Cybersecurity threats are an ever-present danger for organizations; even a single vulnerability can lead to catastrophic consequences. One such vulnerability is CVE-2022-34713, a critical remote code execution vulnerability that affects Microsoft Windows Support Diagnostic Tool (MSDT).
This vulnerability can allow attackers to execute arbitrary code on victims' systems, leading to a complete compromise of the system. In this blog post, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of CVE-2022-34713, including its impact and how InvGate Asset Management can help organizations identify vulnerable devices, making it easier to implement Patch Management processes and ensure that their systems are protected.
About CVE-2022-34713
CVE-2022-34713 is a critical remote code execution vulnerability that affects the Microsoft Windows Support Diagnostic Tool (MSDT). The MSDT is a service in Windows used to analyze diagnostic data to fix and repair issues remotely.
The vulnerability was discovered on August 2022. Microsoft released a patch for it on August 2022 Patch Tuesday.
CVE-2022-34713 arises from a flaw in how MSDT parses XML files. An attacker can create a specially crafted XML file and trick a user into opening it with the MSDT utility. Once the file is opened, the attacker can execute arbitrary code on the victim's system with the same privileges as the logged-in user, leading to a complete compromise of the system.
An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by sending a malicious XML file via email or by hosting it on a website and tricking users into downloading it.
If this vulnerability is not patched, it could lead to devastating consequences for individuals and organizations. An attacker could gain complete control over the victim's system, steal sensitive data, and use the compromised system to launch further attacks.
CVE-2022-34713 affects different versions of Windows 10, Windows 11, Windows 7, Windows 8.1, and Windows Server. To mitigate the risk of exploitation, Microsoft recommends that all users of the MSDT utility update to the latest version as soon as possible. Additionally, users should exercise caution when opening any XML files received from untrusted sources and ensure that their systems are protected by up-to-date antivirus software.
How to find devices exposed to CVE-2022-34713
You can quickly identify devices that the CVE-2022-34713 vulnerability has impacted with InvGate Asset Management. To do it, you can follow these steps:
- Open InvGate Asset Management and go to the Explorer tab.
- Type in the Search bar “Software name, is:Microsoft Windows Support Diagnostic Tool” to filter all Windows devices.
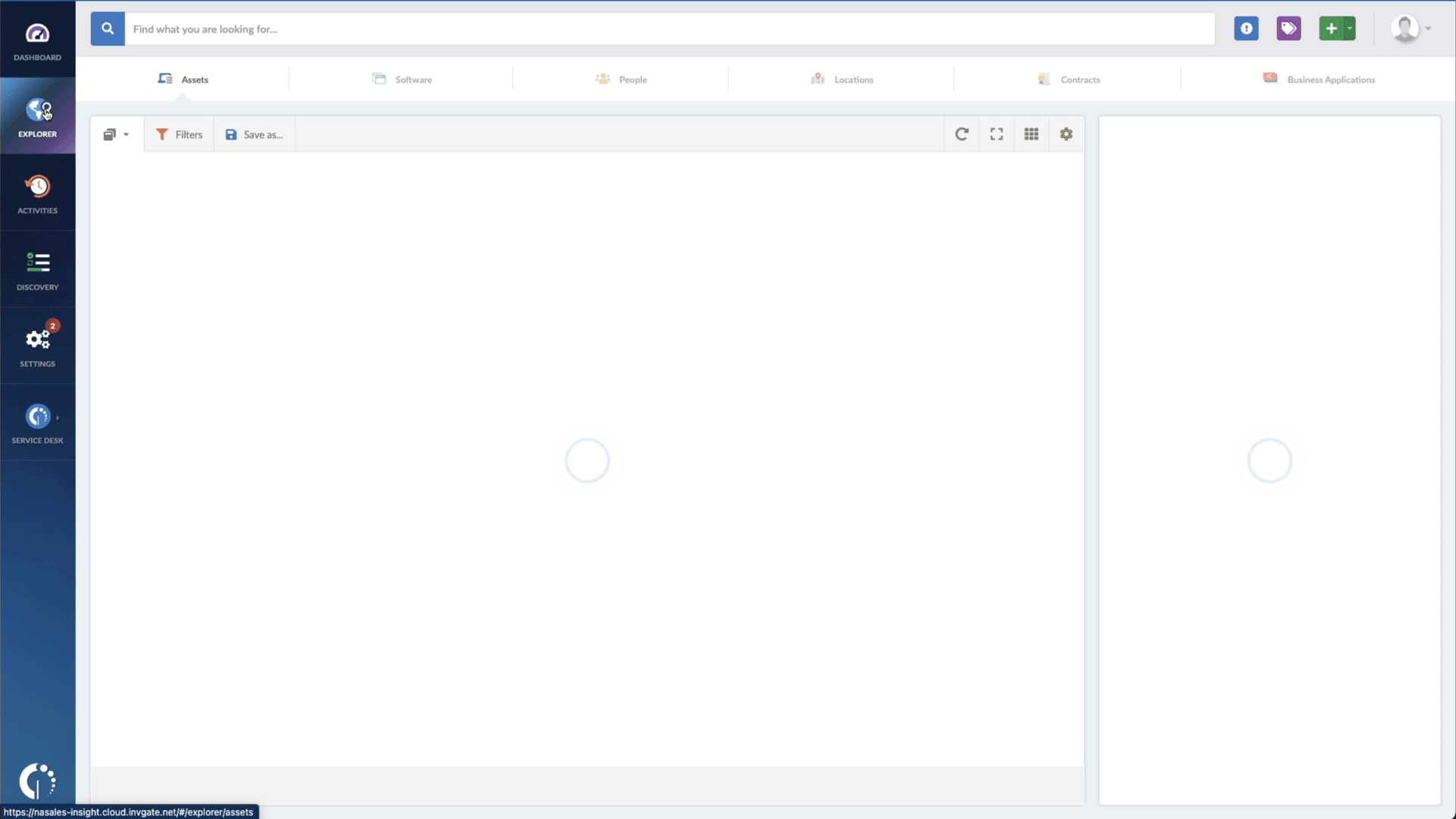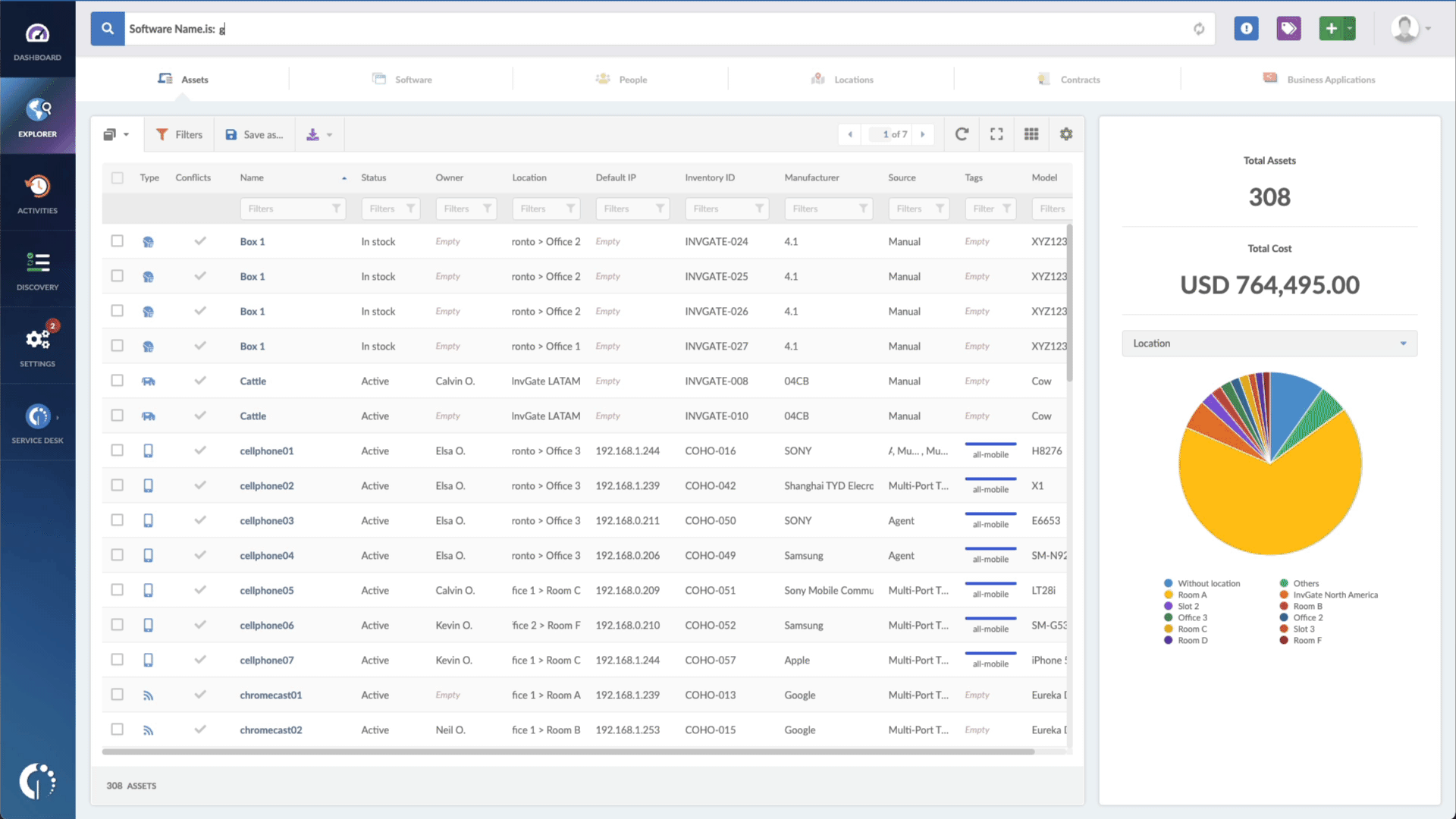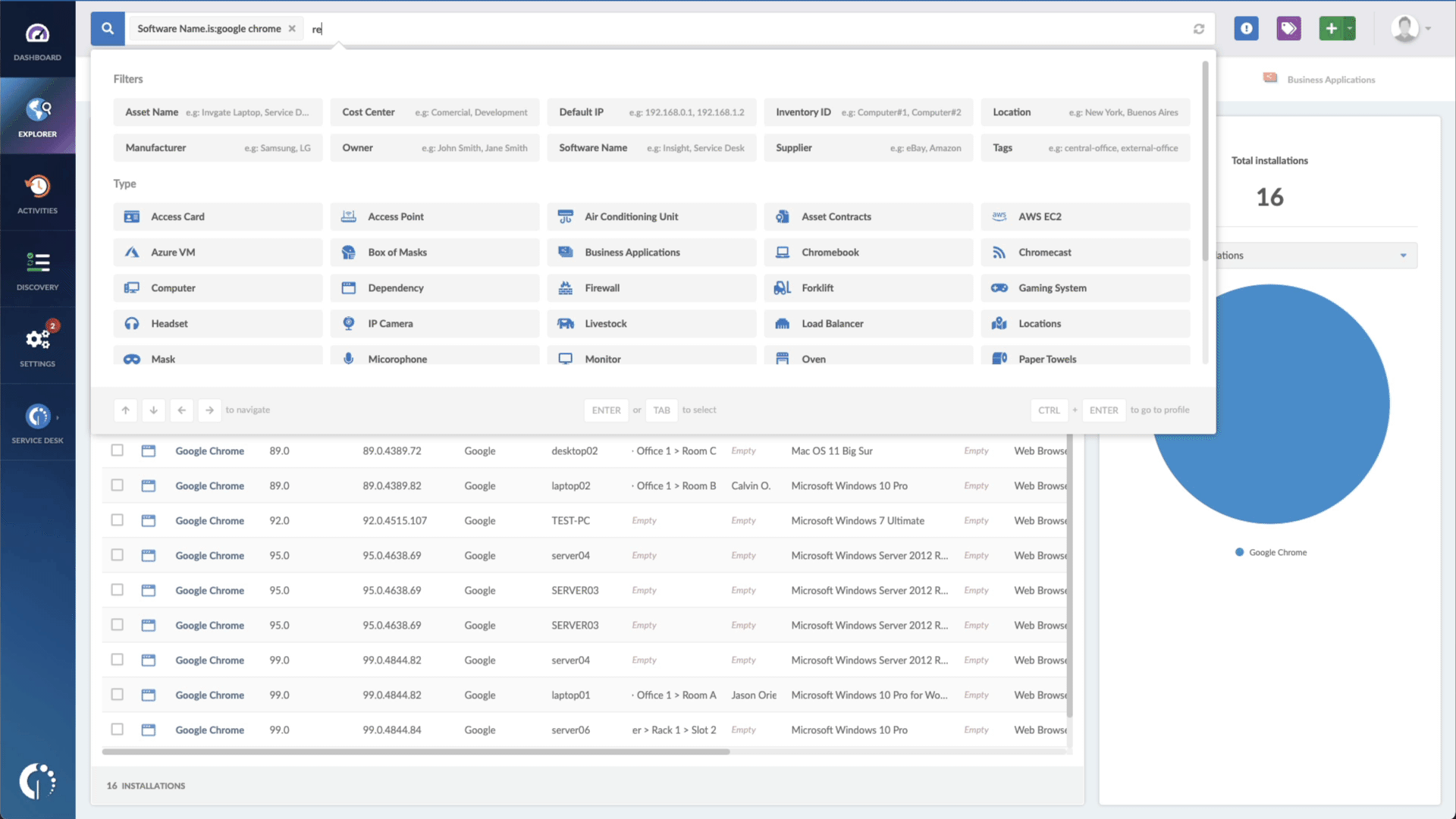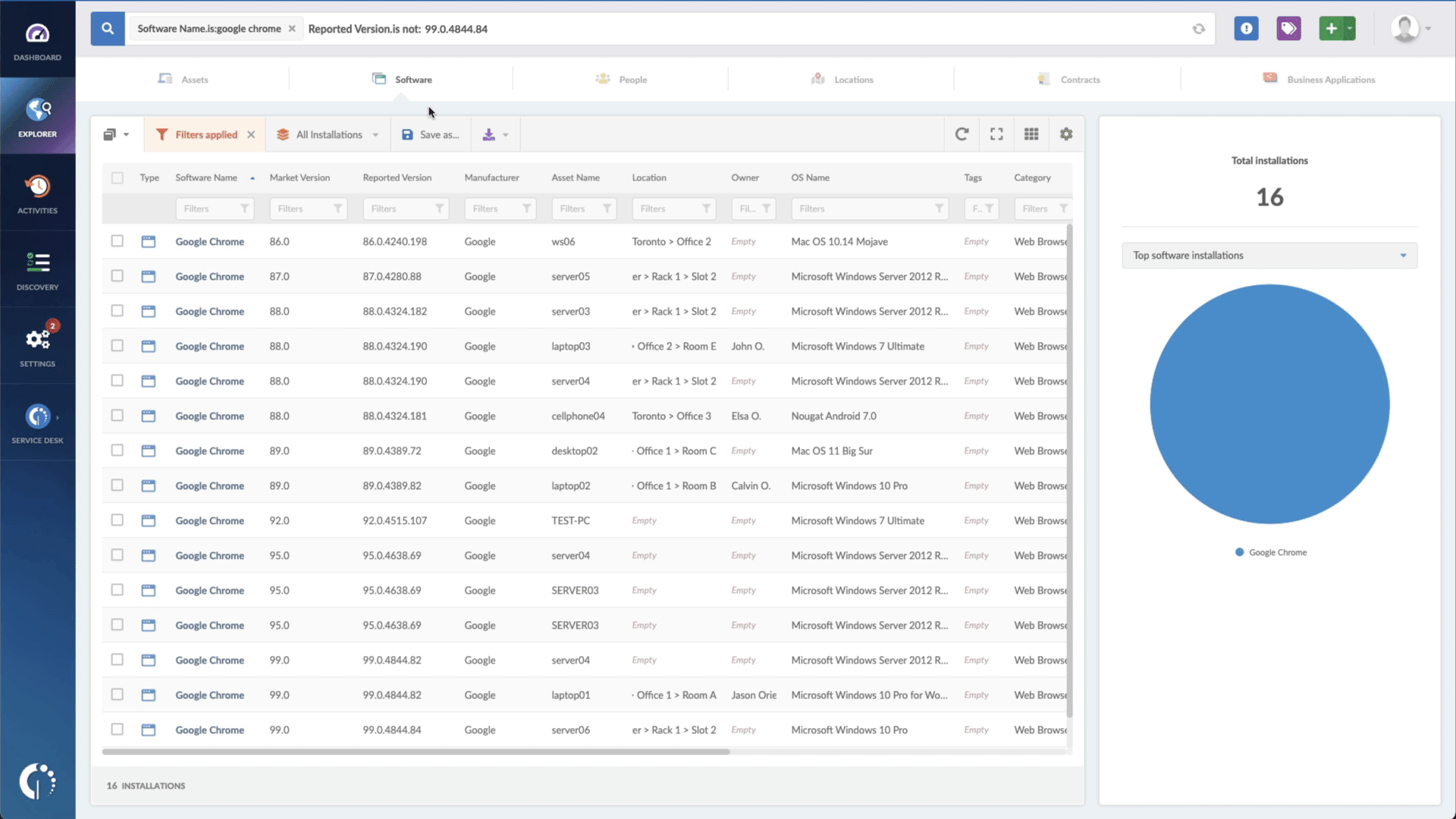
- Add another filter to the Search bar to see all devices missing the security patch. To do that, add the following filter: “Reported version, is not:” and paste Microsoft’s patched version (depending on your product, you’ll find the security update number on Microsoft’s webpage. For example, for Windows 10 for 32-bit Systems, it's KB5013963).
The bottom line
CVE-2022-34713 is a critical remote code execution vulnerability that affects the Microsoft Windows Support Diagnostic Tool (MSDT), which could allow attackers to execute arbitrary code on victims' systems, leading to a complete compromise of the system.
To mitigate the risk of exploitation, all MSDT utility users should update to the latest version immediately and exercise caution when opening any XML files received from untrusted sources.
To simplify the Patch Management process, you can try InvGate Asset Management. This tool helps identify devices impacted by the CVE-2022-34713 vulnerability, making it easier to manage patching processes.
Try it for yourself! Request a 30-day free trial of InvGate Asset Management and ensure your systems are up-to-date and protected against critical vulnerabilities.