Are you curious about what a system administrator does? Maybe you want to become one yourself. This blog will guide you through everything you need to know. From responsibilities to the systems they manage, we've got you covered.
What is a system administrator?
The system administrator role, or sysadmin, involves managing and maintaining an organization’s computer systems. They ensure that these systems run smoothly without interruptions.
Key responsibilities include:
-
Installing and configuring software and hardware: This includes operating systems and application software.
-
Managing user accounts and permissions: Ensuring only authorized users have access.
-
Monitoring system performance: Detecting and resolving issues before they impact users.
-
Implementing security measures: Protecting against hacking and data breaches.
Importance in an organizational IT structure
Sysadmins are crucial for the smooth operation of any organization. Without them, systems could fail, leading to a loss of productivity and revenue. They ensure that all IT resources are available and functioning. They also:
-
IT support and training users: Helping employees solve IT-related problems.
-
Plan for disaster recovery: Ensuring the company's data is backed up and can be restored.

Daily tasks and routines
Sysadmins have varied daily tasks that keep them busy. A typical day might include:
-
Checking system performance logs: Identifying and fixing issues.
-
Updating software: Patch Management to improve security and functionality.
-
Managing backups: Ensuring data is safely stored and can be retrieved.
-
Responding to support tickets within the service desk: Helping users with technical problems.
-
Configuring new hardware: Setting up computer servers, workstations, and network devices.
Sysadmins play a vital role in maintaining the IT infrastructure that keeps businesses running smoothly. Their work behind the scenes ensures that employees can focus on their tasks without worrying about technical issues.
Unlocking Career Progression
Discover the strategies to lifelong learning and evolvement in IT
Download for free
Why become a System Administrator?
Competitive salaries and benefits
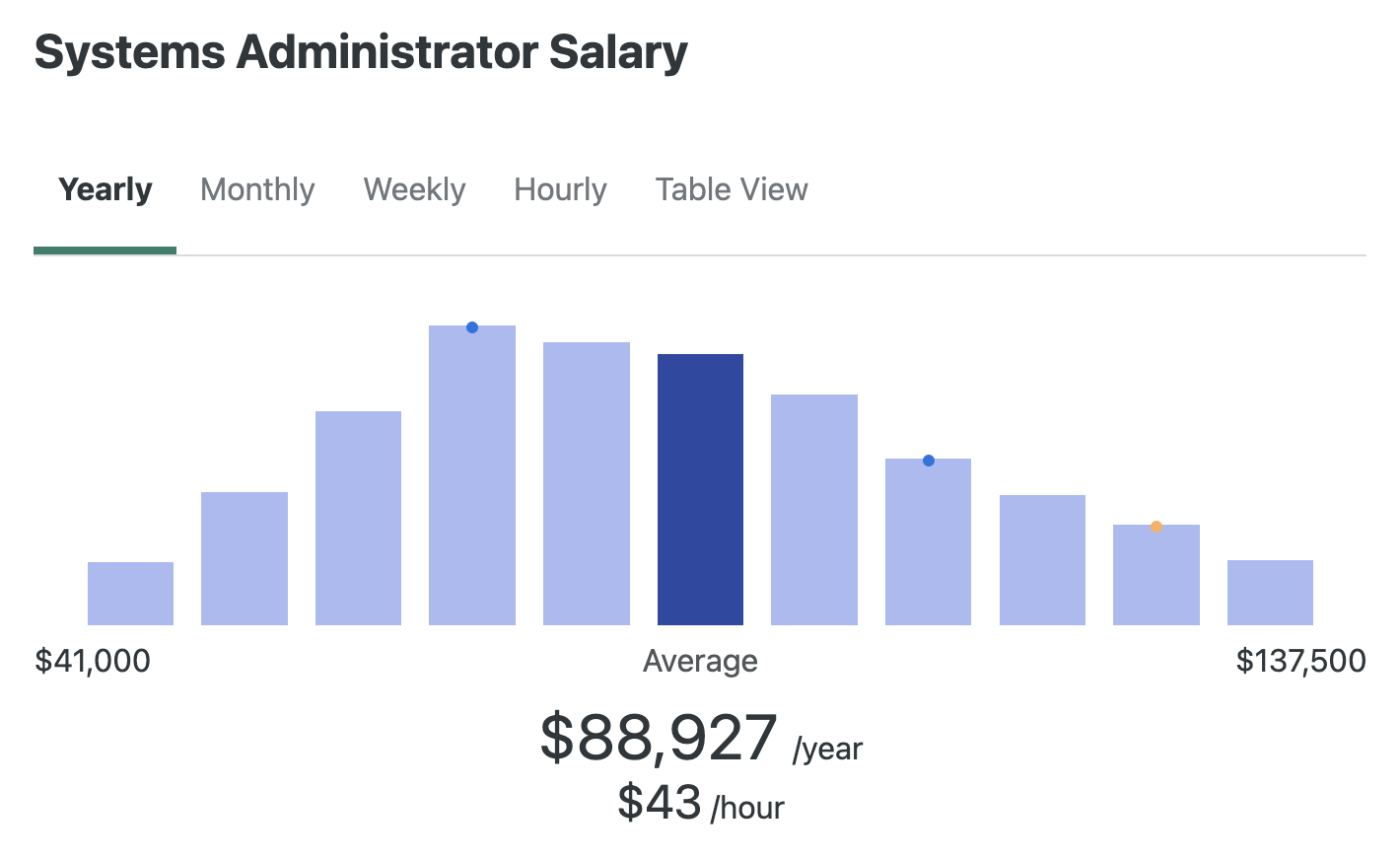
One of the main reasons for pursuing a systems administrator position is the attractive pay. Sysadmins often receive competitive salaries due to the expertise and responsibility their role demands.
According to sources, the average salary for a sysadmin in the United States is around $80,000 per year, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Additionally, many companies offer great benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off.
Job stability and demand in various industries
In today’s digital age, almost every industry needs system administrators. From healthcare and finance to education and technology, sysadmins are essential. This broad demand offers job stability.
Companies depend on their IT infrastructure to function, making sysadmins indispensable. During economic downturns, this role remains critical, ensuring continuous employment.
Opportunities for career advancement
The field of system administration offers many paths for growth:
-
Senior System Administrator: With experience, you can move into senior roles, handling more complex systems.
-
Network Administrator: Specializes in managing and troubleshooting network issues.
-
IT Manager: Oversees entire IT departments, coordinating between different teams.
-
Cloud Architect: Focuses on designing and managing cloud-based solutions.
Satisfaction from solving complex technical issues
If you enjoy problem-solving, this job offers immense satisfaction. Sysadmins face various challenges daily, from troubleshooting network problems to securing systems against cyber threats. Successfully resolving these issues can be very rewarding. Knowing that your work keeps the organization running smoothly provides a strong sense of accomplishment.
Choosing to become a systems administrator can lead to a fulfilling career with numerous benefits. The role offers competitive pay, job security, advancement opportunities, and the satisfaction of overcoming technical challenges.
How to become a system administrator
What are the educational requirements?
Relevant degrees: A strong educational background is important to become a system administrator. Most sysadmins have degrees in Computer Science or Information Technology (IT).
These programs cover essential topics like programming, networking, and database management, providing a solid foundation for the role. Degree programs with an emphasis on hardware, computer networks, and system administration are also highly regarded.
Certifications: Beyond degrees, IT certifications play a crucial role in a sysadmin’s career. Here are some key certifications:
-
CompTIA A+: This certification covers basic IT knowledge, including hardware, software, and networking.
-
CompTIA Network+: Focuses on networking concepts and troubleshooting.
-
Microsoft Certified Azure Administrator Associate: Validates skills in managing Azure environments.
-
Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA): Demonstrates expertise in networking fundamentals.
Certifications show employers that you have up-to-date skills and a commitment to your profession. They can also give you an edge in the job market. Understanding the sysadmin's responsibilities, such as checking on server health and monitoring critical processes, is essential for obtaining these certifications.
What experience is needed?
Entry-level IT roles: Starting in entry-level IT positions helps you gain the necessary experience. Common roles include:
-
Help desk technician: Provides support to end-users.
-
Technical support specialist: Troubleshoots and resolves various IT issues.
-
Junior system administrator: This person assists senior sysadmins with day-to-day tasks. They help manage computer hardware, such as desktops, and maintain computer servers.
These roles build your understanding of IT systems and the customer service skills employers require.
Internships and hands-on experience: Practical experience is vital. Internships offer opportunities to work alongside experienced professionals and tackle real-world problems. Additionally, setting up a home lab can help you experiment and learn:
-
Home Lab: Create a network at home to practice configuring servers, routers, and other devices.
-
Volunteer opportunities: Offer IT support to local non-profits or community groups.
Hands-on experience is invaluable; it helps you apply theoretical knowledge and develop problem-solving skills.
Becoming a system administrator involves a blend of education, certifications, and practical experience. You can become a software engineer, but a bachelor's degree in a relevant field and key certifications can also pave the way. Entry-level roles and internships provide the hands-on knowledge needed to excel.

How to gain practical experience as a system administrator
Starting with entry-level IT jobs is one of the best ways to gain practical experience. These positions allow you to understand the basics of IT support and system management, including gaining familiarity with internal systems.
You'll be developing both your technical skills and interpersonal skills. We mentioned some common roles that are well-received by recruiters; let's take a closer look at their job descriptions.
For example, starting out as a help desk technician can give you hands-on experience resolving user issues, answering technical questions, and helping with software installations. This role teaches you key skills, like troubleshooting hardware and software. You will also be providing technical support to users one-on-one, so it helps improve your customer service and communication skills.
A technical support specialist role could be a great way to start your career, too. You'd handle more complex problems than help desk technicians in this role. These specialists often deal with more intricate issues compared to help desk technicians.
The responsibilities include diagnosing and resolving network-related issues, advanced software troubleshooting, and possibly hardware issues. Handling network operations, which may involve monitoring an organization's network performance, configuring network devices, and ensuring connectivity, can be a significant part of the role.
Volunteer opportunities and internships
Gaining hands-on experience through internships and volunteer work is invaluable:
-
Internships: Many companies offer internships for aspiring system administrators. These positions let you work alongside experienced professionals, giving you insight into advanced tasks like server management and network configuration. Websites like LinkedIn and Indeed list numerous internship opportunities.
-
Volunteer opportunities: Offer your IT skills to non-profits, schools, or community centers. This not only helps you gain experience but also builds your resume. You might set up computer labs, maintain networks, or assist with IT projects.
These experiences are crucial for understanding the system administrator role, which involves maintaining servers, networks, and computer systems, managing software updates, and addressing technical issues.
Home lab setups for practice

Setting up a home lab allows you to experiment and learn in a controlled environment:
-
Hardware: Use old computers, routers, and switches to create a network. This setup gives you a playground to test configurations, install operating systems, and troubleshoot computer hardware without fear of causing real-world problems.
-
Virtual Machines: Tools like VirtualBox or VMware allow you to create multiple virtual machines on a single physical machine. Practice how to set up, install, and configure software. For example, different Linux operating systems, a Windows Server, and more.
Participation in online forums and communities
Engaging with online forums and communities is another great way to learn and grow as a systems administrator:
-
Forums: Websites like Reddit and Stack Exchange have active sysadmin communities. Here, you can ask questions, share knowledge, and solve problems collaboratively.
-
Online Courses and Tutorials: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and YouTube offer courses and tutorials on various sysadmin topics. These resources can help you stay updated with the latest technologies and best practices.
Key takeaways:
-
Entry-level roles: Start with help desk or technical support roles to build foundational knowledge.
-
Internships and volunteering: Gain real-world experience and build your resume.
-
Home labs: Practice in a risk-free environment using old hardware or virtual machines.
-
Online communities: Engage with other sysadmins, ask questions, and learn from their experiences.
Gaining practical experience involves a mix of entry-level jobs, internships, hands-on practice, and community engagement. These steps help you build the skills needed to become a proficient systems administrator.
What tools and technologies do system administrators use?
System administrators rely on a variety of tools to manage and automate tasks efficiently:
- InvGate Asset Management: This ITAM tool provides a centralized platform to track and manage hardware and software assets, ensuring compliance and optimizing resource allocation. It also aids in monitoring asset lifecycle, reducing costs, and improving security through better oversight of IT assets.
-
Nagios: This monitoring tool helps you keep an eye on network services, host resources, and server performance. It sends alerts when something goes wrong, allowing quick responses to issues.
-
Ansible: An open-source automation tool that simplifies complex tasks like software provisioning, configuration management, and application deployment. It uses simple YAML files to describe automation jobs, making it easy to understand and use.
-
Puppet: Another automation tool focused on managing the configuration of systems. Puppet ensures that the desired state of the system configuration is maintained, automating repetitive tasks and reducing human error.
Importance of scripting languages
Knowing scripting languages is crucial for system administrators:
-
Python: Widely used due to its simplicity and readability. Python scripts can automate a variety of tasks, such as file manipulation, data analysis, and even web scraping. It’s also powerful for writing custom scripts to manage servers and networks.
-
Bash: The default shell for many Unix-based systems, Bash scripting is essential for automating tasks in the command line. It’s used for writing scripts to manage system operations, automate daily security backups, and handle repetitive tasks.
Use of monitoring and security tools for system performance
Monitoring and maintaining security are key responsibilities of a system administrator:
-
Monitoring tools: Tools like Zabbix and Prometheus help in monitoring the health and performance of IT infrastructure. They provide real-time data and alert systems for issues, ensuring that you can maintain uptime and service quality.
-
Security tools: Wireshark and Snort are examples of tools used for network security. Wireshark allows you to see what’s happening on your network at a microscopic level, while Snort is an intrusion detection system that helps identify potential threats.
Cloud Service Management
As businesses move to the cloud, system administrators must manage these environments:
-
AWS (Amazon Web Services): AWS provides a wide range of cloud services including computing power, storage, and databases. Knowledge of AWS allows you to set up and manage scalable, reliable, and secure cloud environments.
-
Azure: Microsoft’s cloud platform offers similar services to AWS but integrates well with other Microsoft products. Understanding Azure is crucial for managing cloud-based applications and services in organizations that rely on Microsoft technologies.
Key takeaways:
-
Popular Tools: Nagios, Ansible, and Puppet help automate and monitor IT tasks.
-
Scripting languages: Python and Bash are essential for writing scripts and automating tasks.
-
Monitoring and security: Tools like Zabbix, Prometheus, Wireshark, and Snort ensure system health and security.
-
Cloud services: AWS and Azure are key platforms for managing cloud environments.
A system administrator's toolkit includes automation tools, scripting languages, monitoring and security applications, and cloud service management platforms. These tools and technologies help streamline operations, ensure security, and manage complex IT environments efficiently.
Why is being a System Administrator challenging?
Technical complexities and troubleshooting
Systems administrators face many technical challenges. They must understand and manage multiple OS like Windows, Linux, and Mac. Each operating system has its own set of rules, commands, and quirks.
Additionally, they often deal with complex network configurations, server issues, and software bugs. Troubleshooting these problems requires a deep understanding of how systems interact.
High responsibility for system uptime and security
Uptime and security are critical. A system administrator's responsibilities include ensuring that systems are always available and secure. Downtime can cost a company money and reputation. Security breaches can lead to an organization's data loss and legal issues. Therefore, system administrators must implement robust security policies, monitor for threats, and respond quickly to incidents. This responsibility can be stressful because the stakes are high.
Continuous learning and staying updated with technology
Technology evolves rapidly. To keep up, system administrators must continually learn new skills and stay updated on the latest trends. This means reading articles, attending workshops, and sometimes getting new certifications. For example, cloud services like AWS and Azure frequently update their features and best practices. System administrators need to adapt to these changes to stay effective in their roles.
Managing user issues, user accounts, and expectations
User management is another critical challenge. Users often have problems with their devices or software and expect quick resolutions. Sometimes, these issues are simple, but other times they are complex and require significant troubleshooting. Moreover, users may not always understand the technical limitations or requirements, making it hard to manage their expectations. A good system administrator must communicate clearly and effectively to keep users satisfied while managing their own workload efficiently.
Key challenges:
-
Technical: Mastering multiple operating systems and troubleshooting complex issues.
-
Responsibility: Ensuring system uptime and security to avoid costly downtime and breaches.
-
Learning: Continuously updating knowledge and skills to keep up with rapidly evolving technology.
-
User management: Handling user issues and managing expectations while maintaining a high level of service.
Conclusion
Becoming a system administrator requires a combination of technical skills, problem-solving abilities, and a passion for keeping IT systems running smoothly. System administrators deal with technical complexities, high stakes for uptime and security, the need for constant learning, and people skills. These factors make the role demanding but also rewarding for those who enjoy solving problems and staying on the cutting edge of technology.
FAQs
What qualifications do I need to become a system administrator?
While a bachelor's degree in computer science or a related field is often preferred, it is not always necessary. Many employers value hands-on experience, relevant certifications, and a strong understanding of operating systems, networking, and security.
How much can I expect to earn as a system administrator?
The salary for system administrators varies depending on factors such as location, industry, and experience level. The median annual wage for system administrators is around $80.000 in the U.S.
Is there a high demand for system administrators?
Yes, the demand for skilled system administrators is expected to remain strong as organizations continue to rely on technology to support their operations. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 5% growth in employment for system administrators from 2021 to 2031, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations.