If you work with computers or networks, you've probably heard of ipconfig. This handy command-line utility is essential for managing and troubleshooting network connections on Windows, macOS, and Linux. Whether you're a network administrator or a home user, understanding this tool can help you diagnose and fix network problems more effectively.At its core, ipconfig is a tool for retrieving information about your network connections. While this command line is powerful, it can be intimidating to use at first. In this article, we'll cover everything you need to know about it, including what it is, how it works, how to run it, and how to troubleshoot network issues with it.

What is ipconfig?
Ipconfig (short for Internet Protocol Configuration) is a command-line utility used for managing and troubleshooting network connections. It is available on Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems and provides detailed information about network settings and configurations.
Ipconfig can display information about IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, DNS servers, and more. You can also use it to renew or release DHCP leases, flush caches, and perform other network-related tasks.
How ipconfig works
Ipconfig works by querying the network interface cards (NICs) on a computer and retrieving information about their configuration. When a computer connects to a network, a DHCP server assigns an IP address, subnet mask, and other network settings. Ipconfig can retrieve this information and display it in an easy-to-read format.
Ipconfig also interacts with other network protocols, such as DNS, to resolve domain names into IP addresses. By default, ipconfig displays information about the active NIC on the computer, but it can also be used to retrieve information about other NICs on the system. Before we use the tool, we need to understand what each of these terms means. Let's break them down.
What is Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)?
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) automates the process of assigning IP addresses to devices on a network. When a device connects, the DHCP server assigns a new IP address from a predefined pool, ensuring that each device has a unique identifier. This simplifies network configuration by eliminating the need for manual IP address assignment.
DHCP can also configure other essential settings like the subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS settings, streamlining the entire network connection process. By automating these tasks, DHCP helps prevent network connectivity issues due to misconfigurations or duplicate IPs.
What is a DHCP server?
A DHCP server is responsible for automatically assigning IP addresses and other critical network configuration parameters to devices. It manages the leasing of IP addresses, ensuring that each network adapter on the network has a unique IP address, and preventing conflicts.
Alongside IP addresses, it configures other important settings such as the subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS servers. This IP address assignment can be either dynamic or manual if needed, such as when a static IP address is required for a server or device that needs a permanent address.
DNS Server
A DNS server plays a pivotal role in translating domain names into IP addresses, allowing users to access websites using easily memorable names instead of numerical IPs. This process, called DNS name resolution, is essential for browsing the web. When a computer queries a DNS server, it looks up the corresponding IP address from a set of DNS records.
If the DNS server cannot find the requested domain, it uses additional DNS servers to resolve the query. Issues with the DNS settings or DNS resolver cache can result in connectivity issues, which may require manual troubleshooting or using the ipconfig command to flush the cache.
DNS resolver cache
The DNS resolver cache stores recent lookups of domain names, speeding up subsequent access to frequently visited sites. However, if there are changes to the DNS records or DNS names, outdated information in the cache can cause network connectivity issues.
To resolve these problems, you can use the ipconfig command in the command prompt to clear the cache, which forces the computer to request fresh DNS information from the server.
IP Addresses
An IP address is a unique identifier that allows devices to communicate on a network. IP addresses can be assigned either manually (static) or dynamically by a DHCP server. In addition to the IP address itself, the IP address configuration includes the subnet mask, which defines the network segment, and the default gateway, which routes traffic outside the local network.
Devices on the same network need to have matching network settings, such as the correct DNS server and subnet mask, to communicate effectively.
Static IP Address vs. Dynamic IP address
A static IP address is manually assigned and does not change over time, making it ideal for servers and printers that need consistent, reliable connections. In contrast, dynamic IP addresses are automatically assigned by the DHCP server and can change whenever the device reconnects to the network, making them more suited for general-use devices like laptops and phones.
Knowing when to use static or dynamic IP addresses is crucial for maintaining network connectivity and reducing connectivity problems.
Configuring network settings
To configure IP addresses and other network settings, administrators often use tools like the command prompt. Commands such as ipconfig or ifconfig (for Linux and macOS systems) allow you to view and modify a device's network configuration.
The ipconfig command displays detailed information about the device’s network interfaces, including the IP address, subnet mask, physical address, and default gateway. This information is essential for diagnosing network connectivity problems or verifying that the correct network adapter is being used.
Network interfaces and adapters
Network interfaces refer to the points where devices connect to the network, typically through network adapters such as Ethernet or Wi-Fi. These interfaces are responsible for sending and receiving data across the network.
Proper configuration of the network adapter is crucial to ensure smooth communication, and problems with the adapter can result in connectivity issues. Checking the adapter settings using commands like ipconfig or ifconfig can help gather information about network connectivity and resolve issues.
Ethernet interface vs. Wireless interface
Devices often connect to a network using either an Ethernet interface (wired connection) or a wireless adapter. Wired connections typically provide more reliable network connectivity, but wireless networks offer flexibility and convenience.
Regardless of the connection type, correct network configuration—including the IP address, subnet mask, and DNS settings—is essential to avoid connectivity problems.
Troubleshooting and commands
If a device is experiencing network connectivity issues, administrators can use several built-in tools to gather information and troubleshoot the problem. The ipconfig command in Windows or the ifconfig command in Unix-based systems displays vital network configuration information, such as the current IP address and DNS settings.
If the computer has trouble resolving domain names, the ipconfig command can also be used to flush the DNS resolver cache, resolving outdated DNS information and potentially fixing connectivity problems. Additionally, reviewing the DHCP class ID and ensuring the correct network adapter is specified are key steps in troubleshooting.
How to run ipconfig
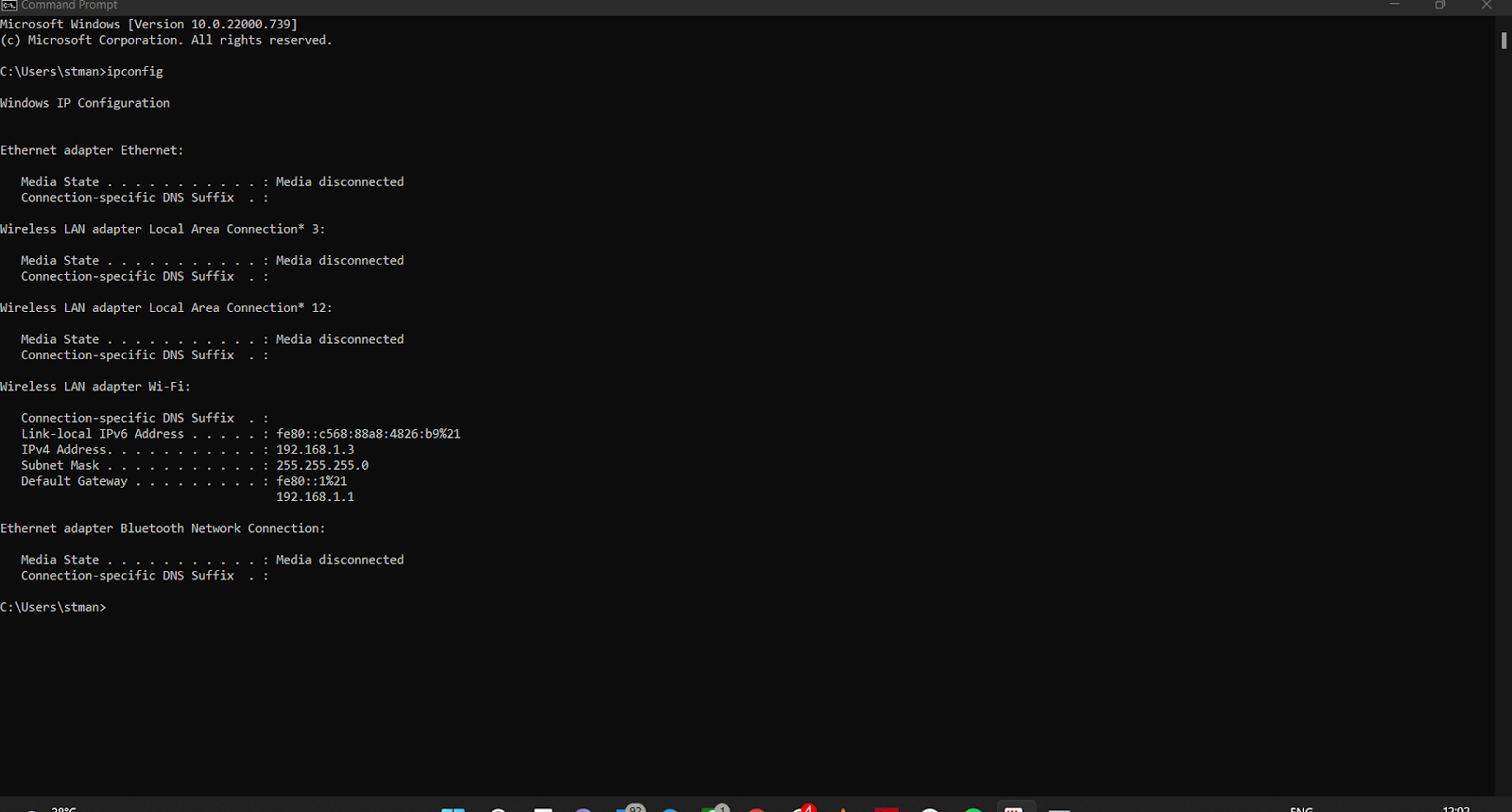 To run ipconfig, you need to open a Command Prompt or terminal window on your computer. Here's how to do it on different operating systems:
To run ipconfig, you need to open a Command Prompt or terminal window on your computer. Here's how to do it on different operating systems:
Windows
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type "cmd" in the Run dialog box and press Enter.
- The command prompt window will open.
- Type "ipconfig" and press Enter.
- That's it! The output of the ipconfig command will be displayed.
macOS
- Open the Applications folder.
- Open the Utilities folder.
- Open Terminal.
- Type "ipconfig" and press Enter.
- You'll see the output of the ipconfig command.
Linux
- Open a terminal emulator, such as GNOME Terminal or Konsole.
- Type "ipconfig" and press Enter.
In two simple steps, you can see the ipconfig command.
Once you've opened a command prompt or terminal window and run the ipconfig command, you should see information about your network connections. If you encounter any errors or need to modify the behavior of ipconfig, you can use various command-line options to do so.
For example, you can use the "/all" option to display more detailed information about your network connections, or the "/release" option to release your DHCP lease.
Troubleshooting with ipconfig
Ipconfig can help you diagnose and fix network issues. Here are some common troubleshooting scenarios and how to use ipconfig to resolve them:
1. Can't connect to the internet
- Run ipconfig and look for your default gateway IP address.
- Open a web browser and enter the default gateway IP address in the address bar.
- If you can't access the router configuration page, try resetting the router or modem.
- If you can access the router configuration page, check the WAN settings and make sure they match your ISP's requirements.
2. Slow internet speed
- Run ipconfig and look for your DNS server IP addresses.
- Ping each DNS server to test their response time.
- If one DNS server is slow or unresponsive, try switching to a different DNS server.
3. Can't connect to a specific website
- Run ipconfig and look for your DNS server IP addresses.
- Open a command prompt or terminal window and type "nslookup" followed by the website's domain name.
- If the DNS server can't resolve the domain name, try switching to a different DNS server.
- If the DNS server can resolve the domain name, check your firewall settings to make sure the website isn't being blocked.
Advanced ipconfig features
Ipconfig offers many advanced features that are useful for network administrators and power users. Here are some of the most useful advanced ipconfig features:
Renewing and releasing DHCP leases
If your computer is configured to obtain an IP address automatically via DHCP, you can use ipconfig to renew or release the DHCP lease. To renew the DHCP lease, type "ipconfig /renew" in a command prompt or terminal window. To release the DHCP lease, type "ipconfig /release".
Displaying detailed information
By default, ipconfig displays basic information about your network connections. However, you can use the "/all" option to display more detailed information, such as your network adapter's physical address, lease expiration date, and DHCP server address. Type "ipconfig /all" in a command prompt or terminal window to display this information.
Flushing the DNS cache
If you're having DNS-related issues, you can use ipconfig to flush the DNS cache. This process clears out any cached DNS entries and forces your computer to look up the DNS information again. To flush the DNS cache, type "ipconfig /flushdns" in a command prompt or terminal window.
Displaying active network connections
If you want to see a list of your active network connections, you can use the "netstat" command. Type "netstat -an" in a command prompt or terminal window to display a list of all active network connections.
Changing the MAC address
If you need to change your network adapter's MAC address, you can use the "ipconfig" command in combination with the "spoofmac" tool. Spoofmac allows you to change your MAC address to a random value or a specific value. To use spoofmac with ipconfig, type "spoofmac ipconfig /all" in a command prompt or terminal window.
These are just a few examples of the advanced features that ipconfig offers. By exploring the various options and command-line switches available, you can gain even more control over your network connections and troubleshoot issues more effectively.
The bottom line
Ipconfig is a powerful and versatile command-line tool to diagnose and troubleshoot various network issues. Whether you're a network administrator or a casual user, ipconfig can provide valuable information about your network connections, including IP addresses, DNS server addresses, and more.
Some advanced features of ipconfig that can be particularly useful for power users and network administrators include renewing and releasing DHCP leases, displaying detailed information, flushing the DNS cache, displaying active network connections, and changing the MAC address.
Overall, ipconfig is a must-have tool for anyone who works with networks on a regular basis. By mastering its features and capabilities, you can become a more effective network troubleshooter and ensure that your network connections are always running smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is ipconfig?
Ipconfig is a command-line tool used to display and manage the IP configuration of network connections on Windows, macOS, and Linux systems. It helps in diagnosing and troubleshooting network issues.
2. How can I use ipconfig to fix DNS-related issues?
You can use the ipconfig /flushdns command to clear the DNS resolver cache, which can help resolve connectivity issues caused by outdated DNS records.
3. How do I view detailed information about my network connection?
Running the ipconfig /all command displays detailed information, including IP addresses, DNS settings, subnet mask, and more for each network interface on your device.
4. How can I renew my IP address using ipconfig?
Use the ipconfig /release command to release your current IP address and ipconfig /renew to request a new IP address from the DHCP server.
5. Can I troubleshoot connectivity problems with ipconfig?
Yes, ipconfig helps identify issues like incorrect IP address assignment or DNS configuration. It can show default gateway, DNS servers, and other network settings essential for resolving connectivity problems.















