The discovery of the critical vulnerability CVE-2022-26500 has raised concerns among organizations using Veeam Backup & Replication software. This exploit can potentially allow attackers to execute arbitrary code on target systems, posing significant risks to data security and operational integrity.
In this blog post, we’ll provide you with comprehensive information about CVE-2022-26500, including how it works, its impact, and how InvGate Asset Management simplifies Patch Management.
Read on to discover how you can safeguard your systems from CVE-2022-26500 and mitigate the risks it poses to your organization's data and operations.
About CVE-2022-26500
CVE-2022-26500 is a critical vulnerability in Veeam Backup & Replication software. It allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code on the target system by sending specially crafted input to the Veeam Distribution Service. The exploit has a CVSS score of 9.8, which is the highest possible.
The vulnerability has been exploited in the wild, which means that there is a high likelihood that attackers are already targeting organizations that use Veeam Backup & Replication.
In October 2022, several threat actors were seen advertising a “fully weaponized tool for remote code execution” that takes advantage of the vulnerability.
How does CVE-2022-26500 work?
The vulnerability is caused by an improper limitation of path names in the Veeam Distribution Service. It allows an attacker to trick the service into executing arbitrary code by sending a path name that contains malicious code. The attacker can then gain control of the target system and execute any commands.
What are CVE-2022-26500 risks?
An attacker who exploits this vulnerability can gain control of the target system and execute any commands they want, allowing them to steal data, install malware, or disrupt operations.
Is CVE-2022-26500 fixed?
Yes, Veeam has released patches for the vulnerability. The latest versions of Veeam Backup & Replication that include the patch are:
- 10.0a
- 11.0a
- If you are using 9.5, you should first upgrade to a supported product version.
Organizations that use Veeam Backup & Replication should install the latest patches as soon as possible to protect themselves from this vulnerability.
How to find devices exposed to CVE-2022-26500
By utilizing InvGate Asset Management, you can quickly pinpoint devices that the CVE-2022-26500 vulnerability has impacted. The following instructions outline the necessary actions to take:
- Open InvGate Asset Management and go to the Explorer tab.
- Type in the Search bar “Software name, is:Veeam Backup & Replication” to filter all NAME devices.
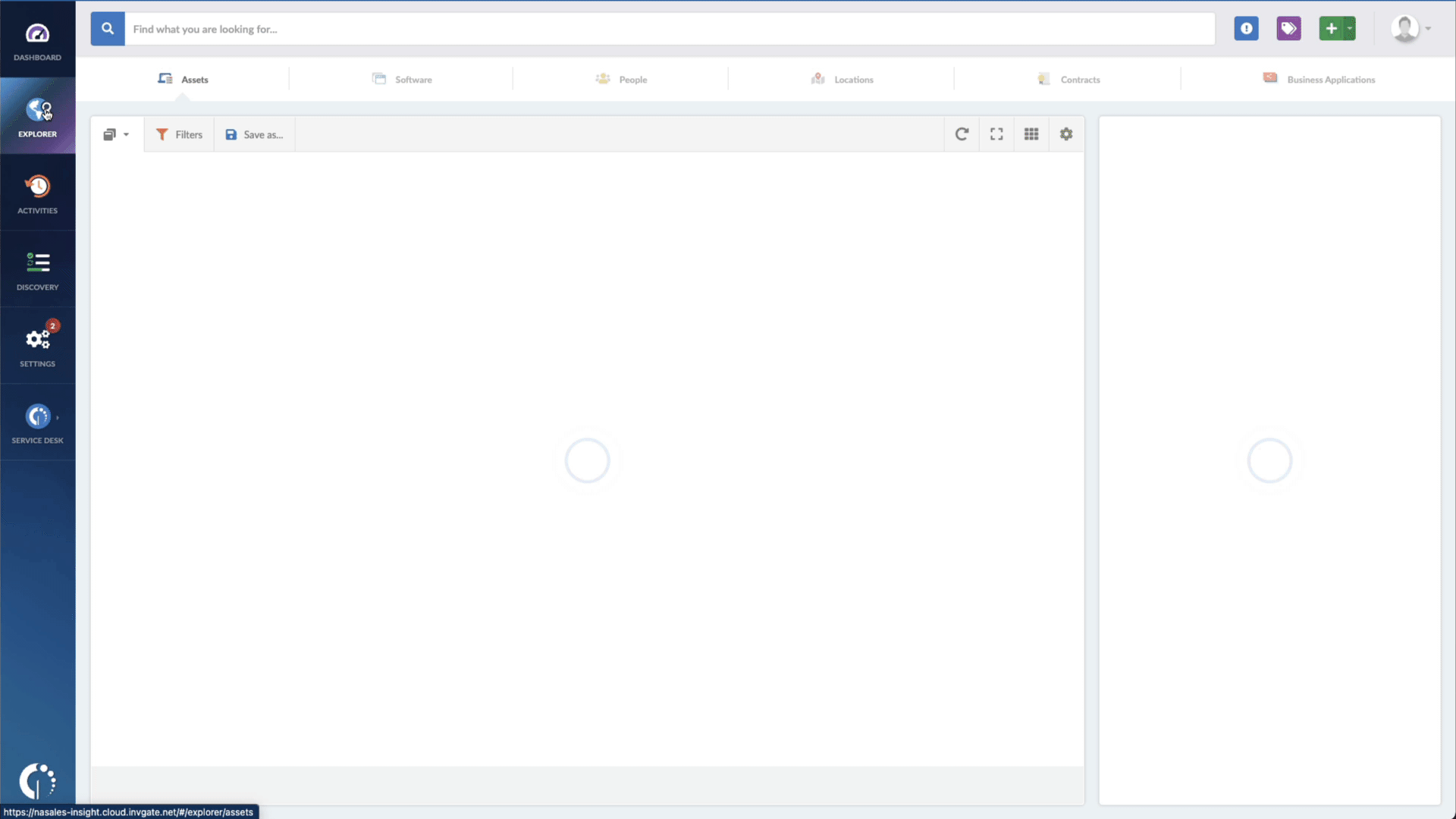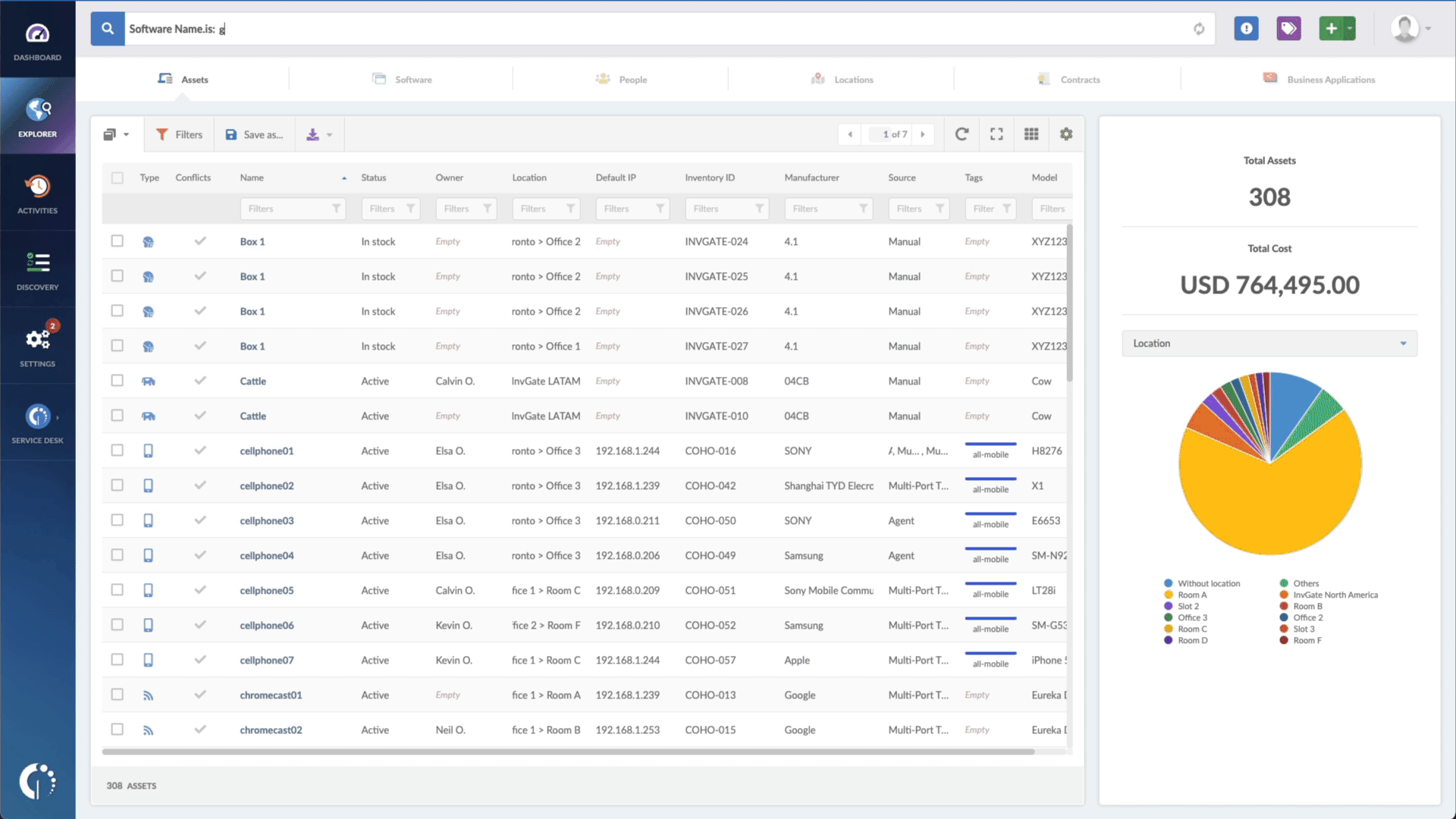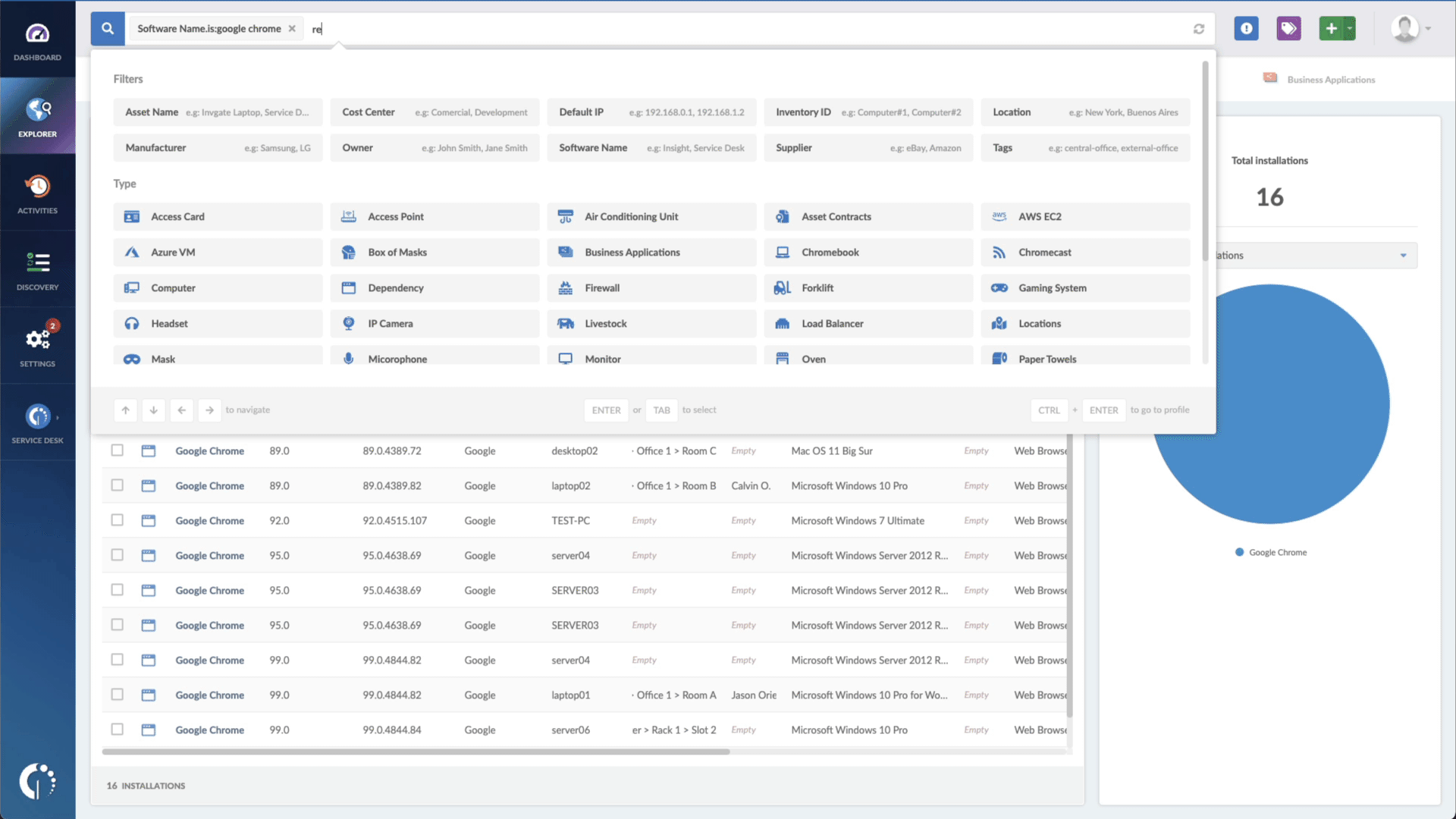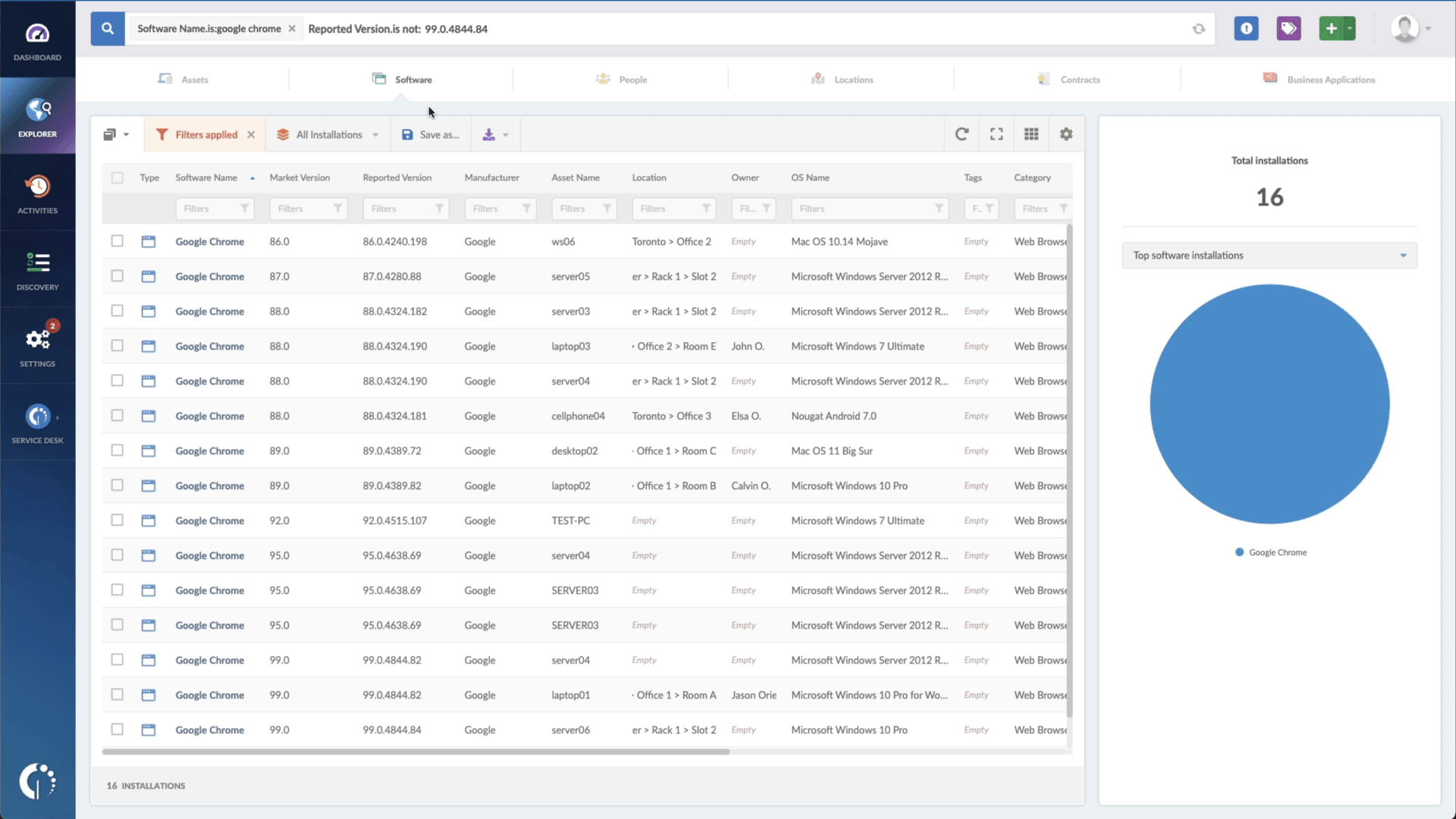
- Add another filter to the Search bar to see all devices missing the security patch. To do that, add the following filter: “Reported version, is not:” and paste Veeam’s patched version (10.0a or 11.0a).
The bottom line
In conclusion, CVE-2022-26500 poses a critical risk to organizations utilizing Veeam Backup & Replication software. This vulnerability allows attackers to execute arbitrary code, potentially leading to data breaches, malware installation, and operational disruptions.
However, Veeam has responded promptly by releasing patches for the vulnerability in their latest versions, namely 10.0a and 11.0a. Organizations must upgrade to these supported versions to mitigate the risk.
To identify devices exposed to CVE-2022-26500 and simplify the Patch Management process, InvGate Asset Management proves to be an invaluable tool. With its capabilities, organizations can swiftly locate affected devices and take proactive steps to safeguard their systems.
Take action today and protect your network from CVE-2022-26500. Request a 30-day free trial of InvGate Asset Management to experience its powerful features and simplify your Patch Management process.