In today's digital landscape, ensuring the security of our systems is of paramount importance. Unfortunately, vulnerabilities in software can leave devices susceptible to exploitation by malicious actors. One such vulnerability that garnered significant attention is CVE-2022-34689, a Windows CryptoAPI spoofing vulnerability.
In this article, we’ll delve into the details of the CVE-2022-34689 vulnerability, exploring its implications, the risks of not patching it, and how InvGate Asset Management's robust Patch Management capabilities can simplify the process of securing your network and devices.
Ready to delve into the intricacies of CVE-2022-34689 and discover effective ways to safeguard your systems? Let's dive in!
About CVE-2022-34689
CVE-2022-34689 is a critical vulnerability in the Windows CryptoAPI that allows attackers to spoof their identity and perform actions such as authentication or code signing as the targeted certificate.
The vulnerability exists in the way that the CryptoAPI validates public key certificates. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by generating a certificate with the same MD5 thumbprint as a trusted certificate but with a different public key. When the CryptoAPI validates the certificate, it will not check the public key and will instead trust the certificate because it has the same MD5 thumbprint as a trusted certificate.
What are CVE-2022-34689 risks?
The risks of CVE-2022-34689 are significant. An attacker could use this vulnerability to impersonate a trusted entity, such as a website or a software developer. This could allow the attacker to steal sensitive information, such as login credentials or credit card numbers. The attacker could also use the vulnerability to install malware or ransomware on a victim's computer.
Is CVE-2022-34689 fixed?
Yes, Microsoft has released patches for CVE-2022-34689 for all supported versions of Windows and Windows Server. Users should install these patches as soon as possible to protect their systems from this vulnerability.
How to find devices exposed to CVE-2022-34689
With InvGate Asset Management, you can swiftly identify devices affected by the CVE-2022-34689 vulnerability. Follow these steps:
- Open InvGate Asset Management and go to the Explorer tab.
- Type in the Search bar “Software name, is:Windows CryptoAPI” to filter all Windows devices.
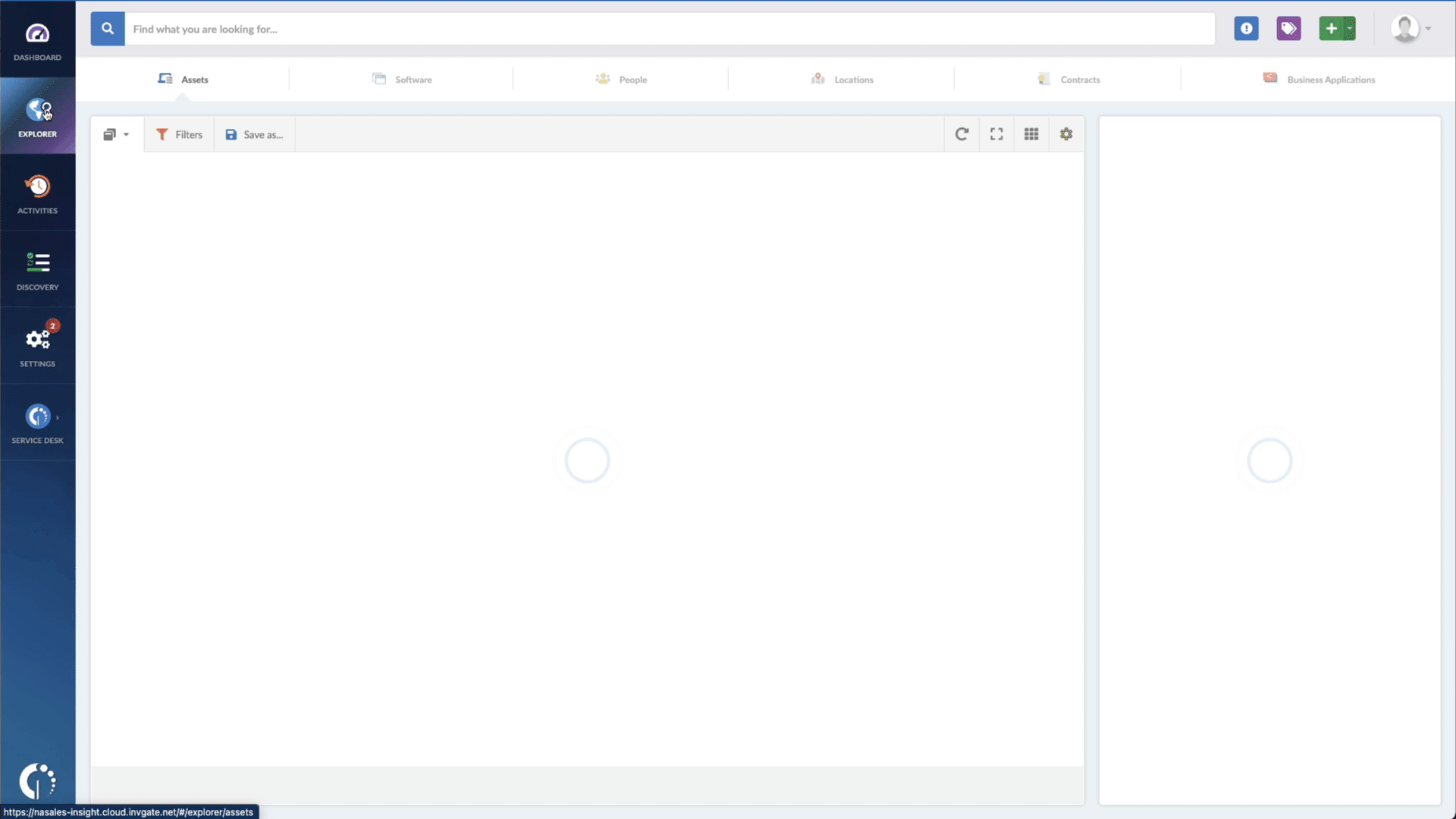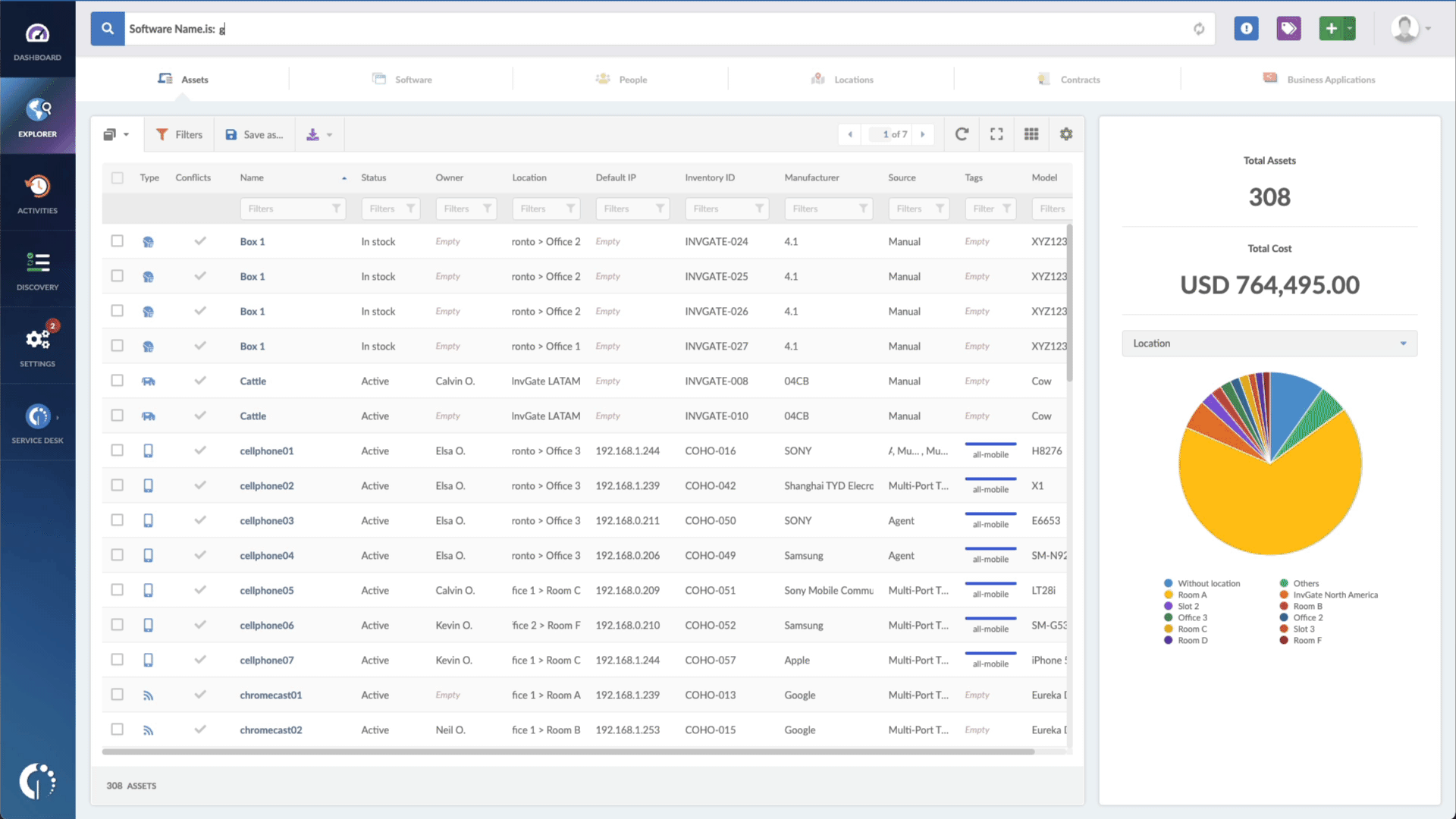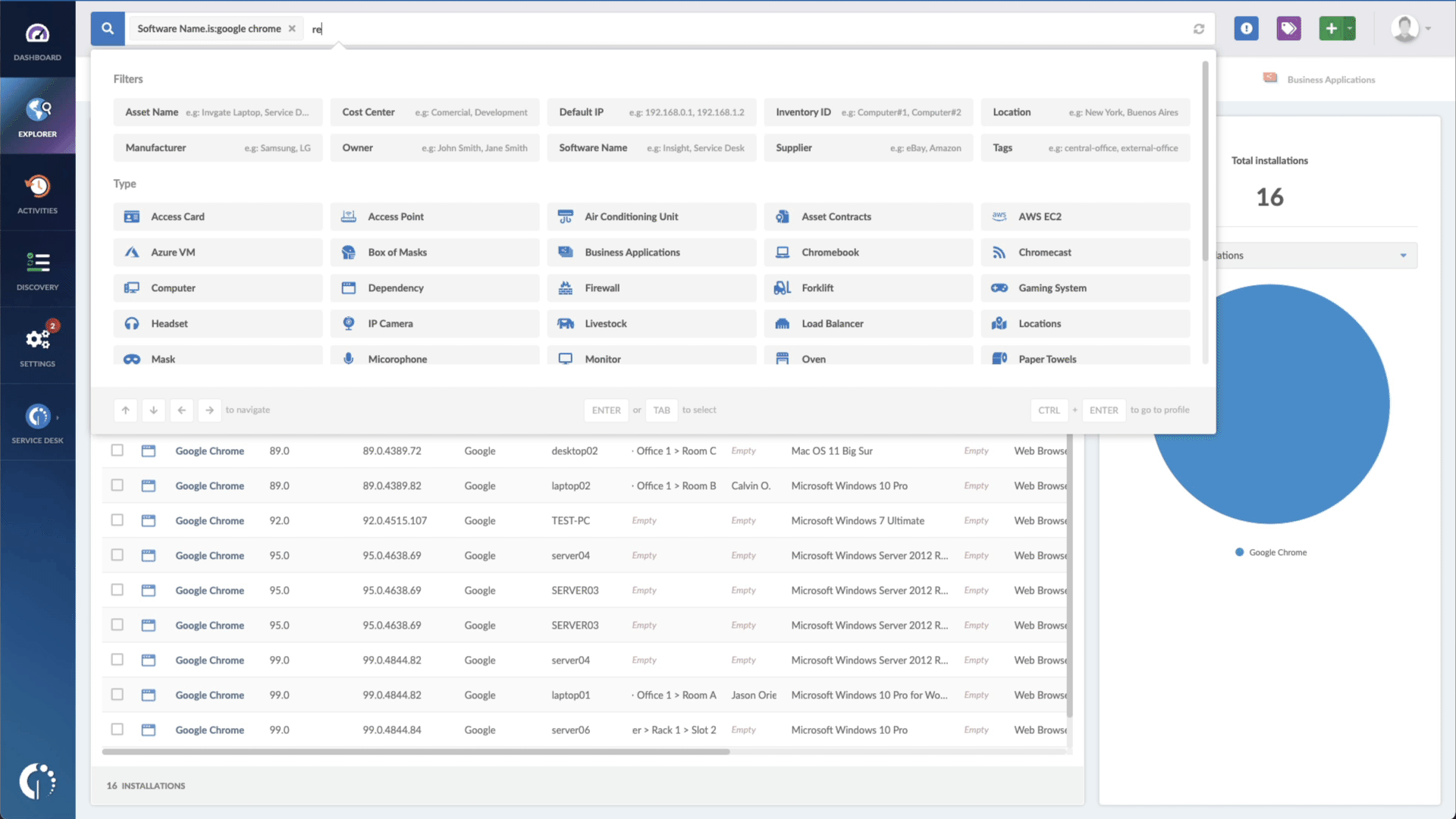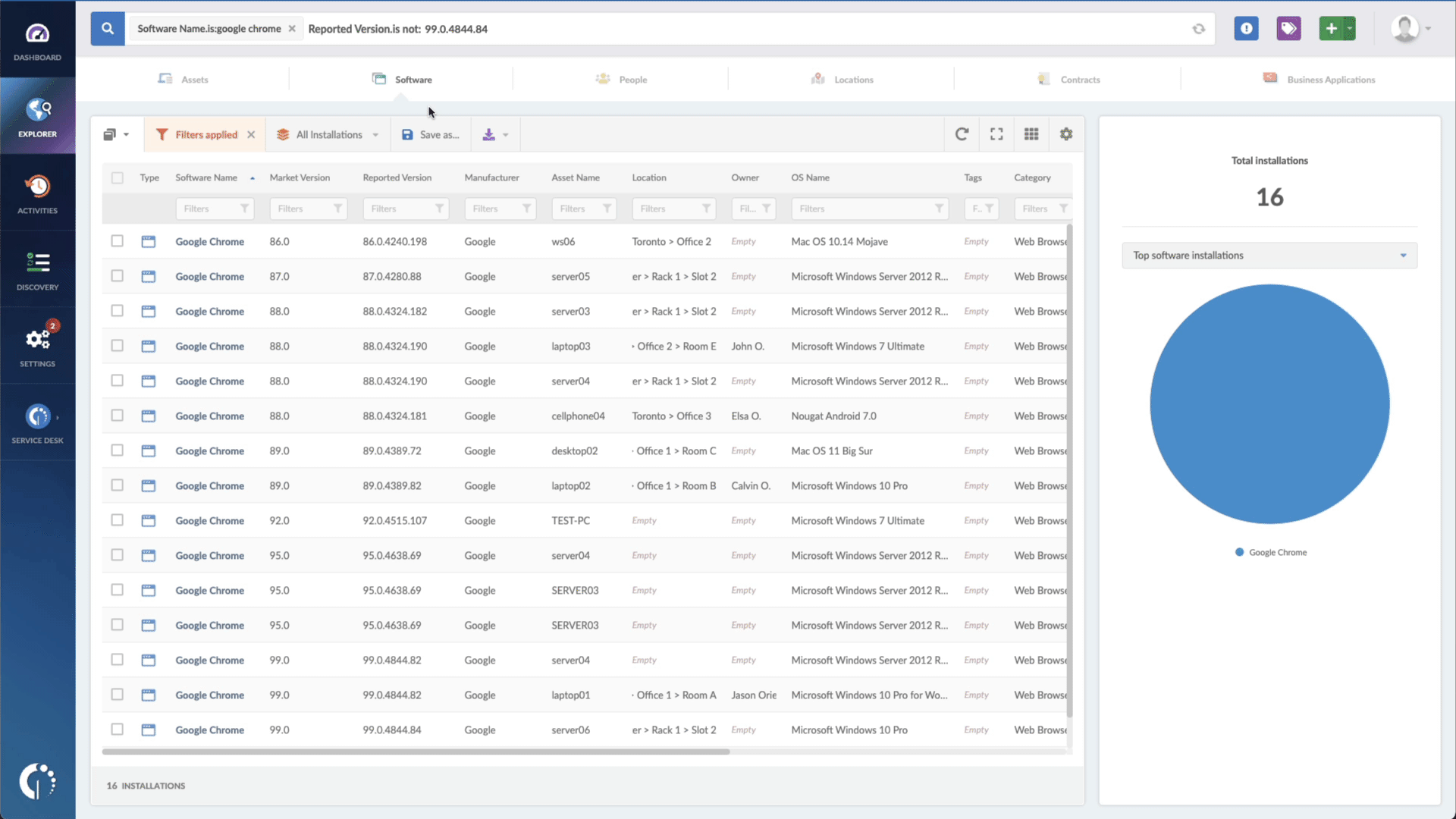
- Add another filter to the Search bar to see all devices missing the security patch. To do that, add the following filter: “Reported version, is not:” and paste Microsoft’s patched version (depending on your product, you’ll find the security update number on Microsoft’s webpage. For example, for Windows 10 for x64-based Systems, it's KB5016639).
The bottom line
The CVE-2022-34689 vulnerability in the Windows CryptoAPI poses a significant risk to systems running affected versions of Windows. This spoofing vulnerability allows attackers to forge digital certificates, potentially leading to the execution of unauthorized code, malware infections, and unauthorized access to sensitive data.
However, Microsoft released a patch for this vulnerability, and users should update their Windows operating system to the latest version and apply all relevant security patches.
Managing patches across a network of devices can be a daunting task, but with the right tools, it becomes more manageable. With InvGate Asset Management, you can effortlessly track and manage the patch status of all devices in your network, ensuring that critical security updates, like the one addressing CVE-2022-34689, are applied promptly.
Don't leave your systems vulnerable to known exploits. Request a 30-day free trial today!