Reported by CVE on December 2nd, 2022, and patched by Google the same day, CVE-2022-4262 is a high severity vulnerability in Google Chrome's V8 engine, which is responsible for executing JavaScript code in the browser.
About CVE-2022-4262
The vulnerability involves a type confusion issue in the V8 engine, which could be exploited by a remote attacker through a specially crafted HTML page. Successful exploitation of this vulnerability could potentially lead to heap corruption, which could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial-of-service (DoS) attack.
The vulnerability has been fixed in Google Chrome version 108.0.5359.94 and later releases, so it is recommended that users upgrade to the latest version of Google Chrome as soon as possible to protect against this vulnerability. Also, the fix for this bug can also be found in the update v108.0.1462.41 for the Microsoft’s Edge browser, as it’s based on the open-source Chromium project.
Find devices with browsers exposed to CVE-2022-4262
With InvGate Asset Management, it’s very easy to see which assets need updating. Just open Insight, go to Explorer, and type in on the Search bar “Software name, is: Google Chrome.” Now you have a list of all the devices where this particular browser is installed. Then, add another filter to the Search bar to see all the outdated assets. In order to do that, add the following filter: “Reported version, is not:” and paste Chrome’s patched version (108.0.5359.94).
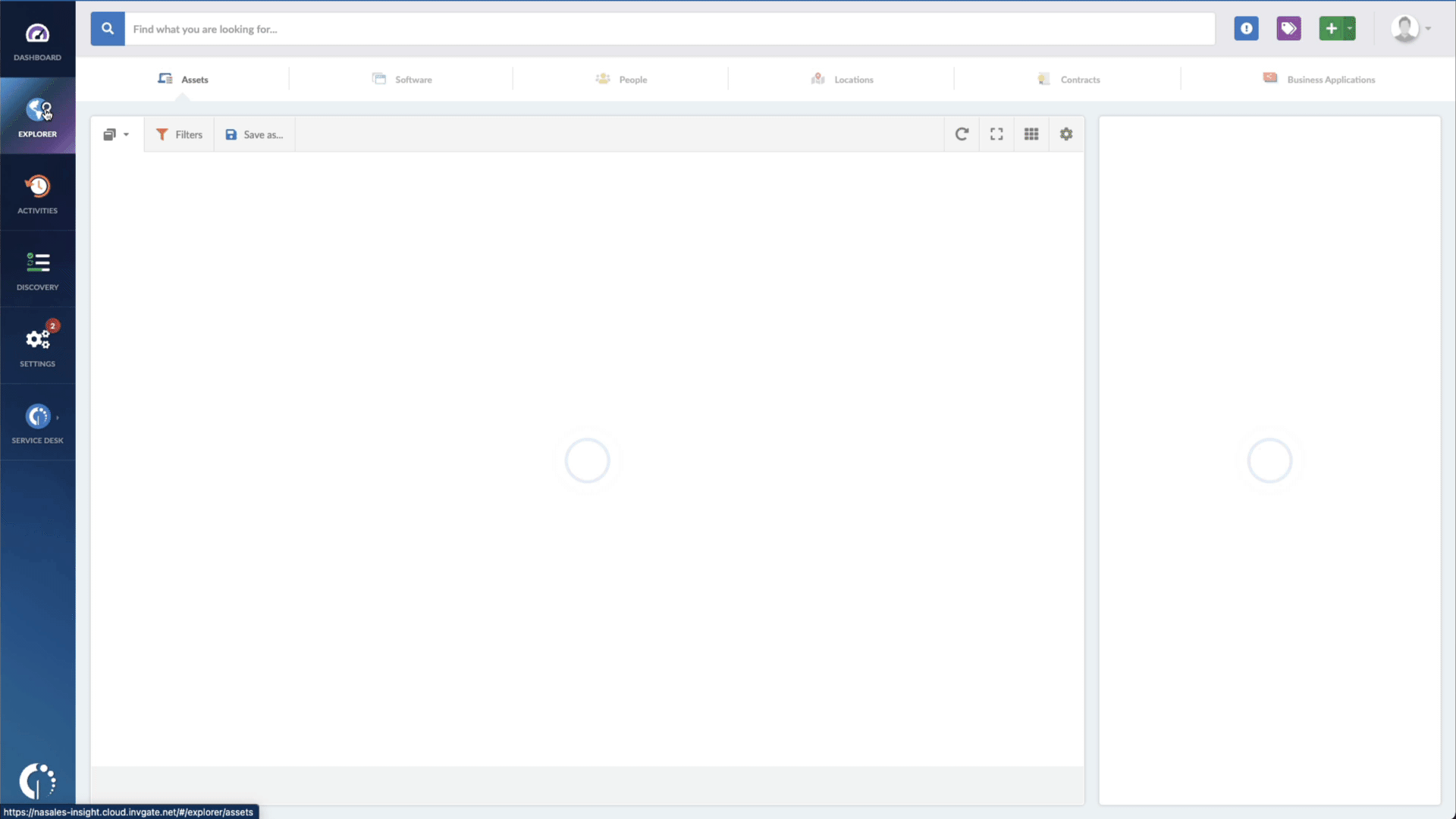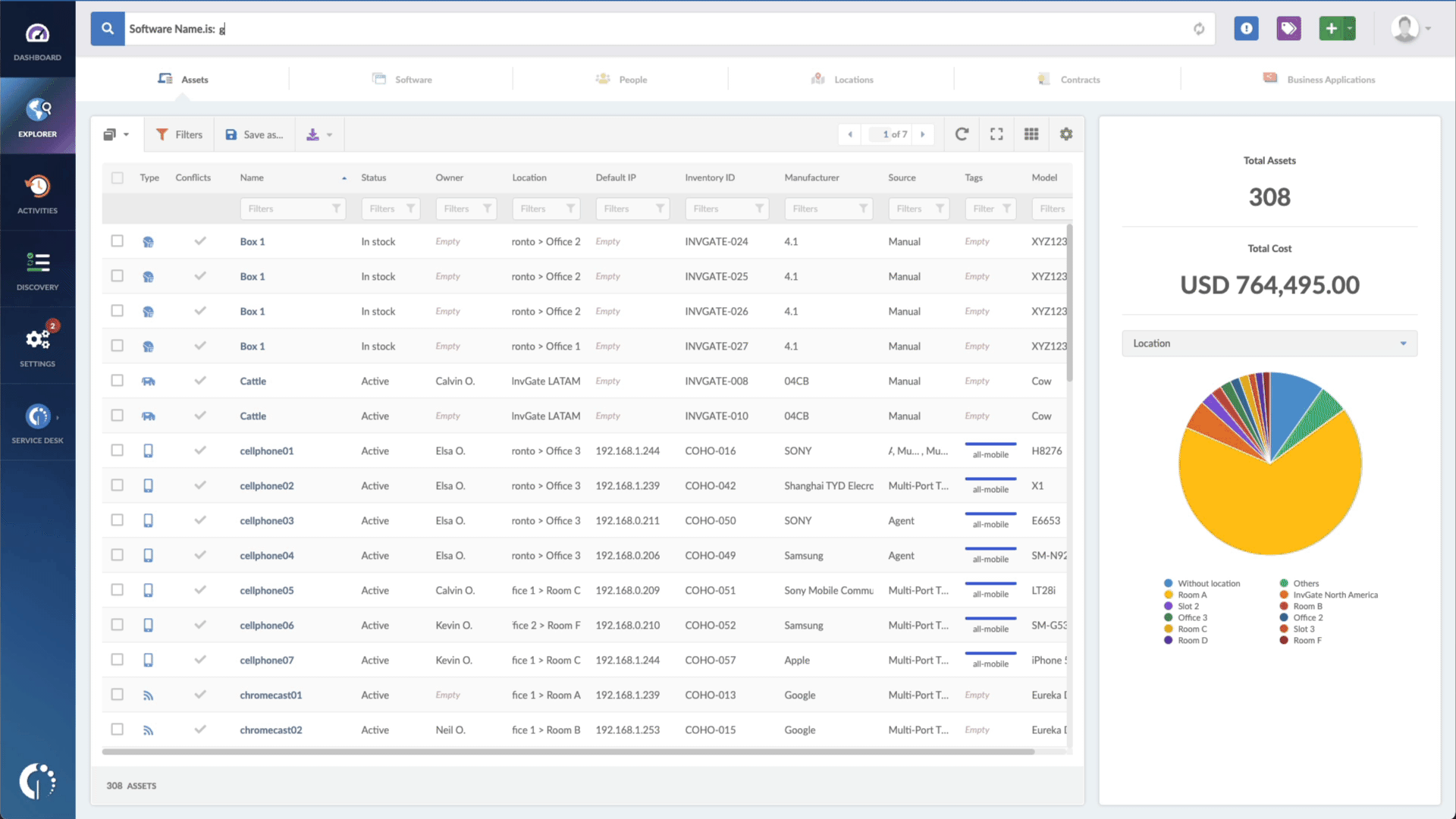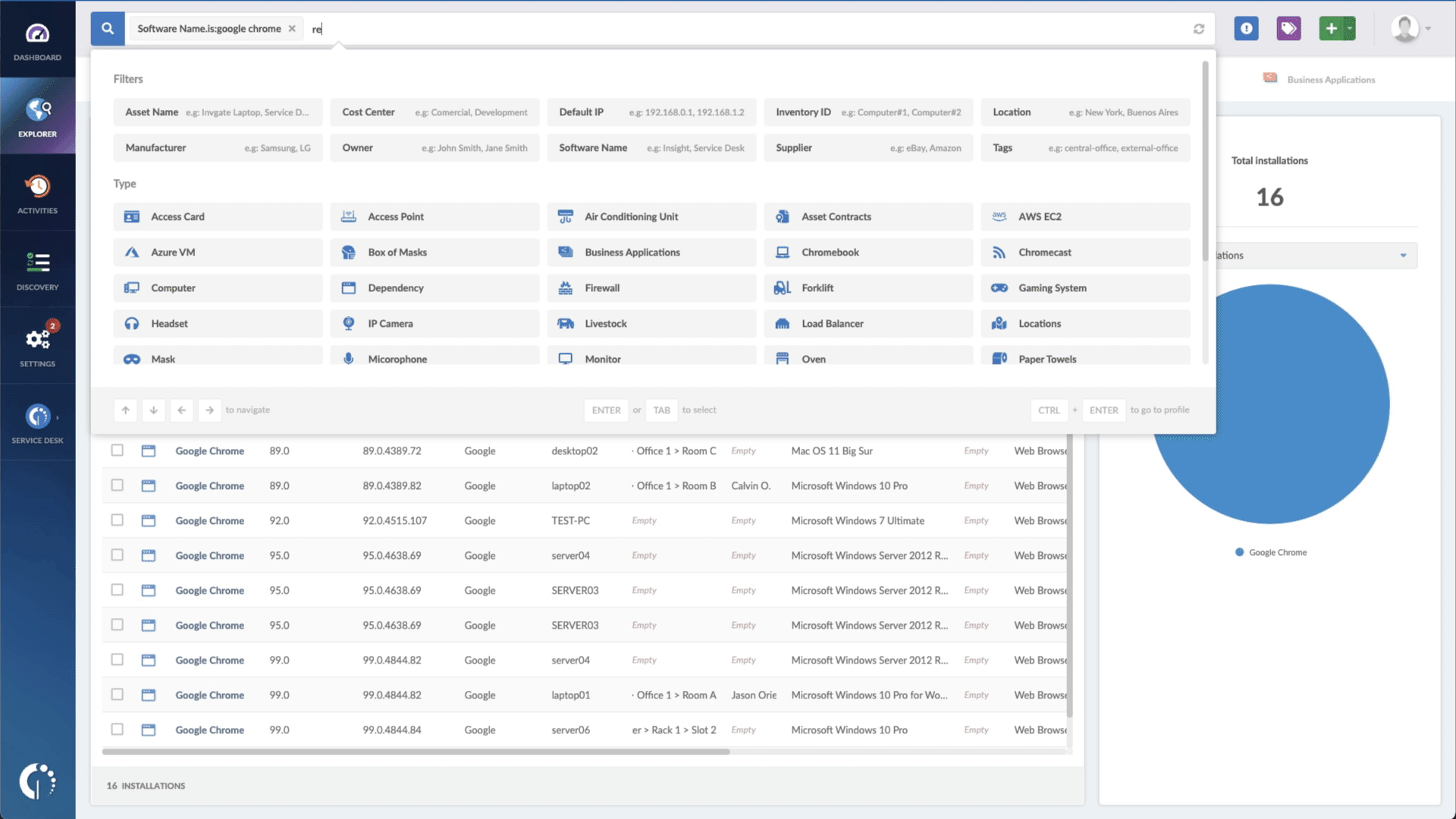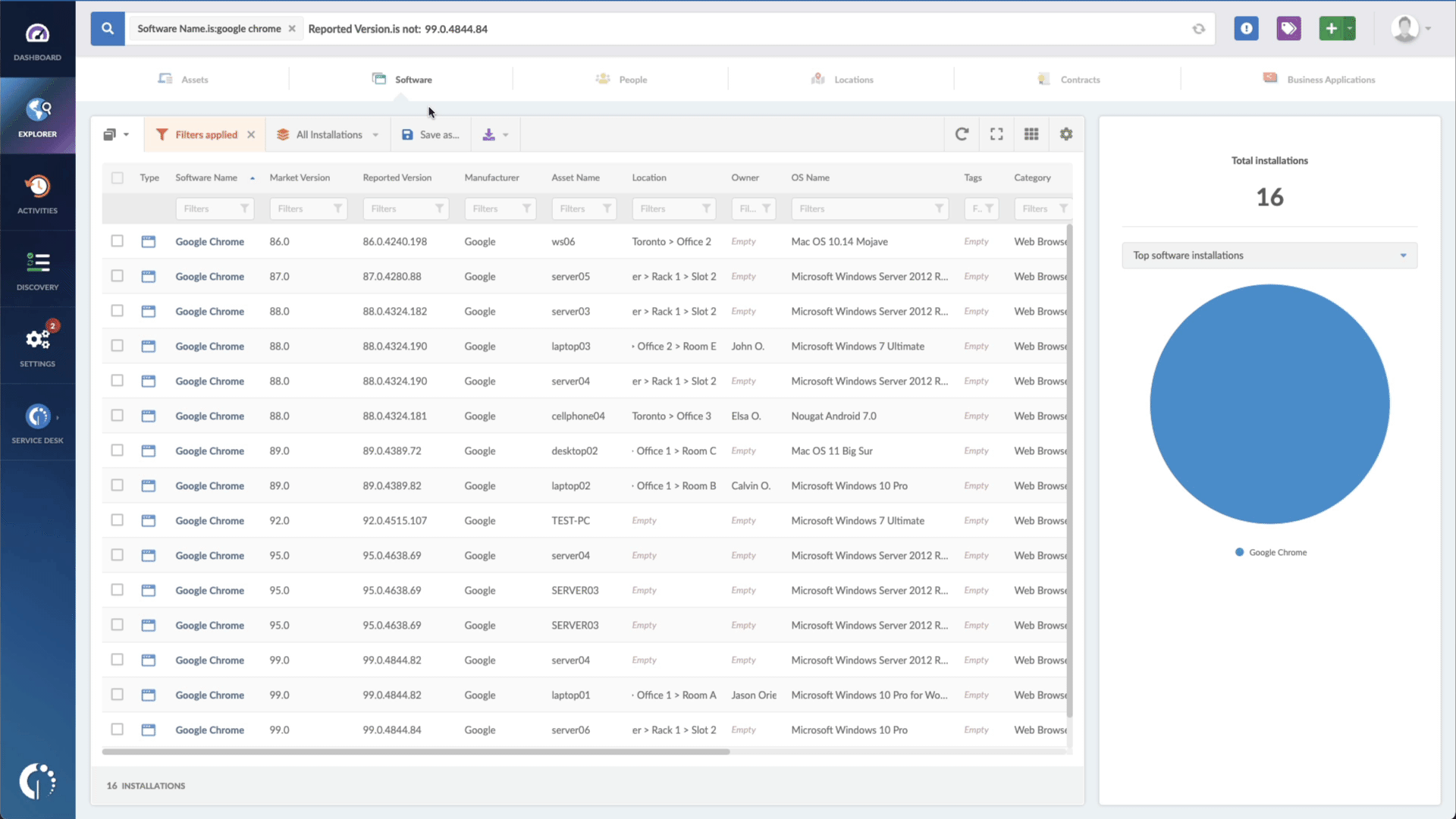
That’s it! With a few clicks, you created a list of devices that need to be updated as soon as possible. You can export it in CSV and give it to one of your agents to patch or create a ticket so they can be manually updated.
Don't let the next Chrome zero-day exploit catch you off guard, try InvGate Asset Management now, and forget about security issues once and for all!

















