But it’s also a concern from a cybersecurity perspective. Bringing all in one place may create a single-point-of-failure in the organization, if someone gains access to the digital workplace, they gain access to everything the organization has online. Experts recommend a micro-segmentation approach as a possible solution to this conundrum. Traditionally, security is seen as creating an all-encompassing perimeter around the cyber assets of an organization. If an attacker gains access to one, they gain access to all. With micro-segmentation, individual security perimeters are created around different assets, providing each of them with its own security layer.
What does a transparent and secure digital workplace look like?
In a digital workplace, convenience equals transparency and as we mentioned earlier, this needs to go hand-in-hand with security. The security features implemented in a digital workplace should not curtail or hinder your employees’ access to it. The digital workplace and all of its functionality have to remain easy to access and use.
A transparent and secure digital workplace understands the role of transparency in its security. That is, even though transparency and security may appear at opposite ends, a non-transparent workplace could create cracks in its security. Take the case of shadow IT. It’s a rising phenomenon in many workplaces, where employees use unauthorized software or tools instead of the ones provided by the organization. And you can’t blame them, good employees want to get their job done, and they want to do it the best possible way. But as you can imagine, this creates a huge security risk.
So while securing the digital workplace, it’s important to ensure the participation of its users, and make sure the end result is still very much accessible. A transparent and secure workplace has secure but easy-to-use authentication systems, segmented but low latency storage systems. It may have a BYOD policy, but also have intensive training programs to keep employees aware of the security risks and precautions. It may have highly secure applications, but also an efficient IT service desk to quickly resolve the IT queries of the employees, so they don’t resort to shadow IT.
Best practices for minimizing the risks around digital workplace security
While the digital workplace is a relatively new concept, cybersecurity experts have come up with a couple of best practices for mitigating or minimizing the risks of a digital workplace.
Integrate all the way, but also add separate security layers
To get the best out of the security tools used for a digital workplace, a high level of integration is required. For example, for tools like IT asset management or automated AI threat detection to do the best job, it has to get the data from all the different tools to differentiate between normal behaviours and anomalies.
But a high level of integration also means one security lapse or loophole could expose the entire digital workplace to foreign threats. Therefore, the security layers of individual services or modules of a digital workplace have to be micro-segmented, to contain and quarantine external threats before it affects the entire system. And customize access control for the individual employee on a need-to basis. Provide access to everything an employee may need, but nothing more.
Extensive training
As we have discussed earlier, extensive employee training is paramount to a successful digital workplace implementation. Inculcate security practices into the work culture and make it second nature. Implement two-factor authentication for every device and service employees use, and encourage employees to use them on their personal devices as well.
Security from the ground up
Integrate security features into the digital workplace from the beginning, and consider security as a primary design parameter.
Leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning for threat analysis, detection, and more
Artificial intelligence tools are capable of analyzing threats and calculating the risk. These tools can also reduce the workload on the cybersecurity team as they can automatically monitor for, detect, and contain threats consistently.
Here’s what you can do in the next month to secure your digital workplace
Implement two-factor authentication throughout the organization
If you haven’t already, implement two-factor authentication for the digital workplace. Make sure all the devices, services, and software used in your organization need two-factor authentication to access. A report from 2019 by Microsoft shows that 2FA prevents 99.9% of all automated attacks.
Account for all the devices and software used in the organization
Once you have an inventory of all the software and devices your employees use, you’ll be a lot closer to a secure digital workplace than you were before.
Once you have these details, analyze every one of them for known security flaws and update your cybersecurity policy to cover them. Replace outdated devices, update device firmware and software to the latest versions, and make sure all the software has the relevant licenses.
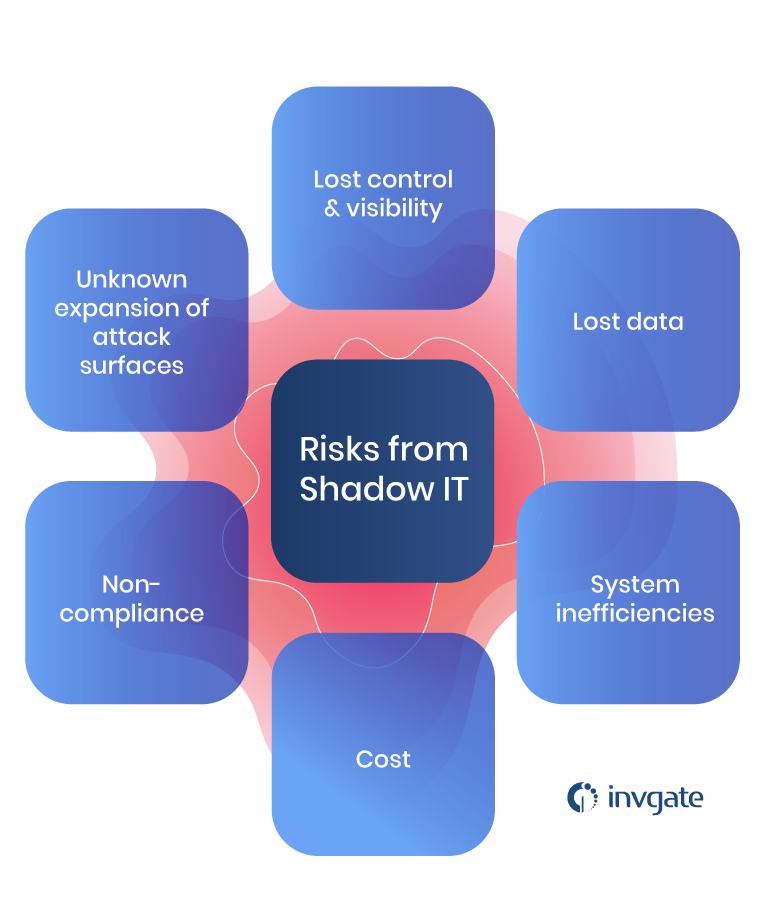
Most organizations have some level of shadow IT. Employees will be using tools they came across or found useful and the IT department will be unaware of them. By getting a complete list, the IT department can either provide more secure alternatives to the employees or take steps to mitigate the risk these apps possess. You can start with a simple excel sheet, but in the long run, an IT asset management software will be your friend here.
Conduct cybersecurity training for all employees
Make sure your employees are aware of the risks and the best safety practices. Conduct exercises and drills to make sure your employees retain this information and put them to practice.
Review your cybersecurity policy
Review your cybersecurity policy to make sure it covers threats like ransomware and crypto-jacking which are on the rise these days. Even if you have a robust cybersecurity team, it’s best to get your security policies evaluated every once in a while by a third party, just to make sure you haven’t missed anything.
Frequently asked questions
What makes digital workplaces susceptible to cyber threats?
Unlike a physical workplace, a digital workplace presents more vectors or access points for a bad actor to gain entry. Since the devices are not located within a physical office space, they may even be able to gain physical access to employee devices. Simply put, a digital workplace creates a lot of access points for attackers to enter, and for the organization to defend.
What are the basic features for a secure digital workplace?
- All devices and services must have two-factor authentication.
- Redundant and secure storage for sensitive data.
- IT asset management tools for keeping software and device firmware updated.
- A robust IT security policy
What is shadow IT and how can it pose a threat for the digital workplace?
Shadow IT is a situation in which employees of an organization use unauthorized services and software for their job instead of the ones provided by the organization. These software and services may have unknown security risks and it presents a threat to the organization’s cyber security.