In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, it is crucial to stay informed about potential vulnerabilities that can compromise our digital safety. One such vulnerability, CVE-2022-26485, has recently come to light, affecting Mozilla Firefox users worldwide.
In this article, we’ll provide comprehensive information about the CVE-2022-26485 vulnerability in Mozilla Firefox, including how it works, its risks, and step-by-step guidance on using InvGate Asset Management to identify and patch affected devices.
About CVE-2022-26485
CVE-2022-26485 is a use-after-free vulnerability in the XSLT processor in Mozilla Firefox. It allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code on a victim's system by crafting a malicious web page.
How does CVE-2022-26485 work?
The vulnerability is caused by a flaw in the way that the XSLT processor handles memory. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by creating a malicious web page that contains a specially crafted XSLT document. When the victim opens the malicious web page, the XSLT processor will be vulnerable to arbitrary code execution.
What are CVE-2022-26485 risks?
An attacker who successfully exploits this vulnerability could execute arbitrary code on the victim's system, allowing it to steal data, install malware, or take control of the victim's system.
Is CVE-2022-26485 fixed?
Yes, Mozilla has released a security update that addresses CVE-2022-26485. Users are urged to apply this security update as soon as possible.
The following are the security updates that address CVE-2022-26485:
- Firefox 97.0.2
- Firefox ESR 91.6.1
- Firefox for Android 97.3.0
- Thunderbird 91.6.2
- Focus 97.3.0
How to find devices exposed to CVE-2022-26485
With the utilization of InvGate Asset Management, you can efficiently detect devices that are impacted by the CVE-2022-26485 vulnerability. The following are the necessary steps to take:
- Open InvGate Asset Management and go to the Explorer tab.
- Type in the Search bar “Software name, is:Mozilla Firefox” to filter all devices with this browser.
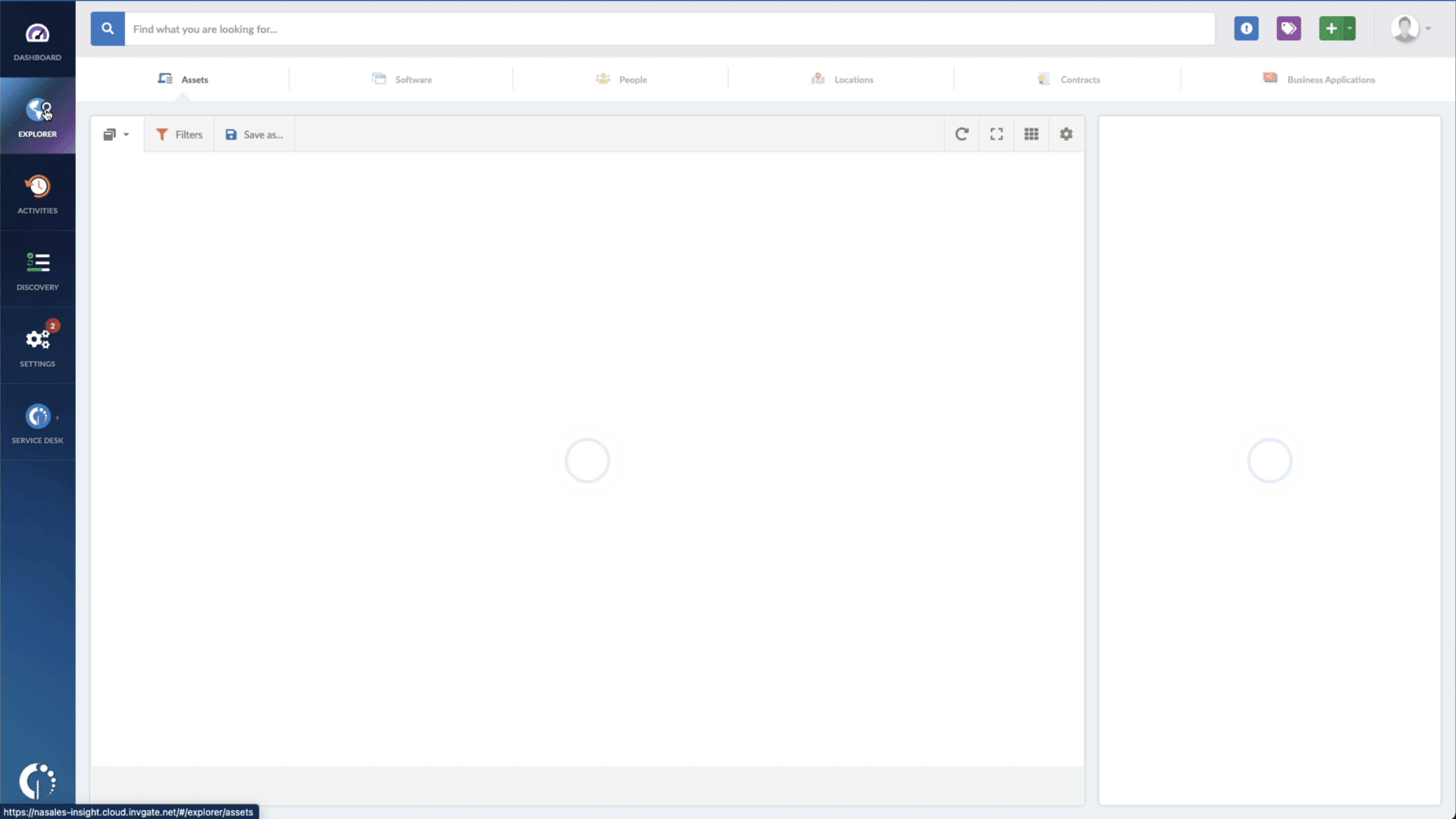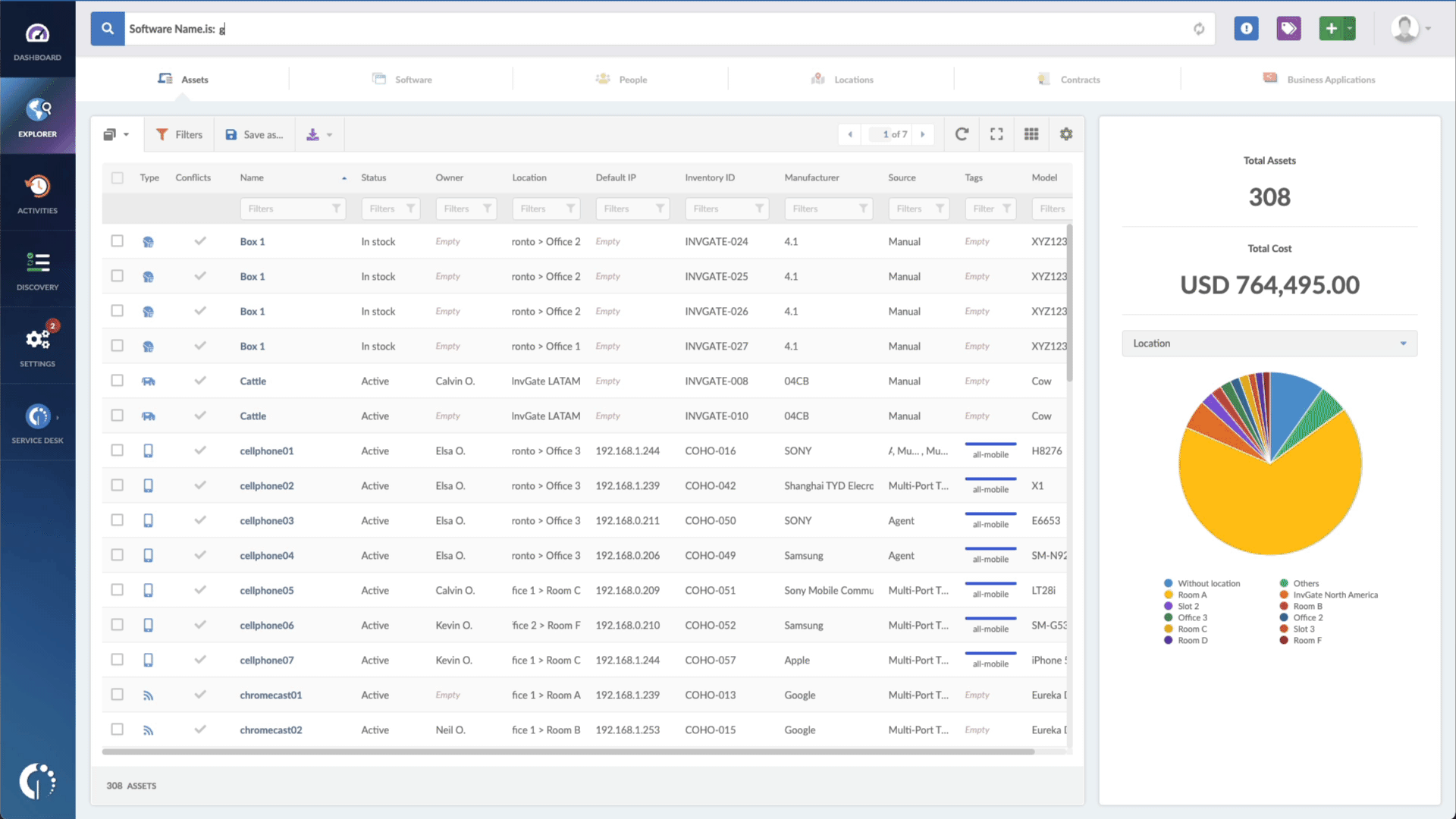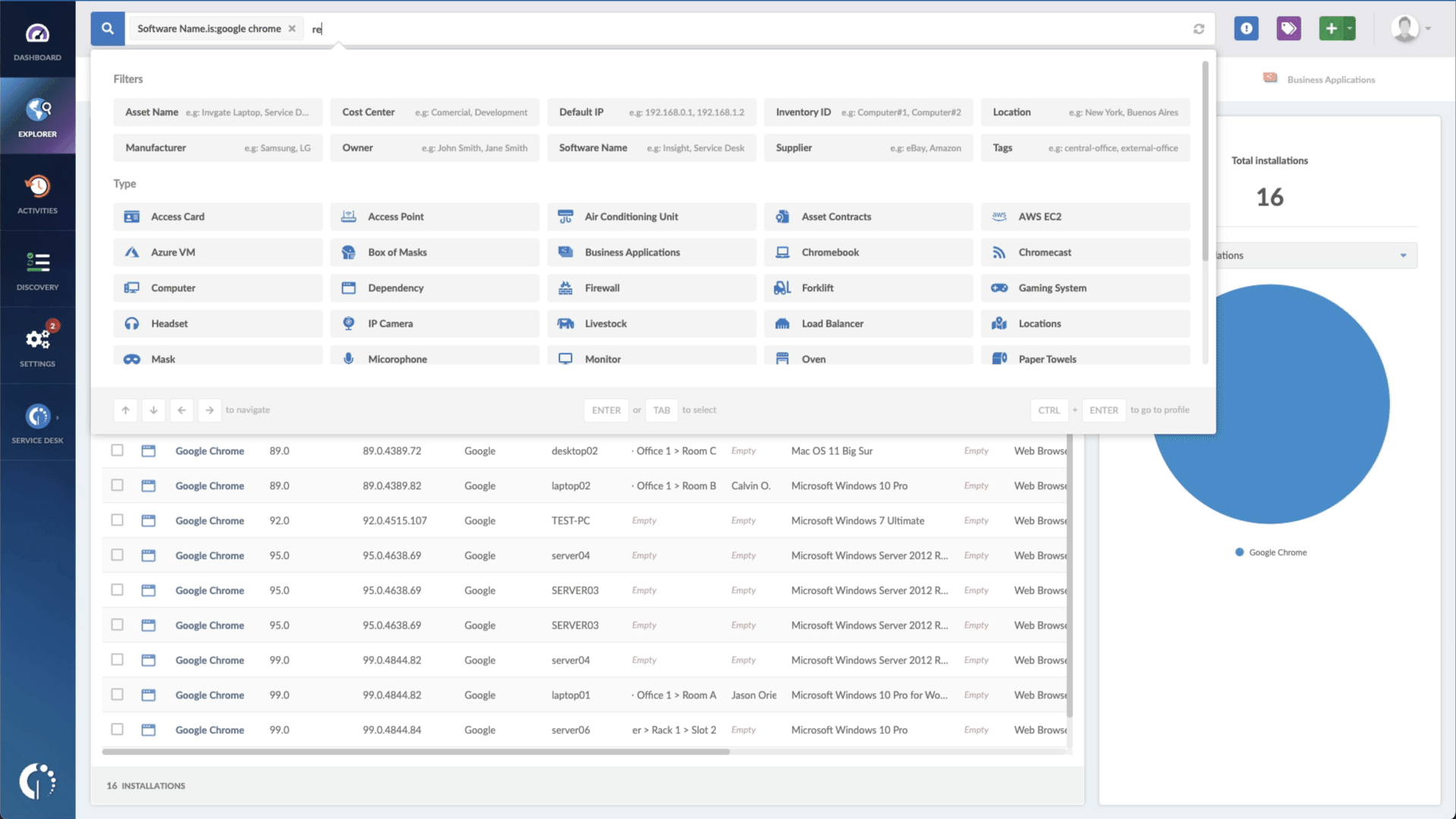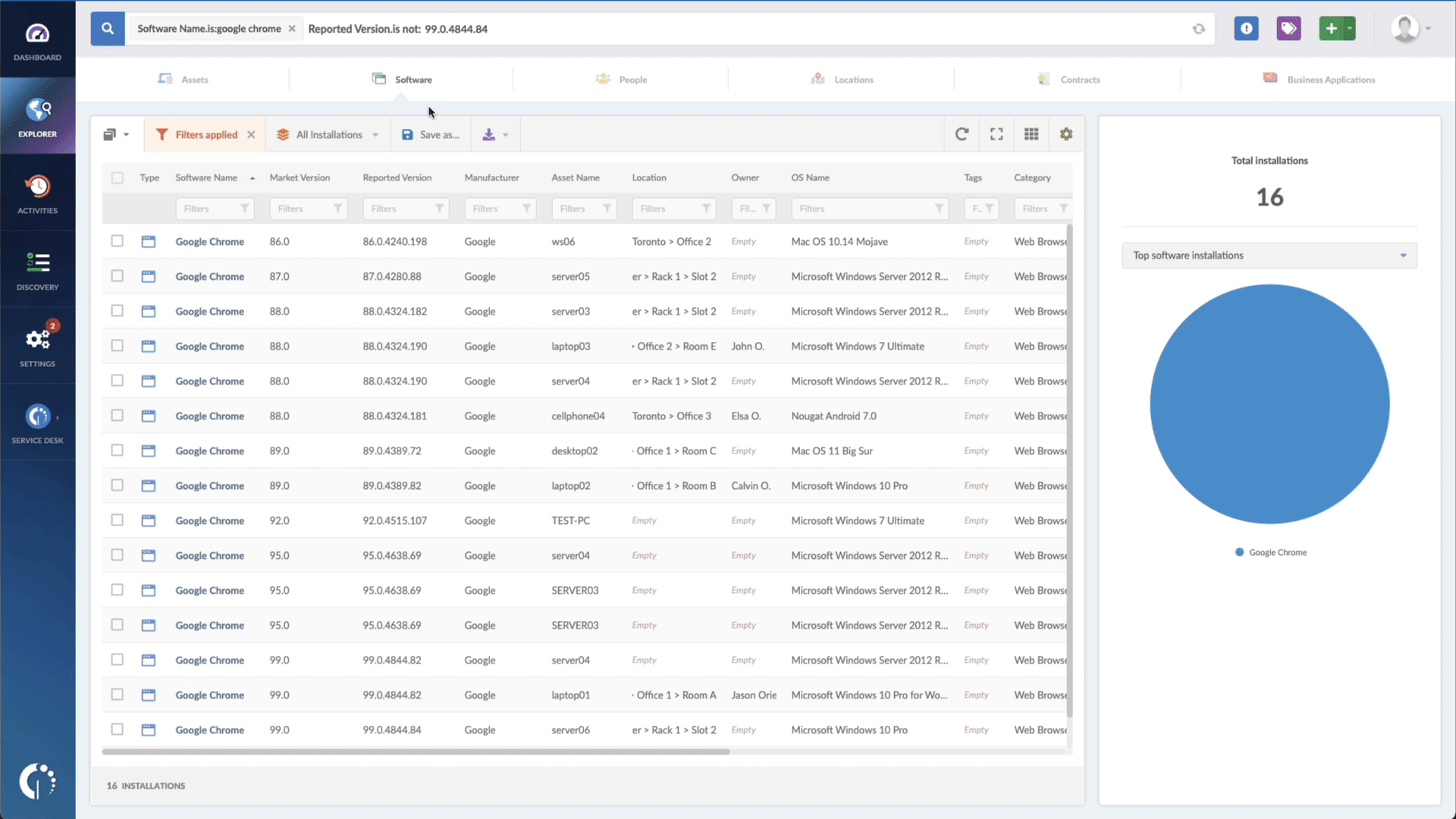
- Add another filter to the Search bar to see all devices missing the security patch. To do that, add the following filter: “Reported version, is not:” and paste Mozilla’s patched version (mentioned above).
The bottom line
In conclusion, the CVE-2022-26485 vulnerability discovered in Mozilla Firefox presents a significant security risk to users. If left unpatched, could enable attackers to execute arbitrary code or gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
However, by ensuring the prompt update to the latest version of Mozilla Firefox, users can safeguard themselves against this vulnerability. To simplify the process of Patch Management and swiftly identify devices affected by CVE-2022-26485, InvGate Asset Management comes to the rescue. With InvGate Asset Management's capabilities, users can efficiently scan their network to pinpoint devices that require the necessary patch.
Take advantage of InvGate Asset Management's features by requesting a 30-day free trial today. Don't leave your network exposed—try InvGate Asset Management and safeguard your systems from potential threats.
















