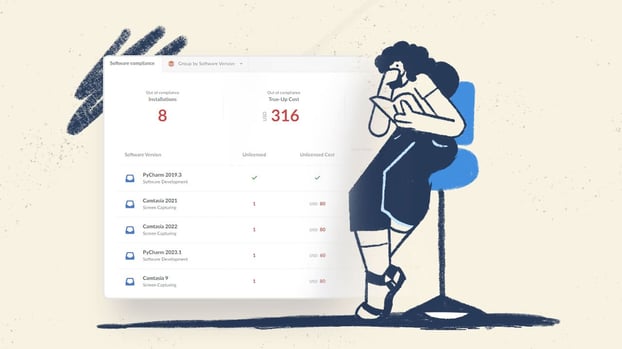
Cybersecurity requires more than just protecting data from threats—you have to manage risks, comply with regulations, and ensure your organization stays resilient in the face of attacks. But what's the role of GRC in cybersecurity? How does it help in shaping your organization’s cybersecurity posture?
In this article, we’ll explain the essentials of GRC in cybersecurity, explore how these practices integrate to create a strong security framework and walk you through actionable steps to improve your company’s security posture.
What is GRC?
GRC stands for Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance, and when applied to cybersecurity, it forms a cohesive framework that helps businesses not only protect their data but also ensure that they’re managing risks effectively and complying with relevant regulations.
- Governance establishes the policies, standards, and responsibilities needed to direct cybersecurity initiatives.
- Risk Management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating cybersecurity risks to reduce their impact.
- Compliance ensures the organization meets all legal, regulatory, and internal cybersecurity standards.
When these three elements are integrated, GRC becomes the backbone of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy, ensuring that security measures are aligned with business objectives, risks are properly managed, and legal obligations are consistently met.

The relationship between GRC practices and your cybersecurity posture
A company’s cybersecurity posture refers to its overall readiness and ability to prevent, detect, and respond to security threats. GRC practices directly influence this posture by providing a structured approach to managing security risks, enforcing policies, and staying compliant with industry regulations.
1. Governance: Setting the foundation for strong cybersecurity
In the context of cybersecurity, governance is about defining the rules, roles, and processes that guide how security is managed within an organization. A well-governed cybersecurity program will have clear policies in place that cover:
- Data protection protocols
- Incident response plans
- Roles and responsibilities for cybersecurity teams
Governance is crucial because it ensures that security efforts are coordinated across the organization. Without strong governance, even the best technical solutions can fall short because they may not align with the organization’s broader objectives or compliance requirements.
For example, if a company handles sensitive customer data, governance policies should dictate how that data is protected, who is responsible for monitoring it, and how incidents will be reported. Clear governance can prevent data breaches and provide a roadmap for swift responses when threats arise.

2. Risk Management: Proactively addressing cyber threats
Risk management is a core component of GRC that focuses on identifying and addressing potential threats before they materialize into security breaches. This process typically involves:
- Risk assessment: Identifying risks such as phishing attacks, malware, or insider threats.
- Risk evaluation: Determining the likelihood and impact of these risks.
- Mitigation: Implementing measures to prevent or minimize the effect of those risks.
Risk management strengthens a company’s cybersecurity posture by proactively addressing vulnerabilities. For example, if outdated software poses a risk of exploitation, a risk management plan would include strategies like updating systems or applying patches to reduce this vulnerability.
A structured risk management approach helps businesses focus on the most significant risks, reducing the likelihood of high-impact incidents.
3. Compliance: Ensuring regulatory and industry standards are met
The compliance aspect of GRC ensures that an organization meets the required legal, regulatory, and industry standards. Compliance frameworks like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) establish minimum security requirements that organizations must follow.
How GRC enhances an organization's resilience against cyber threats
Maintaining compliance not only helps businesses avoid fines and legal penalties but also reinforces their cybersecurity posture by ensuring that they’re adhering to proven security best practices.
For example, a healthcare organization that complies with HIPAA has strict guidelines on protecting patient data. This means they’re required to implement robust cybersecurity measures, such as data encryption, regular security audits, and employee training—all of which improve their overall security posture.
When applied effectively, GRC creates a unified approach that connects governance policies, risk management activities, and compliance requirements.
Ultimately, when they work together, these elements ensure that an organization’s cybersecurity efforts are effective and aligned with broader business goals. The result is a proactive and well-rounded security posture capable of adapting to new threats and regulatory requirements.

Steps to implement GRC in your cybersecurity strategy
For businesses looking to improve their cybersecurity posture, implementing GRC practices can be transformative. Here's how you can start:
1. Conduct a cybersecurity audit
First, start by assessing your current cybersecurity practices. A comprehensive audit will reveal gaps in governance, risk management, and compliance. This can include reviewing your existing policies, risk management processes, and compliance with relevant regulations.

2. Establish a governance framework
Once you’ve identified the gaps, create a governance framework that clearly outlines your cybersecurity policies and procedures. This should cover areas such as:
- Data protection protocols
- Employee roles and responsibilities in cybersecurity
- Incident reporting and response plans
The framework should align with your broader business objectives to ensure that cybersecurity efforts support your organization’s overall goals.
3. Identify and mitigate risks
Third, you should conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential cybersecurity threats. Once you’ve identified the risks, develop mitigation strategies to address them.
For example, if you find that phishing attacks are a significant risk, you might implement email filtering solutions and train employees to recognize phishing attempts.
4. Align with compliance standards
Make sure your organization is up to date with relevant cybersecurity regulations and standards. Assign a compliance officer or team to oversee this process. Many industries have specific frameworks they must follow, such as PCI DSS for payment processing or GDPR for handling personal data.

5. Continuously monitor and improve
Finally, you must be aware of the fact that cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving. 75% of security professionals have observed an increase in cyberattacks over the past year. Which means your GRC framework should be dynamic. Regularly monitor your security posture, update policies as needed, and conduct periodic audits to ensure continued compliance and risk mitigation.
Best practices for maintaining GRC
Once your GRC framework is established, follow these best practices to maintain and improve it:
- Regular audits: Conduct routine audits to ensure your organization remains compliant with regulatory standards and that your governance and risk management efforts are up to date.
- Employee training: Regularly train employees on cybersecurity best practices, incident reporting, and their roles in maintaining compliance.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously assess and update your GRC practices to adapt to new cyber threats and evolving regulations.

Who's responsible for GRC?
In larger organizations, GRC and cybersecurity may be handled by separate teams with distinct roles and responsibilities. The GRC team focuses on establishing policies, managing risks, and ensuring compliance across the organization, while the cybersecurity team is responsible for implementing and maintaining security controls, monitoring threats, and responding to incidents.
Despite the separation, these teams work closely together to align cybersecurity efforts with GRC objectives. The GRC team provides guidance and oversight to the cybersecurity team on risk management and compliance requirements. In contrast, the cybersecurity team informs the GRC team about emerging threats and the effectiveness of security controls.
Integrated GRC and cybersecurity team
In smaller organizations or in cases where cybersecurity is a critical concern, GRC and cybersecurity responsibilities may be combined into a single team. This integrated approach ensures that cybersecurity is embedded within the GRC framework, enabling a more holistic and efficient management of risks and compliance.
The GRC and cybersecurity specialists within this team collaborate to:
- Establish security policies and procedures aligned with business objectives and regulatory requirements.
- Conduct risk assessments to identify and mitigate potential threats to the organization's assets.
- Implement security controls and monitor their effectiveness in preventing and detecting cyber incidents.
- Ensure compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards.
- Develop and test incident response and disaster recovery plans.
Shared responsibility model
In some organizations, GRC and cybersecurity responsibilities are shared across different departments and teams. For example, the IT department may be responsible for implementing and maintaining security controls, while the legal and compliance department oversees regulatory compliance.
The GRC team coordinates and integrates these efforts to ensure a cohesive approach to risk management and compliance.
Regardless of the organizational structure, effective GRC and cybersecurity require close collaboration and communication between all stakeholders, including executive leadership, the board of directors, and employees across various departments.
GRC software and cybersecurity
To complement the work of GRC teams, organizations can adopt GRC software designed to integrate cybersecurity measures and streamline processes.
Here are some benefits:
- Integration of frameworks: Many GRC tools leverage established frameworks like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework to manage cybersecurity risks systematically. This integration allows organizations to assess their security posture and identify gaps effectively.
- Centralized data management: GRC software centralizes data related to policies, risks, and compliance efforts, facilitating better decision-making and visibility across departments. This holistic view helps organizations respond more effectively to cyber threats and regulatory changes.
- Automation of processes: By automating tasks such as policy management, compliance tracking, and risk assessments, GRC tools reduce manual effort and enhance efficiency. This automation is particularly beneficial in maintaining compliance with ever-evolving regulations.
- Real-time monitoring: Many GRC platforms offer real-time monitoring capabilities that help organizations track their cybersecurity posture continuously. This feature enables proactive identification of vulnerabilities and threats, allowing for timely response

Real-world applications of GRC in cybersecurity
Let’s take a look at how GRC practices are applied in various industries:
1. Financial institutions
Banks and financial services companies are subject to stringent regulatory requirements and handle massive amounts of sensitive data. Implementing GRC in cybersecurity helps these organizations manage risks such as fraud, data breaches, and insider threats while ensuring compliance with regulations like the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
2. Healthcare organizations
Healthcare organizations must comply with regulations like HIPAA, which requires strict controls over how patient data is stored, accessed, and transmitted. GRC practices ensure that healthcare providers can manage risks like ransomware and ensure patient privacy, all while staying compliant with HIPAA guidelines.
3. Retail businesses
Retailers often handle sensitive customer payment information, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. GRC in cybersecurity allows retail businesses to protect customer data, reduce the risk of breaches, and meet industry-specific compliance standards such as PCI DSS.
Conclusion
When it comes to protecting your business from cyber threats, relying solely on technical defenses like firewalls and antivirus software is no longer enough. Today, companies need a more structured and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity.
Understanding GRC within a cybersecurity context can benefit your business by providing a structured framework for managing not only external threats but also internal processes and regulatory obligations.
If your organization has not yet implemented GRC practices in its cybersecurity strategy, now is the time to start. A well-rounded GRC framework not only protects your business but also ensures that you’re prepared to meet future challenges head-on.